Berit Packert Jensen
advertisement
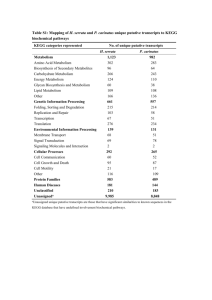
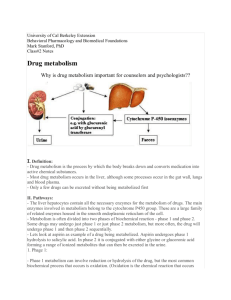
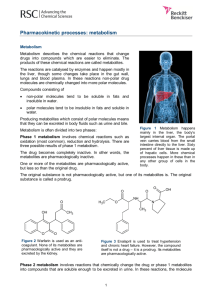
Abstract nr. P1 Ph.d.-studerende Berit Packert Jensen Institut for Analytisk Kemi Studiestart 1. november 2001 Vejledere Bente Gammelgaard, Steen Honoré Hansen, DFH Jan Vanggaard Andersen, Novo Nordisk Titel på forskningsprojekt Alternative Detection Principles in Drug Metabolism Studies - Application of ICP-MS in in vitro and in vivo drug metabolism studies HPLC-ICP-MS IN DRUG METABOLISM STUDIES In Drug Discovery and Development there is a demand for an understanding of the metabolism of the drug candidate. This requires the ability to identify and quantify unknown metabolites from in vitro or in vivo drug metabolism studies. Identification is often achieved using LC-MS, but for quantitative analysis of metabolites, MS as well as UV detection are inadequate as the response is dependent on the molecular structure and authentic standards are rarely available. Furthermore, radiolabelled compounds are normally not available in the early phase of the projects, and synthesis is expensive and time-consuming. Hence, there is a need for alternative methods of quantification. Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) is an element specific detection method and the sensitivity is in principle independent of the structure of the compund. This makes ICP-MS a promising technique for drug metabolism studies. If a drug contains one of the elements Cl, Br, I or S, the drug metabolites will show the same molar sensitivity as the drug, provided that they contain the same element in the same number in the molecule. For ICP-MS to be of value in metabolism studies, coupling to HPLC is necessary. HPLC implies use of high concentrations of organic solvents, which is not readily compatible with the ICP-MS instrument. In this study the influence of solvents on the sensitivities of Cl, Br, I and S in ICP-MS has been investigated. The use of a membrane desolvator to remove organic solvents will be discussed. An example of application of HPLC-ICP-MS in drug analysis will be given.