Disinfection of the Root Canal Space
advertisement

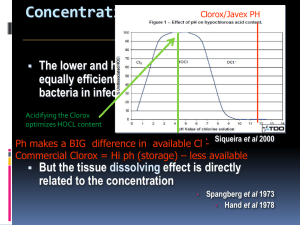
Disinfection of the Root Canal Space ESCN Session 5 Robert S. Roda DDS MS http://web.mac.com/robertroda Purpose of Root Canal Therapy o To prevent and cure apical periodontitis An inflammatory process in the periradicular tissues caused by microorganisms in the infected root canal Initial Infection o Mostly gram negative and anaerobic o eg. Fusobacterium Post-Treatment Infection o Gram positive facultative anaerobes o eg. Enterococcus faecalis Microorganisms o Two forms: Planktonic Sessile Forms a biofilm Biofilm Composition o Bacteria o Polysaccharide Extracellular Matrix Protection Signaling Nutrition Biofilm o Five Stages of Biofilm Development 1. Reversible attachment 2. Irreversible attachment 3. Matrix secretion 4. Growth 5. Differentiation Detachment Biofilm o After attachment to a surface, a bacterium expresses a different set of genes o Microorganisms in biofilms have reduced susceptibility to antimicrobial agents o Biofilms adapt to changing conditions o Becomes more persistent under stress o Less susceptible to second application of disinfectants o Bacteria can transfer acquired resistance to other bacteria Bacteria in Dentinal Tubules Aim of Endodontic Therapy o Removal of the biofilm from the canal space and prevention of reinfection Two Stages of Root Canal Therapy o Reduce / Eliminate Bacteria Mechanical canal preparation Chemical disinfection o Prevent Re-infection Apical seal Sealed obturation Coronal Seal Sealed Restoration Mechanical Preparation o Removal of most organic substrate from the canal system o Development of a purposeful form to allow deep penetration by irrigants for reception of a dense root filling Mechanical Preparation o Broaches o Hand files o Rotary files o Ultrasonically activated files o Sonically activated files o Lasers Instruments Don’t Get Everything Instruments Create Smear Layer Smear Layer o A layer of debris on dentin Organic component Collagen, bacteria, pulp remnants Inorganic component Dentin chips Foreign debris (insoluble) o Created by mechanical scraping of dentin Affects: o Restorative dentistry (bonding) o Periodontics (regeneration) o Endodontics? (disinfection and seal) Should it be removed? o Yes: Potentially infected material / substrate Prevents disinfectants and filling materials from getting into tubules Detriment to apical seal o No: Enhances apical seal Does not affect prognosis Removal may weaken teeth Chemical Disinfection o Irrigation Passive Active o Inter-appointment Medicaments Phenolic Calcium hydroxide Effectiveness is Proximity Dependant Irrigants o Distilled water o NaOCl o EDTA o Chlorhexidine Distilled Water o No antibacterial action o Does not dissolve tissue Sodium Hypochlorite o 6% vs 3% NaOCl o Kills some bacteria (E. faecalis is resistant) o Dissolves necrotic tissue o Does not remove smear layer o Reduces bonding strength o Current Irrigant of Choice EDTA o Kills some bacteria? o Removes smear layer o Erosion of dentin Chlorhexidine o 0.12% vs 2% o Kills some bacteria (similar to NaOCl) o Kills E faecalis o Does not dissolve tissue o Toxicity? Tissue Fixitive Carcinogenic byproducts? Smear Layer Removal o Two stage chemical process o Remove inorganic component Mild acids (chelation) EDTA Citric acid Phosphoric acid Tetracycline o Remove organic component Sodium hypochlorite Current Disinfection Technique o Irrigate thoroughly with NaOCl o Evacuate NaOCl o Syringe EDTA into canal (1-2 min) o Evacuate EDTA o Flush with NaOCl (1 min minimum) o Evacuate NaOCl o Flush with 2% CHX (5 min) o Use paper points to dry BioPure™ MTAD™ Cleanser o Mixture of Tetracycline and Acid - Detergent o Detergent (Tween 80) ™ acts as a surfactant - facilitates penetration o Citric acid removes smear layer o Doxycycline removes smear layer kills resistant bacteria o Removes Smear Layer Properties of MTAD o Effective when combined with any concentration of NaOCl over 1.3% o Kills E. faecalis better than 2% CHX o Kills bacteria in whole saliva better than NaOCl o Sustained effect? (binds to dentin) o Biocompatibility > EDTA, 0.12% CHX, 5.25% NaOCl o Does not affect flexural strength of dentin o Does not decrease bond strength of dentin o FDA Approved 2004 o Allergenicity True allergy is rare Do not use in pregnant women or children under age 8 MTAD™ Cleanser Technique o Irrigate thoroughly with NaOCl o Evacuate NaOCl o Syringe 1ml BioPure MTAD cleanser into canal (5 min) o Flush with 4ml BioPure MTAD cleanser o Use paper points to dry QMix 2in1 o EDTA and Chlorhexidine o Removes smear layer o Kills planktonic bacteria o Kills biofilm bacteria QMix Protocol o Irrigate with NaOCl throughout o Dry canals o QMix for 90 sec o Dry Canals o Obturate Increase Irrigant Effectiveness o Volume o Concentration Temperature Agitation o Combination - NaOCl + ProLube® or RC Prep ® o Change solution frequently o Increase time of contact Irrigation - Two Types o Passive Allow the irrigant to passively work Soaking o Active Add heat or agitation Increase irrigant action Tissue dissolution Increase antimicrobial action Increase irrigant flow Clean canal iregularities Passive Irrigation o Soaking o EDTA 1-2 minutes o NaOCl 1/2 hour* o The longer the better Active Irrigation o Manual Dynamic o Sonic o Ultrasonic o EndoActivator o EndoVac o Ultrasonic Irrigation Manual Dynamic Irrigation o Manual push-pull motion o Use a fitted master gutta percha cone o Forces irrigants into canal ramifications Sonic Instruments (2-3 kHz) o Sonic Handpieces (Micromega 1500/3000) o sonic vibrations created by air/water jet o vibrates in a figure eight motion o difficult to control tip movement o canal walls left rough (creates smear layer) o slow o relatively less expensive than ultrasonic o best use is for coronal instrumentation and for irrigation Ultrasonic Instruments (25-30 kHz) o piezo-electric energy applied to files o o o o o o acoustic streaming (cavitation?) used for canal flaring (middle, coronal 1/3) creates (removes) smear layer? removal of debris from inaccessible fins can use hypochlorite for irrigant (tube damage) potential for instrument fracture Ultrasonic Instruments (25-30 kHz) o Ultra-sonic operates in a linear motion. o Controlled tip motion. o More energy through a predictable range of motion. o Low Power Setting – 1 to 5 o Must use a light paint brush stroke o Cleaning Webs and Fins o C-Shaped Canals EndoActivator o Soft plastic tips o Does not create smear layer o Battery operated (cordless) o Sub-sonic oscillation (10000 rpm max) EndoVac o Attach suction to modified irrigation needle Ultrasonic Irrigation o Irrigation needle attached to ultrasonic o Hypochlorite overextension? Minimally Invasive Endodontics o Conserve peri-cervical dentin o Attempt to reduce incidence of fracture o Minimize size of access o Minimize size of root canal preparation OneStudy o Compared TEC and CEC o WaveOne instrumentation o Static Fx load Instron) o Canal cleanliness - micro CT o TEC – less load to Fx in premolars and molars (incisors unaffected) o CEC – compromised canal cleaning only in lower molar distal roots