Earth Science
advertisement

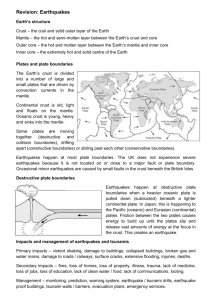
Earth science 1) Earthquake magnitude and intensity: a) What is the difference between the magnitude and the intensity of an earthquake? Magnitude and Intensity measure different attributes of earthquakes. Magnitude measures the energy released at the source of the earthquake whereas intensity measures the strength of shaking made by the earthquake at the location. Magnitude is found from measurements on seismographs. Intensity is found from effects on people, buildings, and the natural environment. b) Why did the February 21st 2011 earthquake in Christchurch cause so much damage? The February earthquake caused so much damage as it was a lot shallower than the September and was during the middle of the day when everyone was out and about. Also because the quake line was only 10km away from the city centre whereas the September one was 35km 2.Plate tectonics a) What do Scientists think causes the earth’s tectonic plates to move? Scientists think the plates move because of circulation of the mantle underneath the crust, because of heat, causing the plates to move 1-2 inches a year at the cracks of the crust. b) Explain what happens at the following plate boundaries: a) Divergent boundaries-is where new crust is made from magma that comes from the mantle as the plates pull away from each other b) Convergent boundaries-is where crust is destroyed as one plate dives under another when pushed together and the crust pushed underneath heats up and becomes part of the mantle c) Transform boundaries-is where crust is not produced or destroyed as the plates slide horizontally past each other c)What is magma? Magma is lava before it has erupted and covers the cracks that happens when the divergent boundaries form d) How is it that new crust forms at divergent boundaries? The magma from underneath the earth’s crust comes up to “set” as the crust from the cracks/plates e) How is it that plate material is destroyed at convergent boundaries? When plates are pushed together the heavier plate (the plate that carries ocean not continent) “slides” under the lighter plate f) What is a subduction zone? Subduction is where the earth’s crust is destroyed from convergent boundaries. That is where the earth’s crust carrying the ocean (making it heavier) dives under the other plate carrying a continent (lighter) causing the crust to heat up and become mantle. g) What plate boundary does New Zealand straddle? New Zealand is straddling the boundary in the middle of the pacific and Indian-Australian plates h) What do the plates do… a) To the north of New Zealand and beneath east North Island, the thin, heavier, Pacific plate moves down beneath the thicker, lighter Indian-Australian plate in a way that is called subduction (see above) b) South of New Zealand the Indian-Australian plate is forced below the Pacific plate also known as convergent c) within the South Island the plate margin is marked by the Alpine Fault and here the plates rub past each other horizontally known as transform boundaries i) What is the result of the plate movement? Plate movement results in volcanic activity in the North Island and earthquakes that are felt throughout the country. Sourceshttp://data.gns.cri.nz/geoatlas/text.jsp http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0mWQs1_L3fA&feature=related%20continental%20drift %20and%20plate http://www.nzherald.co.nz/christchurchearthquake/news/article.cfm?c_id=1502981&objectid=10708024 http://www.3news.co.nz/Answering-questions-about-the-Christchurchquake/tabid/367/articleID/200731/Default.aspx http://www.gns.cri.nz/Home/News-and-Events/Media-Releases/Multiple-factors http://earthquake.usgs.gov/learn/topics/mag_vs_int.php