Air Masses and Fronts
advertisement
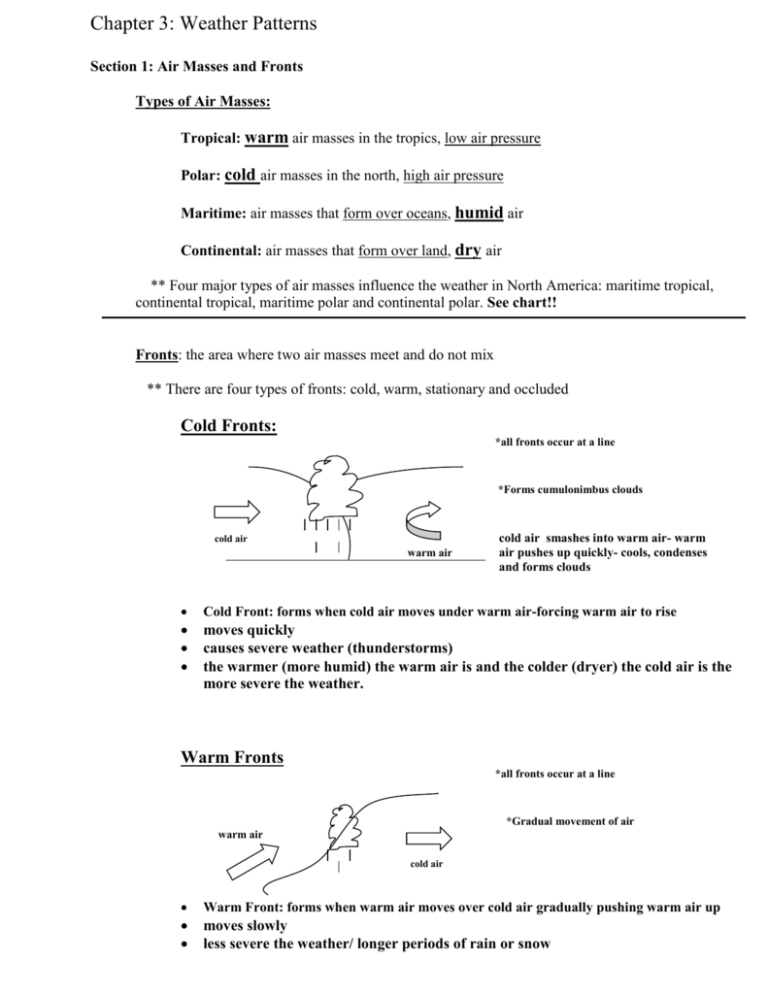
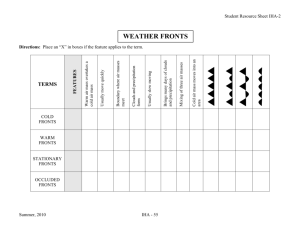
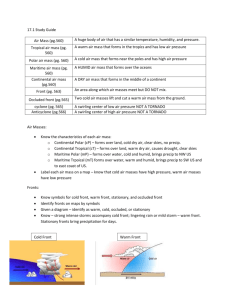
Chapter 3: Weather Patterns Section 1: Air Masses and Fronts Types of Air Masses: Tropical: warm air masses in the tropics, low air pressure Polar: cold air masses in the north, high air pressure Maritime: air masses that form over oceans, humid air Continental: air masses that form over land, dry air ** Four major types of air masses influence the weather in North America: maritime tropical, continental tropical, maritime polar and continental polar. See chart!! Fronts: the area where two air masses meet and do not mix ** There are four types of fronts: cold, warm, stationary and occluded Cold Fronts: *all fronts occur at a line *Forms cumulonimbus clouds cold air warm air cold air smashes into warm air- warm air pushes up quickly- cools, condenses and forms clouds Cold Front: forms when cold air moves under warm air-forcing warm air to rise moves quickly causes severe weather (thunderstorms) the warmer (more humid) the warm air is and the colder (dryer) the cold air is the more severe the weather. Warm Fronts *all fronts occur at a line *Gradual movement of air warm air cold air Warm Front: forms when warm air moves over cold air gradually pushing warm air up moves slowly less severe the weather/ longer periods of rain or snow Stationary Fronts *all fronts occur at a line *air masses move together cold air warm air Stationary Front: forms when cold and warm air masses meet but neither has enough force to move the other moves very slowly causes cloudy, rainy weather for long periods of time not strong enough to take over the other-moves together Occluded Fronts warm air *all fronts occur at a line *Most complex Front cold air cool air warm air mass stuck between a cold and a cool air mass- warm air is squeezed up- cools, condenses and forms clouds Occluded Front: forms when a warm air mass is stuck between a cold and cool air mass Most complex front Moisture rises, cools, condenses and forms clouds Produces rain or snow Cyclones and Anticyclones: Cyclone: Swirling center of low pressure Indicates rain, snow or cloudy weather Spins counterclockwise A hurricane is an entire low pressure system Anticyclone: Swirling center of high pressure Indicates fair weather, little clouds Spins clockwise