SLP06 Evaluation Of Language-CELF-3
advertisement

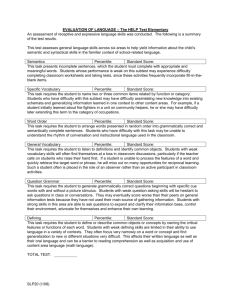
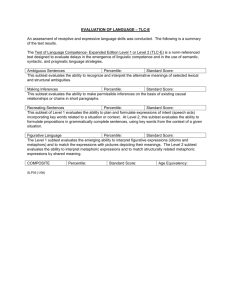
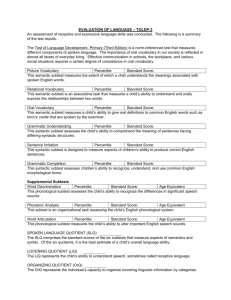
EVALUATION OF LANGUAGE – CELF-3 An assessment of receptive and expressive language skills was conducted. The following is a summary of the test results. CELF-3: The Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals-Third Edition is test is examines a student’s comprehension and use of the basic foundations of content and form that characterize mature language use: word meanings (semantics), word and sentence structure (morphology and syntax), as well as the recall and retrieval of spoken language (memory). Sentence Structure Percentile: Standard Score: This subtest requires a student to listen to a sentence and point to the picture that best represents that sentence. The ability to understand the changes in meaning that arise from different sentence structures (syntax) is essential in pre-reading, early reading, and early writing activities. Students who perform in the below-average range on the Sentence Structure subtest may experience difficulties in expression and comprehension of spoken and written language. These students may also have problems integrating surface structure and deep structure of sentences. Concepts and Directions Percentile: Standard Score: Students who perform in the below average range on the Concepts and Directions subtest may experience school- and home-related difficulties in following directions. Curricular workbooks require students from kindergarten through high school to be able to follow directions that include basic linguistic concepts, such as coordinating conjunctions (and, or, but), references to inclusion or exclusion (either, or, neither, all but), time (when, after, before), condition (that is not), or quantity (some, one, none). Early math story problems are good examples of the need for accurate interpretation or key concepts and the recall of directions and instructions for academic success. Instructions for gym classes, sports or games, and arts and crafts projects are other examples. These students may also have problems following workbook assignments in subject areas such as English and language arts, math, or sciences. They may have difficulty taking notes or writing messages as well. Word Classes Percentile: Standard Score: This subtest requires a student to listen to a set of three or four words and tell which two words in the set best go together. Performance in the below-average range in the Word Classes subtest indicates that the student does not associate related words automatically or efficiently. Adequate ability to perceive relationships in the meaning of words and form word associations is essential for classroom listening and reading comprehension. Deficits in recognizing and using word associations influence a student’s ability to make predictions, create meaning, make inferences, and use analogical reasoning for problem solving. Semantic Relationships Percentile: Standard Score: This subtest requires a student to listen to a sentence or sentences and complete a question with two correct answers provided visually and auditorily. Performance in the below-average range on the Semantic Relationships subtest indicates that the student has difficulty interpreting sentences that (a) make comparisons (comparative relations), (b) identify location or direction (spatial relations), (c) include time relationships (temporal relations), (d) include serial order (sequential relations), or (e) are expressed in passive voice (passive relations). The student may have difficulty following directions for classroom or workbook assignments with comparisons (smaller than, larger than); understanding conventional series (numbers, alphabet, days of the week); prepositions (right, left, next to); order of action (before, after); or use of passive voice (math problems). The student may experience academic difficulties in curriculum areas such as English, language arts, math, sciences, arts, and vocational training. Word Structure Percentile: Standard Score: This subtest requires the student to listen to a partial sentence and end it with a grammatically correct word or phrase. Students who perform in the below-average range on the Word Structure subtest may experience difficulties in verbal and written expression, and delays in reading comprehension. The ability to express and understand distinctions in meaning that arise from grammatical markers, such as plural and possessive word endings, past-tense forms, personal pronouns, and derived forums of nouns, verbs, and adjectives, is essential in early learning of reading and writing. In early reading and writing classroom activities, sentences are generally simple in form (grammar), but subtle meanings and relationships are expressed in the word endings and other grammatical markers. Formulated Sentences Percentile: Standard Score: This subtest requires a student to look at a picture and generate a sentence to include a given target word. Performance in the below-average range on the Formulated Sentences subtest may indicate that the student has difficulties in the generative language aspects related to planning and producing sentences for conversation, classroom discourse, academic interactions, and written language. Recalling Sentences Percentile: Standard Score: This subtest requires a student to listen to a sentence and repeat it back verbatim. Performance in the below-average range on the Recalling Sentences subtest can sometimes be attributed to a student’s inability to immediately recall spoken language. The student often has difficulties with associated classroom tasks, such as writing to dictation, taking notes, remembering the teacher’s instructions, and copying from the chalkboard. Sentence Assembly Percentile: Standard Score: This subtest requires a student to look at blocks of words that are not in order and arrange them to formulate two complete and correct sentences. Performance in the below-average range on Sentence Assembly indicates that the student is experiencing difficulty in formulating descriptions, questions, responses, or conversation. Classroom difficulties can be expected in English and language arts for curriculum activities, such as sentence combining and sentence analysis. Inadequacies in syntactic flexibility can also affect speaking, written composition, and performance in rhetoric, in that there is a lack of variation in sentence structures used to express intents. Listening to Paragraphs Percentile: Standard Score: This subtest requires a student to listen to two short paragraphs and answer questions regarding those paragraphs. Students who perform in the below-average range on the Listening to Paragraphs subtest may exhibit classroom difficulties in listening and reading comprehension. The paragraphs target listening comprehension at the factual and inferential levels. Some students have difficulty remembering facts and details presented in the paragraphs. Generally, they show other evidence of auditory memory difficulties on the CELF-3. Other students remember facts and details, but cannot go beyond the concrete examples given in the paragraphs. They have difficulty understanding causes, effects, outcomes, reasons, and relationships. This causes difficulty in making inferences; understanding the implied reasoning; and problem-solving based on the context. Word Associations Percentile: Standard Score: This subtest requires a student to list as many members in a given category as he can in one minute. Students who perform below average on the Word Associations subtest demonstrate inadequate semantic organization and lack word association strategies to name members of a semantic class rapidly and efficiently. In the classroom, these students may have difficulty speaking or writing. For example, word webbing may be an inefficient strategy for generating words and ideas for these students. In speaking and writing, the student may lack a variety in using words, surface structure cohesion, and coherence in speaking and writing. Receptive Language Expressive Language Total Score: SLP06 (1/08) Percentile: Percentile: Percentile: Standard Score: Standard Score: Standard Score: Age Equivalent: