Cloud Types
advertisement

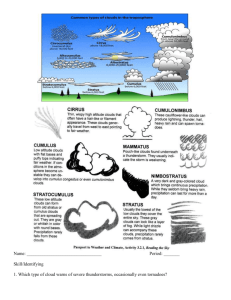
Cloud Types Introduction Clouds are classified into twelve types. The names used for the clouds are based on three factors: the ___________ at which the cloud occurs, the ___________ of the cloud, and whether the cloud is producing ___________. This tutorial will help you learn about the different cloud types so that you can make accurate observations for the Students’ Cloud Observations On-Line (S’COOL) project. There are three altitude ranges, or cloud levels. The height of the cloud base determines a cloud’s level. Clouds with a base below 2,000 meters are considered ___________clouds. Clouds with a base between 2,000 and 6,000 meters are ___________clouds. Those with a base above 6,000 meters are considered ___________clouds. In 1803, Luke Howard classified four main cloud types with Latin terms. ___________ means “pile” and describes heaped, lumpy clouds. ___________ means “curl of hair” and is used to name clouds that look like wispy locks of hair. Featureless clouds that form sheets are named ___________, meaning “layer.” Howard used the term ___________, which means “cloud,” to name low, gray rain clouds. Low-Level Clouds These pictures show examples of low-level clouds. The ___________ and the Earth’s Radiant ___________ System (CERES) satellite cannot distinguish between individual cloud types at this level, but calls all of them “low, water clouds.” There is a continuum among these low-level cloud types, ranging from ___________, to nearly overcast, to individual clouds. This range of low-level clouds is explained in more detail in the next sections. True stratus clouds are ___________ and ___________. The sky looks flat and uniform in all directions, appearing white or gray rather than blue. Generally these clouds obscure the Sun so that its location cannot be pinpointed. When this condition occurs, the cloud is said to be ___________. ___________ is a special kind of ___________ cloud: one that is low enough to touch the ground. It offers students a good personal experience of what a cloud feels like. In addition, it allows students to experience some of the conditions necessary for cloud formation, such as water vapor and cool temperatures. ___________ clouds have both layered and puffy characteristics. Cloud cover tends to be mostly cloudy to overcast, but distinct cloud pieces are visible, in contrast to the uniform and flat character of stratus clouds. There may be areas of clear blue sky, but the clouds appear to be part of a large cloud system. These clouds are common in ___________ and ___________ areas. ___________ clouds are puffy, individual clouds typically associated with fair weather. They are the most common type of cloud and are often described as having a ___________-like or cotton ball appearance. They are made of water droplets and generally have sharp outlines. Cumulus clouds occur in a variety of shapes and sizes, and with a little imagination, you can see all sorts of interesting things in these clouds. Clouds that produce precipitation are designated with the Latin prefix nimbo-. ___________ is a layered, uniform, rain cloud. A cloud can quickly change to or from nimbostratus; that is, it can quickly start or stop raining during your observations. In a situation like that, you can pick a cloud type and make a note in the comments about ___________ rain. These clouds are generally very dark, and are associated with large areas of continuous rain. Nimbostratus can also produce ___________ or ___________. ___________ clouds are convective, meaning that they are formed by the upward movement of warm air currents. They are accompanied by compensating ___________ of cold air. These clouds are most common in warm and humid weather and can produce thunder, lightning, heavy rain, hail, strong winds, and tornadoes. They can extend through a large part of the atmosphere. They can even extend beyond the ___________, which is the boundary between the troposphere (where we live and where all weather occurs) and the ___________ (where the ozone layer is). Despite this range of cloud vertical development, as long as the base of the cloud is below 2,000 meters, it is considered a low-level cloud. Mid-Level Clouds There are two mid-level cloud types, designated by the prefix alto-: ___________ (puffy) and ___________ (layered). Mid-level clouds may be made up of ice crystals at the higher altitudes, but they are more often composed of water droplets. ___________ clouds are a mid-level version of cumulus clouds, consisting of cloud puffs. This cloud type sometimes appears like dozens of small, loose bands or ripples like waves on a sea. These clouds are often associated with the approach of a weather front, and may be an indicator of rain on the way. ___________ clouds are the mid-level version of stratus clouds. They are uniform and diffuse, with little appearance of individual cloud pieces. The sky appears gray or blue-gray, and sunlight is ___________, as though seen through water or frosted glass. When the cloud partially blocks the Sun in this way, the cloud is said to be translucent. High-Level Clouds High-level cloud types are identified with the prefix cirro-: ___________ (thin and wispy), ___________ (layered), and ___________ (puffy). Because all high-level clouds are made of ice particles rather than water droplets, they have