The Cell
advertisement

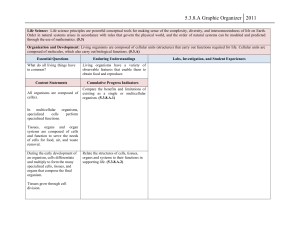
Characteristics of Life UPCO Review Name ________________________________ Date ____________ Due _______________ Directions: Read the paragraphs, then fill in the blanks. Life Processes All living organisms need energy, which is obtained from food. Autotrophs, such as green plants, make their own food. Heterotrophs, such as animals, obtain food from other organisms. During respiration, energy is released from this food. All organisms need energy to survive. The amount of energy an organism needs and how it gets that energy is different from organism to organism. Most organisms use oxygen to release the energy stored in food. This is called aerobic respiration. Organisms that do not need oxygen perform anaerobic respiration. Living organisms need water. Water enables the organism to carry on its life activities. Organisms need living space, which must provide all the organism’s needs. Every organism is adapted to the living space in which it is found. Living things have characteristics that distinguish them from non-living things. All living organisms carry out the same basic life functions in order to maintain an internal equilibrium or balance (homeostasis). An organism’s body plan and its environment determine the way that the organism carries out the life processes. Some common life functions include nutrition (obtaining and breaking down food), transport (carrying nutrients and wastes to and from cells), synthesis (chemical reactions which use nutrients to make materials the cell needs), respiration (the release of energy as glucose and oxygen combine), excretion (removing wastes), regulation (response to changes in the environment), growth (increase in size or number of cells), and reproduction (producing offspring for the survival of the species). nutrition 1. The process by which an organism obtains food is called _________________________. 2. The release of energy stored in food is _________________________. respiration 3. The removal of liquid and gaseous waste is known as _________________________. excretion transport 4. Nutrients are carried to all parts of the body during _________________________. 5. Regulation is a response to changes in the _________________________. nutrition 6. An increase in the size of the organism is _________________________. growth 7. Reproduction is necessary for the _________________________ of the species. survival energy water 8. All living organisms need _________________________, _________________________, and _________________________. living space The Cell For all living things, the cell is the basic unit of structure and function. Life activities are accomplished at the cell level. Humans are an interactive organization of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. A virus lacks cellular organization. Living organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are usually microscopic in size. The way in which cells function is similar in all living things. Cells grow and divide, making more cells. Cells take in nutrients, which provide the cell with energy and with the materials that the cell or organism needs. Cells carry on all the life processes. Cells provide an organism with structure. Organisms composed of one cells are unicellular such as amoeba and bacteria. Organisms composed of many cells are multicellular. Plants and animals are multicellular. Cells are organized for more effective functioning in multicellular organisms. Nerve cells carry messages and muscle cells cause movement. Tissues are made of similar cells. Organs are made of groups of tissues that work together. A group of organs, such as the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine, work together as an organ system. microscopic 9. Most cells are _________________________ in size. grow 10. Cells _________________________ and divide, making more cells. nutrients 11. A cell gets its energy from _________________________. multicellular 12. Organisms composed of more than one cell are called _________________________. processes 13. Every cell can carry on the basic _________________________ of life. similar cells 14. Tissues are made of _________________________. tissues 15. Organs are made of _________________________. 16. Organ systems are made of _________________________ that work together. tissues Plant and Animal Cells Cells are composed of many structures. The cytoplasm of the cell is the watery material in which specialized structures are found. Each cell structure carries out a specific function. The cell membrane separates the interior of the cell from the surrounding environment. It controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell. The cell membrane keeps the internal conditions of the cell constant to maintain homeostasis. The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It controls cell metabolism and reproduction. The nucleus contains the genetic material, DNA, which determines the inheritance of traits. Mitochondria are the “powerhouses” of the cell. They release energy during respiration. Vacuoles store food, water, or wastes in a cell. Animal and plant cells have many of the same cell structures. Yet there are some differences. The plant cell is surrounded by a rigid cell wall. It provides shape and support for the plant cell. Plant cells have chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is the green pigment that enables the plant to absorb sunlight so it can produce food and oxygen by photosynthesis. 17. Complete the chart: Cell Structure Cytoplasm c. nucleus Cell membrane Cell wall k. chloroplast Function a. moves organelles Controls cell activities, Contains genetic material f. controls what goes in and out of cell h. shapes and supports a plant cell Contains chlorophyll for photosynthesis Animal Cell? Yes or No Plant Cell? Yes or No b. yes Yes d. yes e. yes Yes g. yes i. no j. yes l. no m. yes chloroplasts 18. Green plant cells contain _________________________ for photosynthesis. plants 19. Heterotrophs obtain food by eating _________________________ and/or animals _________________________. The Microscope A microscope is an instrument used to magnify objects not visible to the naked eye such as cells. The compound microscope has more than one lens. These are called the objectives and the eyepiece. Images viewed under the microscope are upside down and reversed. If you move the slide to the right, it will appear to move left under the microscope. The area that you can see under the microscope is the field of view. The field of view is smaller under high power than low power. Under low power, more cells or parts of an organism are seen. Under high power, fewer cells, but more detail is seen. The microscope can be used to observe the structure and the size of cells. Cell size can be measured in millimeters. If you know the diameter of the field of view you can estimate the size of a cell. microscope 20. A _________________________ is used to enlarge the appearance of cells. lens 21. A compound microscope has more than one _________________________. upside down 22. Images viewed under the microscope are _________________________ and reversed _________________________. 23. The field of view is larger for _________________________ low power. 24. Under _________________________ power, more cells are seen. low