Weather and Climate 101
advertisement
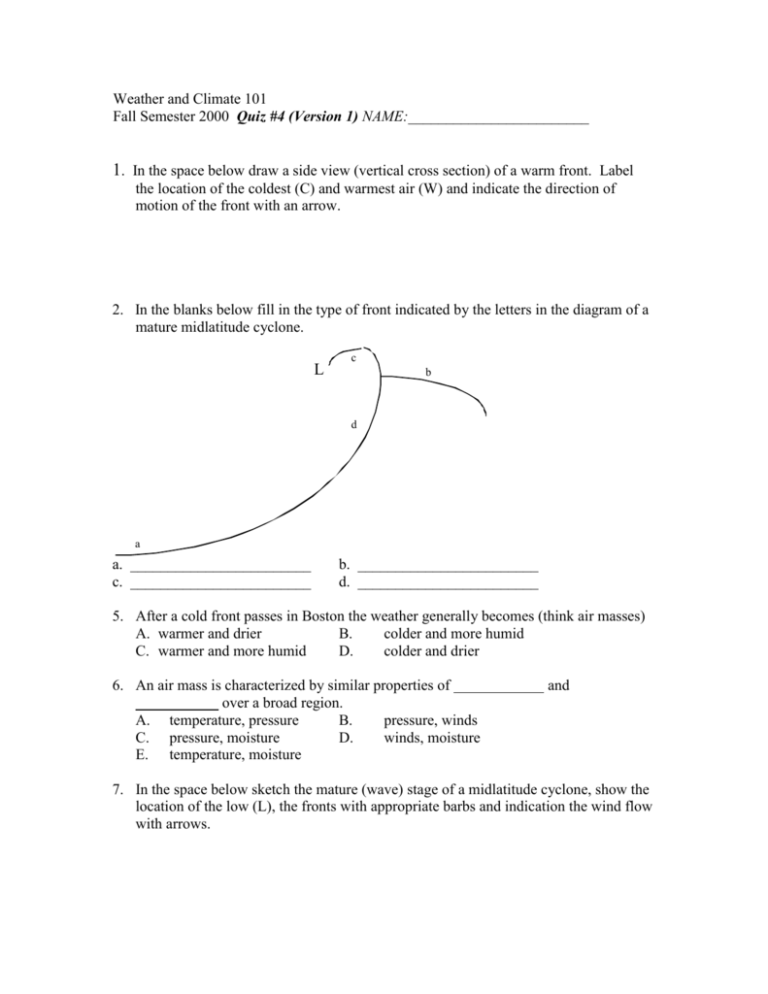
Weather and Climate 101 Fall Semester 2000 Quiz #4 (Version 1) NAME:________________________ 1. In the space below draw a side view (vertical cross section) of a warm front. Label the location of the coldest (C) and warmest air (W) and indicate the direction of motion of the front with an arrow. 2. In the blanks below fill in the type of front indicated by the letters in the diagram of a mature midlatitude cyclone. L c b d a a. ________________________ c. ________________________ b. ________________________ d. ________________________ 5. After a cold front passes in Boston the weather generally becomes (think air masses) A. warmer and drier B. colder and more humid C. warmer and more humid D. colder and drier 6. An air mass is characterized by similar properties of over a broad region. A. temperature, pressure B. pressure, winds C. pressure, moisture D. winds, moisture E. temperature, moisture and 7. In the space below sketch the mature (wave) stage of a midlatitude cyclone, show the location of the low (L), the fronts with appropriate barbs and indication the wind flow with arrows. 8. A good source region for an air mass would be: A. generally flat areas of uniform surface B. mountainous regions C. along coastlines D. in areas characterized by high surface pressure E. A and D Answer the following questions with reference to the sketch of a winter cyclone below 9. In the diagram above, label the most likely location for tornadic thunderstorms to form with the letter (a). 10. In the diagram above, label the most likely location for air-mass thunderstorms to form with the letter (b). 11. In the diagram above, label the most likely location for blizzard conditions to form with the letter (c). 12. In the diagram above, label the most likely location for freezing rain and sleet to occur with the letter (d). 13. The main charge of the National Weather Service is to provide daily weather forecasts (e.g., rain or sunshine) for public consumption. True or False? 14. List four weather related hazards in Hawaii. 15. List four steps in numerical weather prediction. 16. Two factors that make weather prediction in Hawaii difficult are a lack of data over the Pacific Ocean and mountainous island terrain characteristic of the Hawaiian Islands. True or False? 17. List three weather related hazards commonly associated with kona lows in Hawaii. 18. List three factors that contribute to the formation of large swell/waves in Hawaii. 19. How long does it take for a large swell to travel from its source region over the North Pacific Ocean to Hawaii? a) three hours b) three days c) three weeks d) three months 20. Briefly define the following a) Cyclogenesis: b) Frontogenesis: 21. What conditions are conducive to the formation of an air mass? 22. What variables characterize an air mass? 23. What is the source region or origin of mP, cP, mT, and cT air masses that enter the United States? 24. The boundary between two air masses in which warm air is being replaced by colder air is known as a _______________ ________________. 25. Draw below a vertical cross section through a warm front showing slope, airflow and cloud types. 26. a) Why do strong mid-latitude cyclones preferentially form along the east coast of the United States? b) What air masses are present (colliding) in the mid-latitude cyclones that form along the east coast of the United States? 27. List four large-scale weather patterns that cause Hawaii’s weather hazards. 28. a) What are four steps in numerical weather prediction model forecasts? b) What two factors make numerical weather prediction a special challenge in Hawaii? 29. Mountains in Hawaii can enhance rainfall in two ways. What are they? 30. List two reasons why heavy rains quickly produce flash floods in Hawaii. 31. What three factors contribute to the formation of large swell/waves? 32. What two things happen as open ocean waves approach a beach?











