p.1 KIT SAM LAM BING YIM SECONARY SCHOOL F.4 Chemistry
advertisement

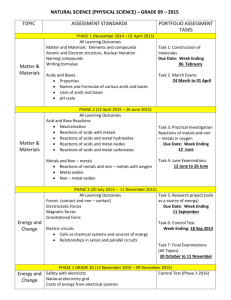
p.1 KIT SAM LAM BING YIM SECONARY SCHOOL F.4 Chemistry Teaching Schedule (2010-11) Teacher: Yu Pui Fun Textbook: Chemistry,A modern view 1 & 2 , Aristo Week Contents 1 Chapter 1: Fundamentals of chemistry 1.1 What is Chemistry? 1.2 Chemistry in our lives today 1.3 Classification of mater 2 1.4 Properties of substances 1.5 Physical and chemical properties 1.6 Working in chemical changes 3 Chapter 2: The atmosphere 2.1 Getting to know our planet Earth 2.2 The atmosphere 2.3 Separation of oxygen and nitrogen 2.4 Properties of oxygen 4 Unit 3 : The ocean 3.1 Introducing oceans and seas 3.2 Composition of sea water 3.3 Extraction of salt 3.4 Tests for sodium chloride 3.5 Electrolysis of sea water 5 Chapter 4: Rocks and minerals 4.1 Rocks 4.2 Extracting metals from their ores 4.3 Formation of chalk, limestone and marble 4.4 Weathering 4.5 Tests for calcium carbonate 6 Chapter 5: Atomic structure 5.1 Element 5.2 Classification of elements 5.3 Classification of metals 5.4 Chemical symbols 5.5 Atoms 7 5.6 Structure of atoms 5.7 Atomic number and mass number 5.8 Isotopes 5.9 Relative masses of atoms 5.10 Arrangement of electrons 5.11 Noble gases 8 Chapter 6: Periodic Table 6.1 Elements with similar chemical properties 6.2 The periodic table 6.3 Group I, II, VII, O elements 6.4 Chemical properties of elements 9 Chapter 7: Chemical bonding: ionic bond 7.1 Formation of ions Practical Work Investigating the action of heat, water and acids on calcium carbonate p.2 10 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 11 Chapter 8 Chemical bonding: Covalent bonding 8.1 Covalent bonds 8.2 Formation of chemical bonds 8.3 Summary 8.4 Relative molecular mass and formula mass Chapter 9 Structure, bonding and properties 9.1 Giant ionic, covalent compounds 9.2 Properties of substances 9.3 Giant metallic structure 9.4 Properties of metals 12 13 14 15 16 Colours and migration of ions Formulae of ions Elements and ions Chemical bonds Ionic bond Structure Formulae Chapter 10: Occurrence and extraction of metals 10.1 Uses of metals and their properties 10.2 Occurrence and extraction of metals 10.3 Conservation of metal resources Chapter 11 Reactivity of metals 11.1 Comparing the reactivity of metals 11.2 Chemical equation 11.3 Displacement reactions Chapter 12 Reacting masses 12.1 Mole concept 12.2 Percentage by mass 12.3 Chemical formulae 12.4 Empirical formulae 12.5 Molecular formulae 12.6 Calculation based on equations Chapter 13: Corrosion of metals and their protection 13.1 Corrosion of metals 13.2 Rusting 13.3 Factors that speed up rusting 13.4 Observe rusting 17-18 Examination 13.5 Protection from rusting 19 13.6 Implications of rusting 13.7 Corrosion resistance of aluminium Chapter 14 Introducing to acids and alkalis 20 14.1 Common acid 14.2 Chemical reactions of acids 14.3 Hydrogen ions 21 14.4 Role of water 14.5 Basicity of acid 14.6 Common alkalis Compare relative ease of obtaining metals from the oxides 1. Reaction of suitable metals with oxygen, water and acids 2. Displacement reactions of metals in aqueous solution 1. Compare corrosion of iron in distilled water and in sea water. 2. Experiment on corrosion of iron and iron coupled magnesium in gel with an indicator. 1. To investigate the properties of acids 2. Compare the actions of dilute and conc. Hydrochloric acid on zinc and sodium carbonate p.3 22 14.7 Chemical reactions of alkalis 14.8 Alkaline properties 14.9 Corrosive nature 23 Chapter 15: Concentration of solutions 15.1 Concentration of solution 15.2 Calculation 24 Chapter 16 Indicators and pH 16.1 pH scales 16.2 Common indicators 16.3 Measuring pH 16.4 Importance of pH 25 Chapter 17 Strengths of acids and alkalis 17.1 Strength of acids and alkalis 17.2 Strong and weak acids, alkalis 26 Chapter 18 Salts and neutralization 18.1 Neutralization of acid and alkali 18.2 Exothermic 18.3 Preparation of salts 18.4 Naming of salt 18.5 Application 27 Chapter 19 19.1 Volumetric analysis 19.2 Standard solutions 28 19.3 Acid-alkali titrations 19.4 Calculation 19.5 Writing a laboratory report 29 Chapter 20:Hydrocarabons from fossil fuels 20.1 Energy source 20.2 Coal 20.3 Petroleum and natural gas 30 20.4 Refining petroleum 20.5 Using petroleum and natural gas Chapter 21 Consequences of using fossil fuel 21.1 Burning of fuels 31 32 33 34 21.2 Environmental problems 21.3 Reducing the emission of air pollutants 21.4 Energy crisis Chapter 22 Hhomologous series 22.1 Organic compound 22.2 Structural formulae 22.3 Classification of organic compounds 22.4 Naming 22.5 Structural formulae Chapter 23 Alkanes and alkenes 23.1 Petroleum 23.2 Cracking 23.3 Cracking in laboratory Volumetric titration of hydrochloric acid against sodium hydroxide solution p.4 35 23.4 Alkenes Chapter 24 Addition polymers 24.1 Plastics 24.2 What is plastic 24.3 Addition polymerization 36 24.4 24.5 24.6 24.7 Properties and uses of some addition polymers Thermoplastics Plastics and economy Environmental issues related to the use of plastics Test for unsaturation by bromine solution. Test for unsaturation by Acidified potassium permanganate