Reading Guide: Unit 1
advertisement

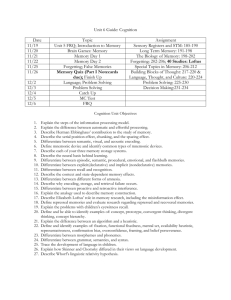
Name ___________________________________ Class Period ____________ Unit #1: COGNITION (Memory, Thinking, Language) RG 1A pg. 255-258 I. Memory- The Basics Explain flashbulb memories List and describe the 3 information-processing steps of memory Explain Atkinson and Shiffrin’s three-stage processing model of memory What are some of the problems associated with this theory of memory? Explain working memory Describe an example of how someone might use their working memory: RG 1B pg. 258-265 II. Step One- Encoding= Two types of encoding: Automatic processing Effortful processing Rehearsal Explain Ebbinghaus’ research on memory What simple principle of learning came out of his research? Next-in-line effectExampleSpacing effectExampleSerial position effectExample- What we encode... Example... Semantic= Acoustic= Visual= What type/kind of information do we remember the most? Explain the self-reference effect. Imagery Describe a mnemonic device Explain.... Method of loci= Peg word= Organizing encoded information Chunking- Acronyms- Explain hierarchies Create an example... RG 1C pg. 265-274 III. Step Two- Storage= Sensory memory= Describe... Give an example.... Iconic memory Echoic memory Short-term memory/working memory= Capacity of short-term memory= What do we remember better? Long-term memory= Capacity? Storing memories Where are memories physically stored in the brain? Explain the idea of a “memory trace.” Explain long-term potentiation. What “hope” has this given researchers? How do stress hormones impact memory? Compare and contrast: Implicit Memories Explicit Memories Describe an example... Describe an example... How do these two types of memories relate to amnesic patients? How is the hippocampus involved in memory? How is the cerebellum involved in memory? What does the dual explicit-implicit memory system help explain? Why? RG 1D pg. 274-278 IV. Step Three- Retrieval= A. Recall- B. Recognition- C. Relearning- Explain retrieval cues and their importance to remembering. What is priming? What are the “best” retrieval” cues? How does context impact memory? Explain déjà vu. Explain mood-congruent memory. How else can our mood influence behavior? RG 1E pg. 278-294 V. Forgetting= Explain encoding failure. Explain storage decay. What is retrieval failure? Compare and Contrast: Proactive Interference Retroactive Interference Describe an example... Describe an example... Come up with a mnemonic device (any kind you want) to remember Proactive and Retroactive interference. Explain motivated forgetting. What is repression? Explain the basic concept of memory construction. What is the misinformation effect and when does it occur? Explain source amnesia (misattribution). How can we tell the difference between real and false memories? How credible are children’s eyewitness reports? Explain the controversy over repressed memories among psychologists. Bottom line…what does evidence say about repression? How can we improve memory, especially when studying? (8 ways) RG 1F pg. 298-312 VI. Thinking Define cognition Explain concepts and prototypes. Describe the following problem-solving strategies… Give an example of each... Algorithm Heuristic Insight Explain the following obstacles to solving problems…be sure to explain WHY it causes issues with solving problems… Confirmation bias Fixation Mental set Functional fixedness Explain the representativenesss heuristic. How can using this heuristic lead to judgmental errors? Explain the availability heuristic. How can using this heuristic lead to judgmental errors? What is overconfidence? Can anything change overconfidence? Explain the positives of overconfidence. Explain framing. Give some examples of framing…(AT LEAST 2) What is belief bias? Explain belief perseverance. How can this have a negative impact on individuals? RG 1G pg. 312-328 VII. Language= Language Structure Explain... Describe an example... a. Phonemes b. Morpheme c. Grammar i. Semantics ii. Syntax Explain the babbling stage of language development. Babbling is NOT… Explain the one-word stage vs. two-word stage of language development. Describe telegraphic speech. How do we learn language????? Skinner’s view… Explain Chomsky’s theory of language development… The Cognitive Neuroscientists’ view today… Explain linguistic determinism. This hypothesis suggests… How does using the pronoun “he” rather than “she” influence the way we think? Give some examples of thinking WITHOUT language. Is this type of thought beneficial? Explain. In the end…how are thinking and language related? List the 5 cognitive skills humans and the great apes seem to share. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Do animals use language? Explain.