Primers - Nature
advertisement

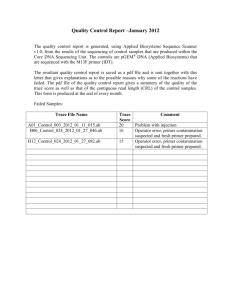
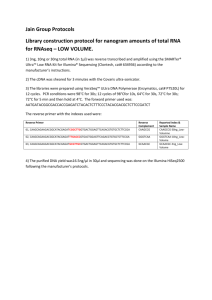
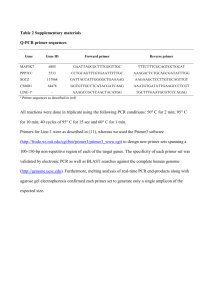
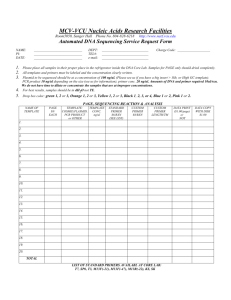
Supplement for the Materials and Method section: Primers ChIP DNA was amplified by PCR using the following primers: Forward FGF9 primer 5’AAGTCGGGGACAGAGAAGGT-3’ and reverse FGF9 primer 5’CACACACACACACGCAGATG-3’; forward FHX primer 5’CTCAGCTGTAGGGGGTGCT-3’ and reverse FHX primer 5’GTGCTGATGAGGGTGGTAGC-3’; forward H2BFC primer 5’TGAAAAGAGCCTTTGGTTCC-3’ and reverse H2BFC primer 5’AAAGTCACCATCGCACAGG-3’; forward RYBP primer 5’ACCACCCCCTAAAAAGGAGA-3’ and reverse RYBP primer 5’GGCCTTGAGGTGTGATTTGT-3’; forward ARHG primer 5’GCCCTGTAACTGGAAGTGGA-3’ and reverse ARHG primer 5’AGGTGTGGAGGGAGACGAC-3’; forward FEN1 primer 5’AATAATCCAGGGATGGACCTG-3’ and reverse FEN1 primer 5’CATGTTCTGGTTCCCAACCT-3’; forward GADD45G primer 5’AAAGCCAGGCGAGATGAAAT-3’ and reverse GADD45G primer 5’GCACCCGCTTTCTGATGTAA-3’; forward APEX primer 5’GGGTGTTTGTCATTCCCTTG-3’ and reverse APEX primer 5’CGGCCGTCTTACTCTTCTTG-3’; forward ORC4L primer 5’TCCCTGGTATTCTGGAGTGG-3’ and reverse ORC4L primer 5’TTTGATCACGTCCCTTCTCC-3’; forward SST primer 5’GGAGGAAATAAAGAGGGCTCA-3’ and reverse SST primer 5’- TGCACACAAATGTACCCAGA-3’; forward ESR2 primer 5’TCACTGAGCTGGTGTGAGGA-3’ and reverse ESR2 primer 5’CTGGAAATGGAAACCGTCAT-3’; forward SREBF2 primer 5’CTGGTCCCATTGACAACAAA-3’ and reverse SREBF2 primer 5’CCATGACACCCGACAACC-3’; forward OAS1 primer 5’TCCAAGCTCAGTCAGCAGAA-3’ and reverse OAS1 primer 5’TGTCAATGGCATGGTTGATT-3’; forward GCN5L2 primer 5’AACTCCTGCAGGGCTCAAG-3’ and reverse GCN5L2 primer 5’GGTGGTGACTTGGGTGTGTT-3’; forward pS2 primer 5’GTGAGCCACTGTTGTCACG-3’ and reverse pS2 primer 5’CGAGCCCCGGATTTTATAG-3’. Peptide synthesis All peptides were prepared on a PAL-PEG-polystyrene resin by continuous flow solid phase synthesis on a PerSeptive Biosystems Pioneer synthesizer (Framingham, MA) using HBTU-activated Fmoc (N-(9-fluorenyl)methoxycarbonyl) amino acids. Peptides were purified using conventional reversed phase HPLC on Vydac C18 (Hesperia, CA) with an overall yield of 25-30%, based on starting resins. The purity of the peptides was confirmed by analytical reversed phase HPLC, capillary zone electrophoresis, and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. The quantity of each peptide was determined by BioRad protein assay as well as running small aliquots on 4-20% or 15% SDS/PAGE followed by silver staining (Silver Stain Plus, Bio-Rad). Sequences of the purified peptides were verified using an ABI PRISM automated sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). The peptides were lyophilized and stored at 4°C prior to use. In Vitro Binding Assays 35 S-labeled HA-cyclin D1 was produced using the TNT Coupled Reticulocyte Lysate System (Promega, Madison, WI). pcDNA3-HA cyclin D1 [a kind gift from Dr. Doris Germain (Russell et al., 1999)] was used to produce the 35S-labeled protein. Binding assays included GST-BRCA1 constructs (1 g) or GST (5 g) and 5 l of TNT reactions and were carried out at 4C overnight. The following day, complexes were washed with TNE150 + 1% NP-40 and TNE50 + 0.1% NP-40. Complexes were separated on a 4-20% SDS-PAGE, dried, and exposed to a PhosphorImager cassette. siRNA Transfections Specific cdk2, cdk4 and cdk9 siRNAs sequences have previously been described (Ammosova T, Berro R, Kashanchi F, Nekhai S. (2005). RNA interference directed to CDK2 inhibits HIV-1 transcription. Virology 341: 171-178; Liang WS, Maddukuri A, Teslovich TM, de la Fuente C, Agbottah E, Dadgar S et al. (2005). Therapeutic targets for HIV-1 infection in the host proteome. Retrovirology 2: 20). The siRNAs were transfected at final concentration of 500 nM using Lipofectamin reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's recommendations. The siRNAs were incubated with cells for 48 h before cells were lysed for Western blotting or ChIP analysis.