Informatics
advertisement

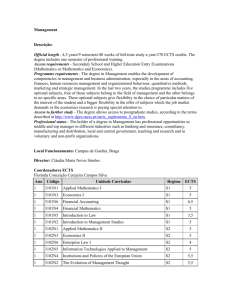
Informatics Descrição: Qualification and title conferred – Masters in Informatics, Mestre. Official length - 2 years/4 semesters/40 weeks of full-time study per year/120 ECTS credits. Access requirements – Degree (180 ECTS) in Informatics Engineering or European recognition of equivalent studies. First cycle course in Technologies and Information Systems or Computation/Informatics/Informatics Engineering. Programme requirements - The Master Course on Informatics aims at providing students with a solid background in both fundamental science and in scientific methods and technologies in Computing. They should then be able to contribute with a critical and creative approach to the application of these methodologies. This should be reinforced with the ability to promote and participate in research and development projects in this area. This course should provide capabilities to participate and lead R&I teams, as well as the indispensable skills of innovation and initiative. Access to further study - The master degree allows access to doctoral studies, according to the terms described at DGES/Academic+Recognition/Diploma+Supplement. Professional Status and Opportunities -Associated with the Masters in Informatics degree are two specialisations freely chosen by the student. Each of those units constitute a coherent higher education proposal in a specific area of application, covering the mutually complementary perspectives of foundations, technologies and knowledge application, and including a transversal practical project component. The Seminar associated with the research project is based on a work plan specifically designed for each student, and it may include additional teaching modules covering, in addition to technical subjects, research methodology, professional ethics and deontology, oral and written expression techniques and other components relevant to the research project execution. The degree structure described above confers to a graduate in Masters in Informatics expertise which allow carrying out a wide range of professional activities, not only directly in the rapidly growing Information Technology related industry, but also in other branches of industry and services. The knowledge and skills taught in this degree also enable the successful prosecution of scientific careers and access to the third cycle of higher education. Local Funcionamento: Campus of Gualtar, Braga Director: José Bernardo Santos Monteiro Vieira Barros Coordenadores ECTS Paulo Jorge Sousa Azevedo Ano Código 1 Unidade Curricular 000007 Option I Software Analysis and Design Bioinformatics Computer Graphics Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Distributed Parallel Computing Cryptography and Information Systems Security Applications Engineering Languages Engineering Regime ECTS A 30,0 Networks and Services Engineering Formal Methods in Software Engineering Distributed Systems Intelligent Systems Decision Support Systems Infrastructure Technologies and Protocols 1 000008 Option II Software Analysis and Design Bioinformatics Computer Graphics Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Distributed Parallel Computing Cryptography and Information Systems Security Applications Engineering Languages Engineering Networks and Services Engineering Formal Methods in Software Engineering Distributed Systems Intelligent Systems Decision Support Systems Infrastructure Technologies and Protocols A 30,0 2 000000 Dissertation A 45,0 2 000335 Seminar S1 15,0 A Opção I e Opção II são constituídas pela mesma lista de UCE opcionais devendo os alunos escolher dua 000007 - Opção I 000008 – Opção II Lista das Unidades Curriculares de Especialização (UCE’s) opcionais: * Software Analysis and Design Regime: A Tipo: Opcional Programa: Pré-requisitos: Resultados de Aprendizagem: Bibliografia: Docentes: Carga Horária: 300 Métodos de Ensino: Métodos de Avaliação: Língua de Instrução: Português Créditos: 30,0 * Bioinformatics Regime: A Tipo: Optional Programa: 1. Molecular and cellular biology Storing and transporting energy within the cells. Glicolysis. Krebs cycle. Oxidative fosforilation. Electron Cellular differentiation. Main methods for studying the cells: citological and biochemical. Biomembranes: function. DNA replication, transcription, translation. RNA molecules. Cytosol: composition, main features. Endopla 2. Biochemical engineering Fundamental problems in Biochemical engineering: role of bioreactors in Bioengineering, organisms, cultu Kinetics of microbial growth: parameters, analysing growth data, Monod kinetics, other equations describi State variables: biomass, substrate, product, experimental design Operation modes of bioreactors: batch and fed-batch cultures, etc. Stoichiometry of microbial reactions. 3. Bioinformatics: algorithms and technologies Major Bioinformatics concepts; Biological databases; Sequence alignment algorithms; Searching sequence Microarray data clustering; Predicting structure of proteins. 4. Statistical methods for Bioinformatics Probability distributions. Statistical Inference. Experimental planning. Linear and logistic regression. Stoch Applications for the analysis of microarray data.. 5. Knowledge extraction from biological databases Decision support systems; Analytical processing; Data Warehousing; Data Mining; Machine Learning: Mo Classification rules; Instance based learning; Neural Networks, Kernel methods; Support Vector Machines protein structure prediction; biomedical text mining.. Pré-requisitos: 1st cycle degree in Informatics. Resultados de Aprendizagem: - Identify, define and describe structural and functionally the main biomolecules, pathways and processes a - Identify and describe the mechanisms of microbial growth and mixture and transfer of mass and heat in b - Identify the main problems in the field of Bioinformatics and know how to select the appropriate algorith available software disponível in the areas of Bioinformatics and Data Mining. - Analyze the results of Bioinformatics tools and interpret their biological meaning as well as to perform th - Know, design and implement the main Bioinformatics algorithms as well as Data Mining and Machine L - Formulate and test hypotheses according to the appropriate statistical method in the context of biological Bibliografia: - D. Mount, Bioinformatics: Sequence and genome analysis, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New Y - A. Baxevanis, F. Ouellete (Eds) Bioinformatics: A Practical Guide to the Analysis of Genes and Proteins - N. C. Jones, P. Pevzner, An Introduction to Bioinformatics Algorithms, MIT Press, 2004 Docentes: Miguel Pereira Rocha (Dep. Informática) Rui Mendes (Dep. Informática) José Teixeira (Dep. Eng. Biológica) Isabel Pereira Rocha (Dep. Eng. Biol.) Rui Oliveira (Dep. Biologia) Pedro Oliveira (Dep. Produção e Sistemas) Carga Horária: 300,0 Métodos de Ensino: Theoretical classes Practical classes Individual study Group work Project work Métodos de Avaliação: Written test Continuous assessment within the internal modules Integrative project Língua de Instrução: Portuguese Créditos: 30,0 * Computer Graphics Regime: A Tipo: Opcional Programa: This Curricular Unit contains four modules, articulated by a laboratorial bus, named Integrated Project, tha outcomes. The modules are: - Computer Vision (5 ECTS) - Illumination and Photo Realism (5 ECTS) - Modeling and Visualization (5 ECTS) - Augmented and Virtual Reality (5 ECTS) - Integrated Project (10 ECTS) Pré-requisitos: Resultados de Aprendizagem: - Identify, Classify and Apply image processing and knowledge extraction techniques from images; - Identify, Classify and Apply the main algorithms and techniques, for the development and conception of - Procedural Modeling and Texturing - Real Time 3D application development taking advantage of both CPU and GPU - Analise, Classify and Implement models and algorithms for photo realistic illumination - Conceive and Evaluate computer graphics applications to obtain the highest quaility and performance acc Bibliografia: OpenGL Programming Guide, Woo, Neider, Davis and Schneider, Addison Wesley. Referência obrigatóri Interactive Computer Graphics, Edward Angel, Addison Wesley. Boa introdução. Real-Time Rendering, Moller and Haines. Boa visão geral do estado da arte. OpenGL Shading Language, Randi J. Rost. Excelente livro de introdução à programação de shaders em GL Rafael C. Gonzalez; Richard E. Woods; “Digital Image Processing”, Addison Wesley Ramesh Jain, Rangachan Kasturi, Brian G. Schunck, “Machine Vision”; McGraw-HILL Robert M. Haralic J.C. Russ; “The Image Processing Handbook”, CRC Press Inc. Physically Based Rendering: from Theory to Implementation”; Matt Pharr and Greg Humphreys; Morgan Web page: http://www.pbrt.org Spatial Augmented Reality: Merging Real and Virtual Worlds, Oliver Bimber and Ramesh Raskar, A.K. P Virtual Reality Technology, Grigore Burdea and Pholippe Coiffet, IEEE Press, 2004. Docentes: António Ramires Fernandes Luís Paulo Santos Manuel João Ferreira Adérito Marcos Carga Horária: 300 Métodos de Ensino: Métodos de Avaliação: Língua de Instrução: Português Créditos: 30,0 * Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Regime: A Tipo: Opcional Programa: Pré-requisitos: Resultados de Aprendizagem: Bibliografia: Docentes: Carga Horária: 300 Métodos de Ensino: Métodos de Avaliação: Língua de Instrução: Português Créditos: 30,0 * Distributed Parallel Computing Regime: A Tipo: Opcional Programa: Pré-requisitos: Resultados de Aprendizagem: Bibliografia: Docentes: Carga Horária: 300 Métodos de Ensino: Métodos de Avaliação: Língua de Instrução: Português Créditos: 30,0 * Cryptography and Information Systems Security Regime: A Tipo: Opcional Programa: Criptografia e Segurança da Informação (CSI), Segurança de Sistemas Informáticos (SSI), Gestão da Segu Conceitos fundamentais da criptografia moderna. Introdução às primitivas, esquemas e protocolos criptogr sistemas informáticos. Certificação digital e a utilização de Infrastruturas de Chave Pública. Aplicações co Aspectos legais da segurança da informação. Privacidade e protecção de dados pessoais. Gestão da confian Tópicos de programação segura com ênfase no dimensionamento de privilégios, protecção de dados, ``stac na operação segura de sistemas informáticos. Perímetros de segurança como elementos estruturantes na no ``fail-over'', salvaguarda e reposição de dados e serviços como técnicas para melhoria da disponibilidade e e avaliação de situações de comprometimento de segurança de sistemas. Pré-requisitos: Resultados de Aprendizagem: - Identificar os problemas da teoria de números mais relevantes à criptografia moderna, e discutir o concei - Explicar os objectivos fundamentais da criptografia moderna e reconhecer as primitivas criptográficas qu - Explicar o funcionamento interno e as noções de segurança associadas às técnicas criptográficas mais rele - Gerir sistemas de certificação digital e PKI e utilizar aplicações correntes/comerciais da criptografia. - Compreender e explorar o paradigma transaccional e a replicação por software no desenvolvimento de sis confiáveis. - Conhecer e dominar as diversas vertentes da administração de sistemas informáticos como forma de asse sua segurança e correcção. - Conhecer, seleccionar e aplicar técnicas de desenvolvimento de aplicações seguras. Bibliografia: * Handbook of Applied Cryptography, Alfred J. Menezes, Paul C. van Oorschot and Scott A. Vanstone, C * Applied Cryptography: Protocols, Algorithms and Source Code in C, Bruce Schneier, John Wiley & Son * Cryptography: Theory and Practice, Douglas R. Stinson, CRC Press. 1995 * A Course in Number Theory and Cryptography (2nd Ed.), Neal Koblitz, Springer-Verlag's Graduate Tex Docentes: Carga Horária: 300 Métodos de Ensino: A escolaridade associada a esta UCE compreende os módulos temáticos, cada um com uma componente d componente laboratorial, denominada Projecto Integrador, que garante a experimentação e aplicação prátic Métodos de Avaliação: A avaliação final da UCE é composta pelas seguintes componentes (todas com nota mínima de 10 valores) * Teste escrito (60%) - No final de cada periodo lectivo (semestre) é realizado um teste escrito. Esses teste leccionados. No final do ano é oferecida a possibilidade de realizar um exame de recurso, podendo aí o alu * Avaliação do Projecto (30%) - Realizada em dois tempos: no final do primeiro semestre e no final do ano trabalho realizado. * Avaliação Seminário (10%) - Consiste numa monografia e numa apresentação (20min.), ambos sobre tem Língua de Instrução: Português Créditos: 30,0 * Applications Engineering Regime: A Tipo: Optional Programa: Multi-tiered application arquitecture, Interactive Systens; Large Database Administration; Data Center Infr Pré-requisitos: Resultados de Aprendizagem: To analise the main design and behaviour patterns of multi-tiered, complex large-scale applications, desi To identify the main characteristics of application servers and use service-oriented technologies as a mea To understand and explore several techniques for developing the interactive layer, designing user interfa To design, evaluate and manage very large volumes of data, fully understanding concepts such as data ac To understand and explain the trade-offs between cost, performance and dependability in datacenters, co infrastructure and operation of datacenters. To be aware of the security risks and techniques to reduce them in large-scale applications. To successfully carry out a life-size multi-tiered software project. Bibliografia: Please refer to the Web site Docentes: António Nestor, António Sousa, Francisco Moura, José Creissac, Manuel Barbosa. Carga Horária: 300,0 Métodos de Ensino: lectures, seminars and practical sessions. Métodos de Avaliação: Written tests (60%) and (mandatory) project (40%) Língua de Instrução: Portuguese Créditos: 30,0 * Languages Engineering Regime: A Tipo: Opcional Programa: Pré-requisitos: Resultados de Aprendizagem: Bibliografia: Docentes: Carga Horária: 300 Métodos de Ensino: Métodos de Avaliação: Língua de Instrução: Português Créditos: 30,0 * Networks and Services Engineering Regime: A Tipo: Optional Programa: Structured into five Modules (6 ECTS each): Network Security Management of Networks and Services Real-time and Distributed Programming Multimedia Systems and Services Seminars and Integrated Project Pré-requisitos: None Teaching Methods: Theoretical subjects will be transmitted to the students in slots of 4x50min (formal lecture). Each slot w under study and ask questions to the teacher. Theoretical teaching is complemented by three componen work). Resultados de Aprendizagem: To identify the main network management tasks, to select and apply appropriate technologies for network To select the most versatile environment and languages aimed to distributed and real-time distributed appli To select and compare suitable tools and devices for multimedia content creation, management, storage an To develop an integrated project for distributed services in communication networks Bibliografia: Mark Rhodes-Ousley, et al. "Network Security: The Complete Reference," 2003. Network Management, MIBs and MPLS: Principles, Design and Impl., S. Morris, Addison Wesley, 2003 Markus Aleksy, Implementing Distributed Systems with Java and CORBA, Springer, 2005 F. Halsall, Multimedia Communications: App., Networks, Protocols and Standards, Addison-Wesley, 2002 Docentes: Bruno Dias António Costa Maria João Nicolau Henrique Santos Carga Horária: 360,0 Métodos de Ensino: Métodos de Avaliação: Students are to be evaluated continuously during classes according to their involvement and interest. The f 20% is based upon practical development exercises and 30% is based on integrated projects development. Língua de Instrução: Portuguese Créditos: 30,0 * Formal Methods in Software Engineering Regime: A Tipo: Opcional Programa: The unit consists of 4 thematic modules worth 5 ECTS each: (1) FM: Formal Methods. (2) PVT: Program Calculus of Information Systems. These are linked together by a laboratorial bus of 10 ECTS (the so-calle unit's main learning outcomes. Project themes are proposed by the unit's industrial sponsors. ACM Classifi Software/SOFTWARE ENGINEERING/Metrics --- 2 ECTS * Software/SOFTWARE ENGINEERING/R ENGINEERING/Software Architectures --- 6 ECTS * Software/SOFTWARE ENGINEERING/Software/P and Debugging --- 4 ECTS * Theory of Computation/LOGICS AND MEANINGS OF PROGRAMS/Spec Pré-requisitos: * Experience in programming * Familiarity with declarative languages (logical, functional) * Predicate log Resultados de Aprendizagem: * Create, analyse, refine, classify, animate, test, transform and calculate with abstract models of requireme systems into efficient implementations on diverse technologies and platforms. * Model, analyse, classify an objects, services) and software architectural schemes. * Specify, express, and verify the validity of properti and assisted proof tools. * Perform software quality control and plan / execute projects in software testing. modelling and reasoning. * Manage software engineering projects in an integrated way from conception to Bibliografia: L*07] Luca Aceto, Anna IngÛlfsdÛttir, Kim Guldstrand Larsen, Jiri Srba Reactive Systems: Modelling, S University Press.; [FL98] J. Fitzgerald and P.G. Larsen. Modelling Systems: Practical Tools and Techniqu Gorm Larsen, Paul Mukherjee, Nico Plat, and Marcel Verhoef. Validated Designs for Object-oriented Sys logic, language, and analysis. The MIT Press, Cambridge Mass., 2006. ISBN 0-262-10114-9. ; [Jon86] C Computer Science. Prentice-Hall International, 1986. C. A. R. Hoare. ; [Mi99] Robin Milner Communica Press, 1999. ; [Ol07] J.N. Oliveira. Data Transformation by Calculation (Post-proceedings version: PDF) School, July 2-7. Tutorial slides: (PDF). ; [UK07] Mark Utting, Bruno Legeard Practical Model-Based Te 13: 978-0123725011. ; [SW01] Davide Sangiorgi, David Walker The pi calculus: A Theory of Mobile Pro Docentes: Jorge Sousa Pinto José Bernardo Barros José Nuno Oliveira (coord.) Luís Soares Barbosa Manuel Alcino Cunha Maria João Frade Carga Horária: 300 Métodos de Ensino: Theory and practical classes. Lab assignments. One cohesive project throughout the whole year. Métodos de Avaliação: Individual exam papers + lab assignments. One year-long group project. Língua de Instrução: Português Créditos: 30,0 * Distributed Systems Regime: A Tipo: Opcional Programa: Pré-requisitos: Resultados de Aprendizagem: Bibliografia: Docentes: Carga Horária: 300 Métodos de Ensino: Métodos de Avaliação: Língua de Instrução: Português Créditos: 30,0 * Intelligent Systems Regime: A Tipo: Opcional Programa: Intelligent Agents Databases, Learning and Knowledge Extraction Natural Computation and Evolutive Intelligence Autonomous Systems Project Pré-requisitos: