90189 Describe properties and reactions of groups of
advertisement

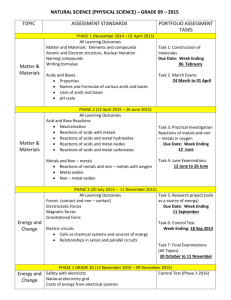
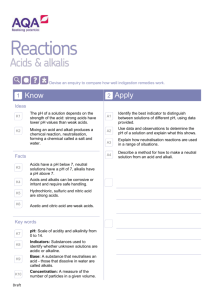
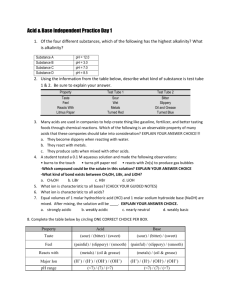
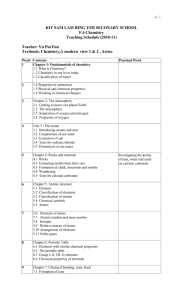
Number AS90189 Version 1 Page 1 of 3 Achievement Standard Subject Reference Science 1.4 Title Describe properties and reactions of groups of related substances Level 1 Subfield Science Domain Science - Core Registration date Credits 13 December 2001 5 Assessment Date version published External 13 December 2001 This achievement standard involves the description of characteristic properties and reactions of metals, acids, alkalis, simple hydrocarbons and alcohols. Achievement Criteria Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence Describe characteristic properties and reactions of related substances. Explain characteristic properties and reactions of related substances. Apply an understanding of characteristic properties and reactions of related substances. Explanatory Notes 1 This achievement standard is derived from Science in the New Zealand Curriculum, Learning Media, Ministry of Education, 1993, achievement objectives 6.1 and 6.2, p. 100; Chemistry in the New Zealand Curriculum, Learning Media, Ministry of Education, 1994, achievement objectives 6.1 and 6.2, p. 18; and Pütaiao i roto i te Marautanga o Aotearoa, Learning Media, Ministry of Education, 1996, 'Ö Kawekawe: Te Waonui', pp. 64-65. 2 Related substances are limited to: metals, acids, alkalis, and simple hydrocarbons and alcohols. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 Number AS90189 Version 1 Page 2 of 3 3 Metals are limited to Li, Ca, Mg, Al, Zn, Fe, Pb, Cu and Au. Assessment of the characteristic properties of metals will involve a selection from the following: physical properties - electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, density, lustre, malleability and ductility relating the properties of metals to their uses observations of reactions of metals with air, water, and acids (HCl, H2SO4, CH3COOH) word equations for reactions of metals with oxygen, water and acids (HCl, H2SO4). 4 Acids and alkalis - assessment of the characteristic properties and reactions will involve a selection from the following: effects on litmus, universal indicator pH value visible effects of acids on carbonates and hydrogen carbonates naming products and writing word equations for reactions of acids (HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, CH3COOH) with metal compounds (oxides, hydroxides, carbonates, and hydrogen carbonates of Ca, Na, Cu (II), Fe (II), Fe (III) and Mg, where they exist) naming or writing the formula of a given salt of type AB, A2B or AB2, and salts that require a bracket around a polyatomic ion such as Al2(SO4)3 or Ca(OH)2, (using a given table of ions). 5 Simple hydrocarbons are limited to C1-C6 straight chain alkanes, ethene, and propene. Alcohols are limited to methanol and ethanol. Assessment of the characteristic properties and reactions of simple hydrocarbons and alcohols will involve a selection from the following: naming and writing structural formulae naming the products of complete and incomplete combustion comparing the products and the amount of energy released from the complete and incomplete combustion of fuels writing balanced equations for complete combustion comparing the solubility of simple hydrocarbons with that of methanol and/or ethanol linking the physical state of hydrocarbons to melting and/or boiling points and chain length. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 Number AS90189 Version 1 Page 3 of 3 Quality Assurance 1 Providers and Industry Training Organisations must be accredited by the Qualifications Authority before they can register credits from assessment against achievement standards. 2 Accredited providers and Industry Training Organisations assessing against achievement standards must engage with the moderation system that applies to those achievement standards. Accreditation and Moderation Action Plan (AMAP) reference 0226 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016