Extended School Year Eligibility Worksheet
advertisement

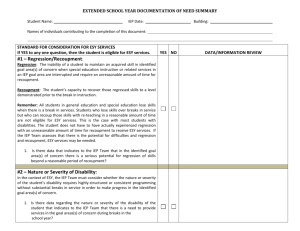
ISD 200 Special Services Practices Statement Dev. 4/98 Rev. 1/12 EXTENDED SCHOOL YEAR (ESY) SERVICES Extended school year (ESY) services are defined by Minnesota Rule and refer to special education and related services for pupils with a disability who demonstrate the need for continued service on days when school is not in session. School districts are required to provide ESY services at no cost to the parents when the IEP team determines that services are necessary beyond the normal school year in order to provide a free appropriate public education. All ESY programming must be addressed on an individualized basis through the IEP process, as outlined in and consistent with the student’s IEP. The school district may not unilaterally limit the type, amount, or duration of these services nor limit services to specific disabilities. On an annual basis, the IEP team must consider whether a pupil is in need of ESY services by meeting conditions A, B, or C. A. There will be significant regression of a skill or acquired knowledge from the student’s level of performance on an annual IEP goal that requires more than the length of the break in instruction to recoup (unless the IEP team determines a shorter time for recoupment is more appropriate). B. Services are necessary during the break for the pupil to attain and maintain self-sufficiency, because of the critical nature of the skill addressed by an annual goal, the student’s age and level of development, and the timelines for teaching the skill. To attain self-sufficiency, a student must maintain skills consistent with IEP goals designed to promote a reasonable degree of personal independence in any of the following skill areas: basic self-help skills, muscular control, physical mobility, impulse control, personal hygiene, stable relationships with peers and adults, basic communication, or functional academic competency (including basic reading and writing skills, concepts of time and money, and numerical or temporal relationships). C. The IEP team otherwise determines, given the pupil’s unique needs, that ESY services are necessary to ensure that the pupil receives a free appropriate public education. The IEP Team must use the following information sources when determining ESY eligibility: 1. Prior observation of the student’s regression and recoupment over the summer. 2. Observations of the student’s tendency to regress over extended breaks in instruction during the school year. 3. Experience with other students with similar instructional needs. The following factors must be considered, where relevant, when determining ESY needs: 1. The student’s progress and maintenance of skills during the regular school year. 2. The degree of the student’s impairment. 3. The student’s rate of progress. 4. The student’s behavioral or physical problems. 5. The availability of alternative resources. 6. The student’s ability and need to interact with non-disabled peers. 7. The areas of the student’s curriculum which need continuous attention. 8. The student’s vocational needs. IEP Documentation Requirements In the section of the IEP titled Extended School Year please do the following: Check the appropriate box (i.e. yes, no, more data needed) o If “more data needed” is checked, a decision must be made by mid-March, to allow sufficient time for summer program planning. Identify the area of eligibility (i.e. regression/recoupment, self-sufficiency, unique needs) o Document on an Extended School Year Eligibility Worksheet (see below). List specific IEP goals and objectives to be addressed o Include the area of need (e.g. reading comprehension or intelligibility) Document the services/program needed (see below) Note necessary supports that will be needed during ESY (i.e. PSA, assistive technology, health supports, special transportation) (NOTE: These needs may be different in ESY than during the school year.) Program Options Special Education Program Alternatives The special education summer programs listed below will meet the extended school year needs of many of our students. A student must meet ESY criteria and have the appropriate documentation on his/her IEP to participate in one of these summer program options. Early Childhood Special Education (for children 3 – 6 on an IEP) Elementary DCD-3 (for elementary learners who receive the majority of their programming in a special education environment) Elementary Resource Room (for elementary age students who may participate in the targeted services Summer Adventure Program part of the time) Clinical Reading & Math (for learners who require intense small group instruction, service may be scheduled to coincide with a regular education summer program in which the student is enrolled ) Summer Skill Builders (for middle school students with mental and/or physical disabilities) Life Skills (for high school students with mental and/or physical disabilities) Special Education Service Alternatives Special Education services that require more individualized programming are also available as extended school year services. Services may include but are not limited to speech/language therapy, occupational therapy, physical therapy, assistive technology training, or social skills instruction, for students who meet ESY eligibility criteria for these services. Regular Education Program Alternatives On occasion a regular education summer program may meet the ESY needs of a student who is already eligible for ESY as documented on the IEP and has identified ESY goals and objectives that can best be met in this context. Examples include: Summer Adventure (elementary) and Raider Prep or Enrichment Classes (middle school). Legal References: Minn. Rules Part 3525.0755 20 U.S.C. § 1400 et seq. (Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act of 2004) 34 C.F.R. Part 300 Extended School Year Eligibility Worksheet . Rev 12/07, 8/08, 1/11 Special Education: Hastings Area Schools Student: Date: The IEP team must consider on an annual basis whether a pupil is eligible for ESY services by meeting Conditions A, B, or C below. A. There will be significant regression of a skill or acquired knowledge from the student’s level of performance on an annual goal that requires more than the length of the break in instruction to recoup. The following information must be considered when determining ESY eligibility: 1. Evidence of the student’s regression and recoupment over the summer or over extended breaks in instruction during the school year. [Compare baseline performance before and after a break (regression) and the amount of time it takes to regain the performance level (recoupment) relative to other students.] 2. Experience with other students who have similar instructional needs. Explain: B. ESY services are necessary for the pupil to attain and maintain self-sufficiency because of: 1. The critical nature of the skill addressed by an annual goal. 2. The student’s age and level of development. 3. The timelines for teaching the skill. To attain self-sufficiency, a student must maintain skills consistent with IEP goals designed to promote a reasonable degree of personal independence in any of the following skill areas: basic self-help skills, muscular control, physical mobility, impulse control, personal hygiene, stable relationships with peers and adults, basic communication, or functional academic competency (including basic reading and writing skills, concepts of time and money, and numerical or temporal relationships). C. The IEP team otherwise determines, given the pupil’s unique needs, that ESY services are necessary to ensure that the pupil receives a free appropriate public education. Explain: