Use case relationships
advertisement
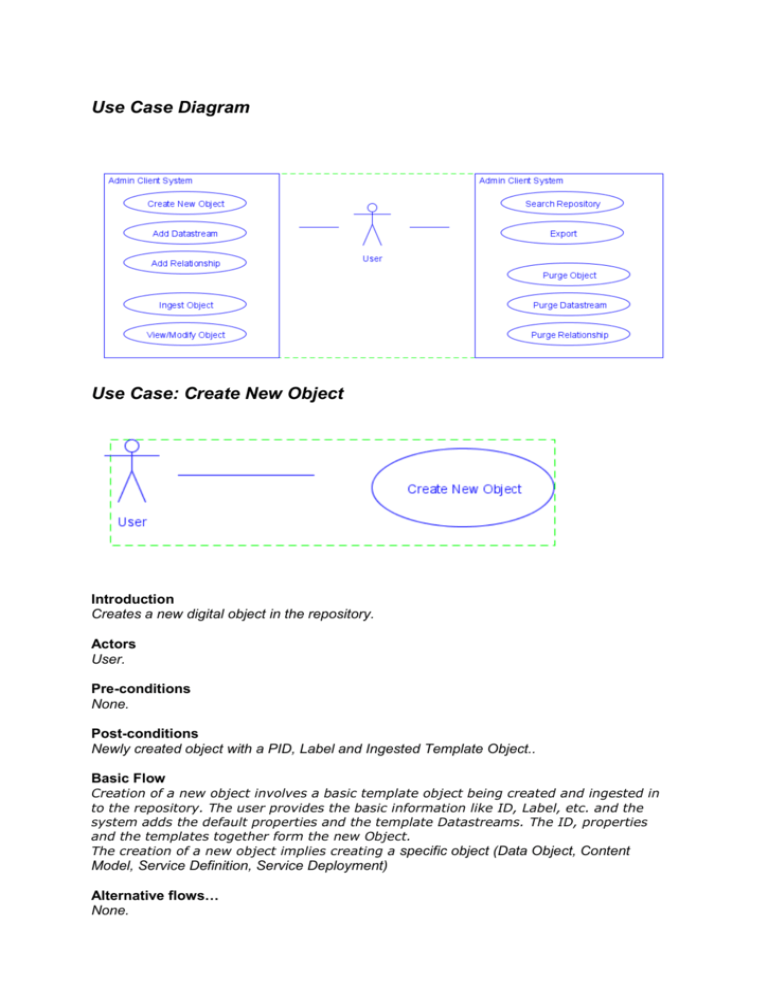
Use Case Diagram Use Case: Create New Object Introduction Creates a new digital object in the repository. Actors User. Pre-conditions None. Post-conditions Newly created object with a PID, Label and Ingested Template Object.. Basic Flow Creation of a new object involves a basic template object being created and ingested in to the repository. The user provides the basic information like ID, Label, etc. and the system adds the default properties and the template Datastreams. The ID, properties and the templates together form the new Object. The creation of a new object implies creating a specific object (Data Object, Content Model, Service Definition, Service Deployment) Alternative flows… None. Special Requirements None. Use case relationships Generalizations: The generalization relationship describes that the Digital Object is of type Data Object (or) Content Model (or) Service Definition (or) Service Deployment Include: The Creation of Data Object includes the creating PID, Label and Ingest of a new Template Data Object Use Case: Add Datastream Introduction Creates a new datastream in the object. Actors User. Pre-conditions Active Digital Object. Post-conditions Newly added Datastream with datastreamID. Basic Flow Addition of the Datastream. Alternative flows… None. Special Requirements None. Use case relationships None. Use Case: Add Relationship Introduction Creates a new relationship in the object. Actors User. Pre-conditions Both the Object and the Predicate exists. Post-conditions Adds the specified relationship to the object's RELS-EXT datastream. Basic Flow Addition of Relationship. Alternative flows… None. Special Requirements None. Use case relationships None. Use Case: View/Modify Object Introduction View/Modify an object. Actors User. Pre-conditions Existing object. Post-conditions Returns the timestamp of modification according to the server. Basic Flow View/Modify an object. Alternative flows… None. Special Requirements None. Use case relationships None. Use Case: Ingest Object Introduction Creates a new digital object in the repository. Actors User. Pre-conditions None. Post-conditions Ingest One Object: Returns the pid of the newly created object. Ingest Multiple Object: Returns counts of objects successfully ingested, objects failed, and time elapsed. Basic Flow View/Modify an object. Alternative flows… None. Special Requirements Ingest From Directory: All objects in the directory must be in the same format.. Use case relationships None. Use Case: Search Repository Introduction Provides a mechanism for searching and retrieving object from the Fedora repository. Actors User. Pre-conditions None. Post-conditions The search result containing the relevant objects are displayed. Basic Flow Search the repository. Alternative flows… None. Special Requirements None.. Use case relationships None. Use Case: Export Introduction Exports the entire digital object in the specified XML format Actors User. Pre-conditions Existing object. Post-conditions One Object: Returns the digital object in the requested XML format Basic Flow Exports the entire digital object in the specified XML format Alternative flows… None. Special Requirements None. Use case relationships None. Use Case: Purge Object Introduction Permanently removes an object from the repository. Actors User. Pre-conditions Existing object. Post-conditions Returns the timestamp of the operation according to the server. Basic Flow Permanently removes an object from the repository Alternative flows… None. Special Requirements None. Use case relationships None. Use Case: Purge Datastream Introduction Permanently removes one or more versions of a datastream from an object.. Actors User. Pre-conditions Existing object. Post-conditions Returns the creation date/time of each deleted datastream. Basic Flow Permanently removes one or more versions of a datastream from an object.. Alternative flows… None. Special Requirements None. Use case relationships None. Use Case: Purge Relationship Introduction Delete the specified relationship. Actors User. Pre-conditions Existing object. Post-conditions Remove the specified relationship(s) from the RELS-EXT datastream. Basic Flow Delete the specified relationship. Alternative flows… None. Special Requirements None. Use case relationships None. Glossary of Terms Actors: List the actors that interact and participate in this use case. Pre-conditions: Pre-conditions that need to be satisfied for the use case to perform. Post-conditions: Define the different states in which you expect the system to be in, after the use case executes. Basic Flow: List the basic events that will occur when this use case is executed. Include all the primary activities that the use case will perform. Be fairly descriptive when defining the actions performed by the actor and the response of the use case to those actions. This description of actions and responses are your functional requirements. These will form the basis for writing the test case scenarios for the system. Alternative flows: Any subsidiary events that can occur in the use case should be listed separately. Each such event should be completed in itself to be listed as an alternative flow. A use case can have as many alternative flows as required. But remember, if there are too many alternative flows, you need to revisit your use case design to make it simpler and, if required, break the use case into smaller discrete units. Special Requirements: Business rules for the basic and alternative flows should be listed as special requirements in the use case narration. These business rules will also be used for writing test cases. Both success and failure scenarios should be described here. Use case relationships: For complex systems, it is recommended that you document the relationships between use cases. If this use case extends from other use cases or includes the functionality of other use cases, these relationships should be listed here. Listing the relationships between use cases also provides a mechanism for traceability. Extras: