Thinking, Language, Intelligence Review Guide
advertisement

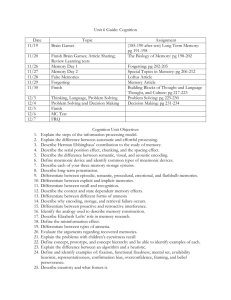
Unit 6 Guide: Cognition Date 11/19 11/20 11/21 11/22 11/25 11/26 12/2 12/3 12/4 12/5 12/6 Topic Unit 5 FRQ; Introduction to Memory Brain Games: Memory Memory Day 1 Memory Day 2 Forgetting; False Memories Memory Quiz (Part I Notecards due); Finish Up Language; Problem Solving Problem Solving Catch Up MC Test FRQ Assignment Sensory Registers and STM: 185-190 Long Term Memory: 191-198 The Biology of Memory: 198-202 Forgetting: 202-206; 40 Studies: Loftus Special Topics in Memory: 206-212 Building Blocks of Thought: 217-220 & Language, Thought, and Culture: 220-224 Problem Solving: 225-230 Decision Making:231-234 Cognition Unit Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. Explain the steps of the information processing model. Explain the difference between automatic and effortful processing. Describe Herman Ebbinghaus’ contribution to the study of memory. Describe the serial position effect, chunking, and the spacing effect. Differentiate between semantic, visual, and acoustic encoding. Define mnemonic device and identify common types of mnemonic devices. Describe each of your three memory storage systems. Describe the neural basis behind learning. Differentiate between episodic, semantic, procedural, emotional, and flashbulb memories. Differentiate between explicit(declarative) and implicit (nondeclarative) memories. Differentiate between recall and recognition. Describe the context and state-dependent memory effects. Differentiate between different forms of amnesia. Describe why encoding, storage, and retrieval failure occurs. Differentiate between proactive and retroactive interference. Explain the analogy used to describe memory construction. Describe Elizabeth Loftus’ role in memory research, including the misinformation effect. Define repressed memories and evaluate research regarding repressed and recovered memories. Explain the problems with children’s eyewitness recall. Define and be able to identify examples of: concept, prototype, convergent thinking, divergent thinking, concept hierarchy. Explain the difference between an algorithm and a heuristic. Define and identify examples of: fixation, functional fixedness, mental set, availability heuristic, representativeness, confirmation bias, overconfidence, framing, and belief perseverance. Differentiate between morphemes and phonemes. Differentiate between grammar, semantics, and syntax. Trace the development of language in children. Explain how Skinner and Chomsky differed in their views on language development. Describe Whorf’s linguistic relativity hypothesis. Vocab 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Information Processing Model Sensory Memory/Sensory Registers Short-Term Memory/Working Memory Iconic v. Echoic Memory Long-Term Memory Automatic v. Effortful Processing Rote v. Elaborative Rehearsal Spacing Effect Serial Position Effect Visual, Acoustic, and Semantic Encoding Chunking Long-Term Potentiation Flashbulb Memory Implicit Memories Explicit Memories Recall v. Recognition Priming Mood and State Congruent (Dependent) Memory Due: 11/26 1. Concept 2. Prototype 3. Concept Hierarchy 4. Algorithm v. Heuristic 5. Confirmation Bias 6. Fixation 7. Mental Set 8. Functional Fixedness 9. Representativeness Heuristic 10. Availability Heuristic 11. Overconfidence 12. Belief Perseverance 13. Framing 14. Phoneme v. Morpheme 15. Grammar 16. Semantics 17. Syntax 18. Babbling Stage 19. One-Word Stage 20. Two-Word Stage 21. Telegraphic Speech 22. Linguistic Determinism Due 12/5 Names 1. Richard Atkinson and Richard Shiffrin 2. Allan Baddeley 3. Fergus Craik and Endel Tulving 4. Hermann Ebbinghaus 5. Elizabeth Loftus 6. H.M. (Henry Molaison) 7. George Miller 8. Noam Chomsky 9. Daniel Kahnerman and Amos Tversky 10. Wolfgang Kolher 11. B.F. Skinner 12. Peter Wason 13. Benjamin Lee Whorf