Predation III Co
advertisement

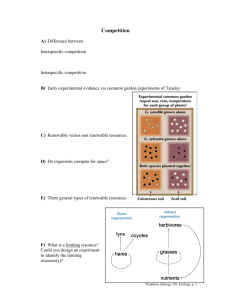
PREDATION III CO-EVOLUTION I. “Prudent Predators” “Predators act to maximize their return without threatening the stability of the prey system” A. Fisheries and other human harvesting of wild populations 1) Maximum sustainable yield 2) Other models of sustainable exploitation. B. Natural predators – are they “prudent”? 1) What would be required? 2) How would it evolve? 3) Do we see this in nature? II. What can predators do? – plasticity A. Prey choice – electivity B. Switching C. morphological adaptations III. What can Prey do? A. Inducible defenses B. Behavioral modifications IV Community level effects A. 2 and 3 (odd and even) level systems B. Top down control C. Higher order interactions Becerra J. X. 1997 Insects on plants: Macroevolutionary chemical trends in host use. Science 276: 253-256 Becerra, J. X. 1994 Evo: 75: 1991-1996 Cotton, P. A., Rundle, S. D., Smith, K. E. 2004: Trait compensation in marine gastropods: shell shape, avoidance behavior, and susceptibility to predation. Ecology: Vol. 85, No. 6, pp. 1581–1584. Dale, B. W. et al. 1994 J. Anim Ecol. 63: 644-652 Dean et al. 1990. Defensive spray of the bombardier beetle: A biological pulse jet. Science 248:1219-1221. Farrell et al. 1991 Escalation of plant defense: Do latex and resin canals spur plant diversification? Am. Nat. 138:881-900. Finke, D. L., Denno, R. F. 2002: Intraguild predation diminished in complex-structured vegetation: implications for prey suppression. Ecology: Vol. 83, No. 3, pp. 643–652. Freed, A. 1980 Ecol 61: 461 Greene et al. 1987 A terphitid fly mimics the territorial displays of its jumping spider predators Science 236: 310312. Johnson & Nelson 1984 Side-scan sonar assessment of gray whale feeding in the Bearing Sea Science 225: 1150-1152. Lampert, W. 1994 Limnol & Oceanogr. 39: 997-1006 Lloyd & Wing. 1981. Nocturnal aerial predation of fireflies by light-seeking fireflies. Science 2222: 634-635. Marquis & Whelan 1994 Ecol. 74: 2007-2014 Martin T. e. On the advantage of being different: Nest predation and the coexistence of bird species PNAS 85: 2196-2199. Mather & Roitberg 1987 A sheep in wolf’s clothing: Tephritid flies mimics spider predators Science 236: 308-310. Mertz 7 Wade 1976 Am. Nat. 100: 489 Oedekoven, M. A., Joern, A. 2000: Plant quality and spider predation affects grasshoppers (Acrididae): food-quality-dependent compensatory mortality. Ecology: Vol. 81, No. 1, pp. 66–77. Pace & Vague 1994 Limnol & Oceanogr 39: 985-996 Purcell et al 1994 Predation by gelatinous zooplankton and resource limitation as potential controls of Acartia tonsa copepod populations in Chesapeake Bay. Limnol. & Oceanogr. 39: 263-278 Resnick & Endler 1982 The impact of predation on life history evolution in Trinidadian guppies (Poecilia reticulata) Evolution 36: 160-177. Reznick et al 1997 Evaluation of the rate of evolution in natural populations of guppies (Poecilia reticulata) Science 275: 1934-1937. AND Lewin R. Science 2 Rosemond et al. 1993 Ecol. 74: 1264-1260 Schmidt, K. A. 2000: Interactions between food chemistry and predation risk in fox squirrels. Ecology: Vol. 81, No. 8, pp. 2077–2085. Siegfried & Knight 1976 Ecol. 57: 603 Sieving & Willson 1998. Nest predation and avian species diversity in northwestern forest understory Ecology 79: 2391:2402. Slobodkin, L. 1974 Am. Nat. 108: 665-678 Steinberg P. D. 1984 Algal chemical defense against herbivores: allocation of phenolic compounds in the kelp Alaria marginata. Science 223: 405-407. Suhonen, J. et al. 1994 Ecol 75: 1626-1634 Vorndran, Iris C., Reichwaldt, Elke, Nürnberger, Beate. 2002: Does differential susceptibility to predation in tadpoles stabilize the Bombina hybrid zone?. Ecology: Vol. 83, No. 6, pp. 1648–1659.