Supplementary Information (doc 26K)
advertisement

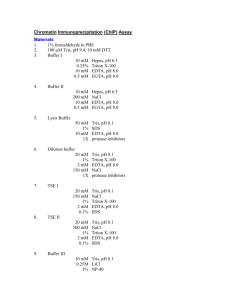
Material and Methods ChIP assays To prepare chromatin, cells were harvested and resuspended in -estradiol-free media at a concentration of 1 x 107 cells / ml. Formaldehyde was then added to a final concentration of 1% (v/v) for 15 minutes at room temperature with rocking to crosslink proteins and DNA. Following the addition of glycine to a final concentration of 1.25 M, cells were washed in PBS and lysed in 300 l of cell lysis buffer (85 mM KCl, 0.5% NP-40, 5 mM PIPES pH 8.0, 1 mM PMSF and EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche)) per 107 cells. Following a 10 minute incubation on ice, cell nuclei were pelleted by centrifugation at 8000 rpm for 5 minutes at 4 oC in a benchtop Microfuge. The nuclei were then resuspended in 200 l of SDS lysis buffer containing protease inhibitors (Deng et al., 2003) per 107 cells and sonicated to reduce DNA length to between 200 and 600 bp. The sheared chromatin extract was then frozen in aliquots at –80 oC until required. Pre-blocked protein A sepharose beads for use in immunoprecipitations were prepared by incubating 100 l of a 50% protein A Sepharose (Sigma) slurry with 550 g single-stranded sonicated salmon testes DNA (Sigma) for 30 minutes at 4 oC with rotation. Chromatin extract (100 l) was then diluted 10-fold in immunoprecipitation dilution buffer (Deng et al., 2003) containing 1 mM PMSF and EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail and pre-cleared for 30 minutes at 4 oC with rotation using 45 l of pre-coated protein A sepharose slurry. A 40 l aliquot was then removed from the supernatant as an input control and the remaining extract incubated with 10 g of polyclonal antibodies or 4 g of monoclonal antibodies overnight at 4 oC with rotation. An additional sample of lysate containing no antibody was also incubated overnight at 4 oC with rotation (no antibody control). For immunoprecipitations carried out with monoclonal antibodies, a further 2 hour incubation with 5 l of rabbit anti-mouse immunoglobulins (Dako) was performed. Immune complexes were collected by incubating with 45 l of pre-coated protein A sepharose slurry for 2-3 hours at 4 oC with rotation and then washed for 10 minutes at 4 oC with rotation using 1 ml of a series of different wash buffers. Complexes were washed once in low salt wash buffer (0.1% SDS, 1% Triton X-100, 2 mM EDTA, 20 mM Tris pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl), once in high salt wash buffer (0.1% SDS, 1% Triton X-100, 2 mM EDTA, 20 mM Tris pH 8.0, 500 mM NaCl), once in LiCl wash buffer (250 mM LiCl, 1% NP40, 1% Na deoxycholate, 1 mM EDTA, 10 mM Tris pH 8.0) and twice in TE buffer (10 mM Tris pH 8.0, 1 mM EDTA). Immune complexes were eluted in 150 l of TE elution buffer (10 mM Tris pH 8.0, 5 mM EDTA, 1% SDS) at 65 oC for 15 minutes. 150 l of TE elution buffer was added to the input control sample and all samples were then incubated at 65 oC overnight to reverse the crosslinks. Following incubation at 50 oC for 2 hrs with 150 l TE containing 45 g Proteinase K to digest proteins, a further 100 l of TE was added and DNA was then purified by three rounds of phenol-chloroform extraction followed by ethanol precipitation. DNA pellets were resuspended in 100 l of distilled water. Antibodies used for chromatin immunoprecipitation were anti-EBNA 2 (PE2, gift from M. Rowe), anti-pol II (N-20, sc-899, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.), anti-pol II phosphoserine 5 (H14) and antipol II phosphoserine 2 (H5) (Covance Research Products). Comparative experiments confirmed that the background signal obtained using secondary antibody alone, control IgM plus secondary antibody or IgG control antibodies did not differ significantly from the backlground signal obtained in the absence of antibody. A ‘no antibody control’ was therefore performed for all ChIP assays.