Genetics Problems Assignment
advertisement

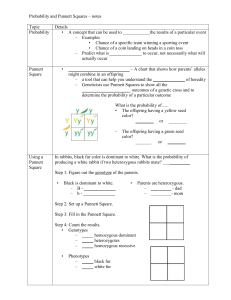
Genetics Problems Assignment /47 + /13 = /60 Name: _________________ Answer neatly on lined paper, showing parent genotypes, Punnett squares etc to communicate HOW you arrived at your answers 1. In humans, normal pigmentation is dominant over albinism, which is a condition in which a person’s skin, hair and eyes have very little pigment. A normal heterozygous man marries a homozygous albino woman. (5) A. What is the F1genotypic ratio? B. What is the F1 phenotypic ratio? C. What is the chance that these parents could have an albino offspring? 2. In humans, brown eyes are dominant over blue eyes. A brown-eyed man marries a blue-eyed woman and one of their children has blue eyes. (5) A. Write the F1 phenotypic and genotypic ratios. B. What is the genotype of their blue-eyed child? 3. Mrs. and Mr. Smith both have widow’s peaks (dominant). Their first child also has a widow’s peak, but their second child doesn’t. Mr. Smith accuses Mrs. Smith of being unfaithful to him. (4) A. Is he necessarily justified? Why or why not? B. What is the F1 phenotypic and genotypic ratio? 4. A chicken which is homozygous for black feathers is bred with a chicken which is homozygous for white feathers. ALL of their offspring have checkered black & white feathers. (5) A. This type of inheritance is called _______________________ B. What is the genotype of a checkered chicken? C. Cross two checkered chickens using a Punnett square. What is the F1 phenotypic and genotypic ratio? 5. A person with Blood type AB mates with a person with type A blood, one of their children has type B blood. (5) A. What are the genotypes of the two parents? B. What is the genotype of their type B offspring? C. What is the probability that their next child would have type A? D. What is the probability that they could have a child with type O blood? 6. A male with hemophilia marries a normal woman with a hemophilic father. (5) A. What are the F1 phenotypic and genotypic ratios. B. What is the probability that the two would have a hemophilic son? A hemophilic daughter? 7. In cats, the genes that control coat color are sex-linked and incompletely dominant. When yellow animals (XY) are crossed with black (XB), a tortoise shell (XBXY) pattern results. A tortoise shell female is bred with a black male. (6) A. What are their genotypes? B. What are the F1 phenotypic and genotypic ratios. C. Is it possible to breed cats to get a male tortoise shell? Explain. 8. Elizabeth is married to John, and they have 4 children. Elizabeth has a straight nose (recessive) and is able to roll her tongue (dominant). John is also able to roll his tongue, but he has a convex (Roman) nose (dominant). Of their four children, Ellen is just like her father, and Dan is just like his mother. The other children—Anne, who has a convex nose, and Peter, who has a straight nose—are unable to roll their tongues. (10) A. What are the genotypes of Elizabeth and John? B. Elizabeth’s father was a straight-nosed roller, while her mother was a convex-nosed non-roller. What can you figure out about Elizabeth’s parents’ genotypes? C. John’s father was a straight-nosed roller, while his mother was a convex-nosed roller. What can you determine about their genotypes? D. Diagram the three described generations of this family in accepted pedigree form, including the phenotypes for these two traits. 9. In certain portions of the Jewish population, there is a genetic disease called Tay Sachs disease, which is fatal to infants within the first five years of life. This disease is caused by a recessive allele of a single gene. Why does this disease persist, even though it is invariably fatal long before the afflicted individual reaches reproductive age? (In other words, why doesn’t the allele for Tay Sachs disease simply disappear?) (2)