BIO101 F`98
advertisement

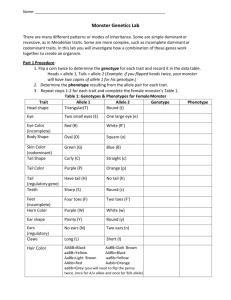
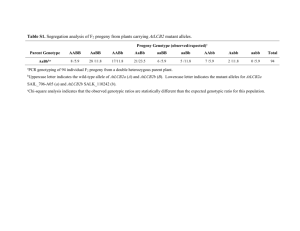
BIOL276 Dr. Young Name _______________________ Due _________________________ Genetics Problems Set #1 On separate paper, complete the following problems. For problems in genetics, if no particular order is specified, you can assume that a specific order is not required. 1. What is the probability of drawing one card at random from a deck and obtaining the following? (A deck has 52 cards. Each card has a suit—spade, heart, diamond, or club— and a number [1-10] or a face—jack, queen, king. Thus, there are 13 cards of each suit and four cards of each number or face.) Express your answers as both a fraction and a percentage. a. The queen of diamonds b. Any heart c. A 10 (any suit) d. Any even-numbered card e. An even-numbered spade 2. In a family of seven children, what is the probability of obtaining the following numbers of boys and girls? a. All boys b. All children of the same sex c. Six girls and one boy d. Four boys and three girls e. Four girls and three boys 3. Two gene loci, A and B, are unlinked (and thus assort independently), and alleles A and B are dominant over alleles a and b. Indicate the probabilities of producing the following. a. An AB gamete from an AaBb individual? b. An AB gamete from an AABb individual? c. An AABB zygote from a cross AaBb × AaBb? d. An AaBb zygote from a cross AaBb × AABB? e. An Aabb zygote from a cross AaBb × AAbb? f. An AB phenotype from a cross AaBb × AaBb? g. An AB phenotype from a cross aabb × AABB? h. An aB phenotype from a cross AaBb × AaBB? 4. A man has either an AaBB or AABb genotype with equal probability. a. Assume these genes are unlinked (i.e., assorting independently). What is the overall probability that the man will produce an Ab gamete? b. What is the probability of the man producing an AB gamete? 5. In snapdragons, the allele for red flowers is incompletely dominant over the allele for white flowers, and thus heterozygotes have pink flowers. What ratios of snapdragon flower colors would you expect to see among progeny generated from the following crosses? a. red × white b. red × pink c. white × pink d. white × white e. pink × pink f. red × red 6. Two pea plants with purple flowers are crossed. Among the offspring, 63 have purple flowers, and 17 have white flowers. With a chi-square test, compare the observed numbers with a 3:1 ratio and determine the probability that the difference between observed and expected could be a result of chance. 7. In a plant species, you notice that purple and yellow leaf colors, as well as hairy and smooth stems, segregate. You cross a plant with purple leaves and hairy stems to a plant with yellow leaves and hairy stems, and generate the progeny indicated below: Class 1 2 3 4 Total: a. b. a. Phenotypes 68 yellow leaves, hairy stems 66 purple leaves, hairy stems 22 purple leaves, smooth stems 25 yellow leaves, smooth stems 181 Indicate the most likely genotypes for each parent. Propose a hypothesis to explain the progeny results. Based on this hypothesis, what ratios are expected for each of the four classes of progeny? Using the chi-square method, test your hypothesis and indicate whether you accept or reject it. 8. In animals, the inability to make the pigment melanin results in albinism, a recessive somatic condition. Two normal parents, who have decided to have three children, have a first child that is albino (genotype aa). Determine the following probabilities: a. That the second and third children are also albino. b. That the second and third children are normal. 9. In sailfin mollies (fish), gold color is due to an allele (g) that is recessive to the allele for normal color (G). A gold fish is crossed with a normal fish. Among the offspring, 88 are normal and 82 are gold. a. What are the most likely genotypes of the parents in this cross? b. Assess the plausibility of your hypothesis by performing a chi-square test. 10. In guinea pigs, the allele for black coat color (B) is dominant over the allele for white coat color (b). At an independently assorting locus, an allele for rough coat (R) is dominant over an allele for smooth coat (r). A guinea pig that is homozygous for black color and rough coat is crossed with a guinea pig that has a white and smooth coat. In a series of matings, the F1 are crossed with guinea pigs having white, smooth coats. From these matings, the following phenotypes appear in the offspring: 24 black, rough guinea pigs; 26 black, smooth guinea pigs; 23 white, rough guinea pigs; and 5 white, smooth guinea pigs. a. Using a chi-square test, compare the observed numbers of progeny with those expected from the cross. b. 11. What conclusions can you draw from the results of the chi-square test? (How’s your logic?) Lori collects her laundry from the dryer and places it in a basket. She has nine pairs of socks in the load. If she randomly pulls socks from the basket, what is the probability that she will pull nine different socks from the basket before she pulls a sock that completes a pair?