Resultados de Aprendizagem: To assess the adequacy of an intelligent agent based system to problem solving. To understand how to use the available information to develop a learning system, model selection and test. To understand the advantages and disadvantages of studied intelligent agent based systems, and to decide w To apply virtual intellects, artificial neural networks, genetic and evolutionary programming and particle sw To understand the relation between a model complexity and its performance, using such knowledge to defi To develop the notion of conception and development of an engineering project. Bibliografia: Rocha, M., Cortez, P., and Neves, J. Análise Inteligente de Dados - Algoritmos e Implementação em Java. Russel S., Norvig P., Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, Prentice-Hall, 2nd Ed., 2003, IBSN: 0-1 Wooldrige M., An Introduction to Multiagent Systems, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN: 0 47149691X, 2002. Docentes: Cesar Analide José Neves Paulo Novais Carga Horária: 300 Métodos de Ensino: Métodos de Avaliação: Língua de Instrução: Português Créditos: 30,0 * Decision Support Systems Regime: A Tipo: Opcional Programa: Pré-requisitos: Resultados de Aprendizagem: Bibliografia: Docentes: Carga Horária: 300 Métodos de Ensino: Métodos de Avaliação: Língua de Instrução: Português Créditos: 30,0 * Infrastructure Technologies and Protocols Regime: A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Tipo: Optional Programa: Structured into five Modules (6 ECTS each): Access and Core Network Technologies Wireless and Mobile Communication Networks Advanced IP Networks Multiservice Networking Seminars and Integrated Project Pré-requisitos: None Resultados de Aprendizagem: To explain the main theorectical concepts underpinning the major access and core network Technologies To describe the several types of mobile networks, explaining their evolution and discussing their functiona To identify and discuss IPv4 and IPv6 protocols and extensions in advanced IP networks To identify, define and relate the main concepts, algorithms for supporting real-time applications with grou To develop an integrated project supporting fixed and mobile communications Bibliografia: A. Gumaste and Tony Antony, First Mile Access Networks and Enabling Technologies, Cisco Press, 2004 Yi-Bing Lin, Imrich Chlamtac, Wireless and mobile network architectures, John Wiley & Sons, 2001 William Stallings, Data and Computer Communications, Prentice Hall, 7 ed, 2003 Olivier Hersent, Jean-Pierre Petit, David Gurle, "IP Telephony: Deploying Voice-over-IP Protocols", John Docentes: Alexandre Santos Paulo Carvalho Pedro Sousa Adriano Moreira Carga Horária: 360,0 Métodos de Ensino: Theoretical subjects will be transmitted to the students in slots of 4x50min (formal lecture). Each slot will under study and ask questions to the teacher. Theoretical teaching is complemented by three components: work). Métodos de Avaliação: Students are to be evaluated continuously during classes according to their involvement and interest. The f 20% is based upon practical development exercises and 30% is based on integrated projects development. Língua de Instrução: Portuguese Créditos: 30,0 000000 - Dissertation Regime: A Tipo: Compulsory Programa: The students must developed research work in order to present an original dissertation in Informatics unde Pré-requisitos: To complete successfully the 1st year of the Master degree, i.e. two optional courses in a total of 60 ECTS. Resultados de Aprendizagem: To promote individual research work in Informatics. Bibliografia: Depends on the topic under research. Docentes: One supervisor. Eventually a co-supervisor. Carga Horária: 0 (??) Métodos de Ensino: Individual research work under scientific supervision. Métodos de Avaliação: Assessment and public discussion of a written dissertation. Língua de Instrução: Portuguese or English Créditos: 45,0 000335 - Seminar Regime: S1 Tipo: Compulsory Programa: Selected set of multidisciplinary seminars on Informatics related topics. Development of a project in applied Informatics under the supervision of one or more Professors who are e Pré-requisitos: None. Resultados de Aprendizagem: To promote group work and skills in applied Informatics. Bibliografia: Depends on the topic under study. Docentes: Pedro Rangel Henriques (co-ordinator) Carga Horária: 24,0 (??) Métodos de Ensino: Interactive seminars. Group development work under scientific supervision. Métodos de Avaliação: Assessment and public discussion of the final project and corresponding final report (paper format). Paper peer reviewing. Project poster presentation. Língua de Instrução: Portuguese or English Créditos: 15,0