a fairly distinct appearance. The boundaries of ice clouds tend to be more diffuse, or fuzzier, than the generally sharp boundaries of water clouds. They can also produce optical effects such as halos and sun dogs. ___________ clouds are the classic and distinct high-level cloud. They are sometimes called “mare’s tails” because they appear to be brushed across the sky and are hair-like in appearance. ___________ ends are common in this cloud type. They are usually quite thin and wispy, and blue sky is visible through portions of the cloud. These clouds are generally white. ___________ clouds are the high-level version of stratus. They are sheet-like, nearly transparent clouds that cover a large part of the sky. When these clouds are present, the Sun may appear to be surrounded by a colored ___________ due to ___________ of light by the ice particles in the cloud. ___________ clouds are the high-level cumulus clouds. They are thin ice clouds that have a patchy or wavelike appearance. ___________, or condensation trails, are clouds created by airplanes. They are also found at the high level. Students often mistakenly assume that contrails are smoke and exhaust from an airplane, but contrails are actually clouds formed when the tiny particles (aerosols) and warm water vapor in the plane’s ___________ combine with the ambient water vapor to form ice crystals. The presence and character of contrails can tell us about the state of the atmosphere along the plane’s flight path. If the air is very dry and there is not enough water vapor to condense, no cloud forms. If the air is a little moister, a contrail may form and quickly ___________ (which is called a short-lived contrail). If the air contains enough water vapor, a contrail may form and remain for hours (known as a persistent contrail), or even spread to cover very large areas. ___________ are very interested in these clouds that humans cause. When making cloud observations, you should therefore note the presence and number of contrails. Multi-Level Clouds Some scientists estimate that as much as half the time, more than one cloud level is present in the sky. When you observe ___________ cloud levels, you should record the cloud information for each level of cloud that you see—but be careful to distinguish between different cloud levels and the possible occurrence of more than one layer of cloud within a given level. When more than one layer of ___________ cloud occurs, for example, you may just note this in the comments. If a thick, ___________, low layer is present, then you obviously cannot observe anything about the presence or absence of upper level clouds. In situations like these, the ___________ and ___________ observations are very complementary: the satellite observes from above and will see any upper layer clouds, and the observers on the ground can see the lower level clouds. Determining Cloud Level A good way to determine the level of cumulus clouds is to assess the size of the individual cloud Determining Cloud Level A good way to determine the level of cumulus clouds is to assess the size of the individual cloud ____________. Low-level cumulus clouds are about the same size, or larger than, your fist held at arms’ length. One exception to this rule is when a small ____________ cloud is developing or evaporating. In that case, its direction or speed of motion may indicate that it is in the same layer as nearby larger cumulus clouds. ____________ cumulus clouds are farther away and the individual cloud pieces appear substantially smaller, about the size of your thumb at arms’ length. High-level cumulus clouds are smaller still, with individual cloud pieces about the size of the nail on your little finger at arms’ length. Stratus clouds have no distinct cloud pieces to measure. For these clouds, a general rule is that cloud opacity tends to ____________ with height. Thus, lowlevel clouds are generally thicker than mid-level clouds, and a high-level ____________ is very thin. Thus, by observing how much the cloud obscures the Sun, you can estimate the ____________of a stratus cloud. If there is ____________, the chances are very good that you are dealing with a low-level cloud. Mid-level clouds occasionally precipitate, but this is a rare occurrence. . Low-level cumulus clouds are about the same size, or larger than, your fist held at arms’ length. One exception to this rule is when a small cumulus cloud is developing or evaporating. In that case, its direction or speed of motion may indicate that it is in the same layer as nearby larger cumulus clouds. Mid-level cumulus clouds are farther away and the individual cloud pieces appear substantially smaller, about the size of your thumb at arms’ length. High-level cumulus clouds are smaller still, with individual cloud pieces about the size of the nail on your little finger at arms’ length. Stratus clouds have no distinct cloud pieces to measure. For these clouds, a general rule is that cloud opacity tends to decrease with height. Thus, low-level clouds are generally thicker than mid-level clouds, and a high-level cirrostratus is very thin. Thus, by observing how much the cloud obscures the Sun, you can estimate the level of a stratus cloud. If there is precipitation, the chances are very good that you are dealing with a low-level cloud. Mid-level clouds occasionally precipitate, but this is a rare occurrence.