The Course of Imperialism: US Expansion & Hawaii Annexation
advertisement

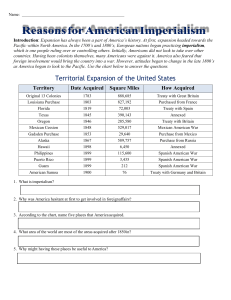
The Course of Imperialism Mid 1800’s to late 1900’s-powerful nations engaged in a mad dash to extend their influence across much of the world. Imperialism-the policy by which a stronger nation extends their political, military , and economic control over a weaker territory or territories. Imperialists Seek Economic Benefits Desire for raw materials and natural resources Extractive Economics-the imperial country extracted or removes raw materials. U.S.-issue was not a shortage of materials, but had a surplus of goods. Imperialists Stress Military Strength To expand and protect interests around the 1. 2. 3. world the nation’s had to build up military strength. “The Influence of Sea Power Around the World”-Alfred T. Mahan Build a modern fleet Acquire foreign bases for ships to refuelHawaii, Cuba, Philippines, Guam Canal across Central America Imperialists Believe in National Superiority Racial, National, and Cultural superiority Social Darwinism Certain nations and races were superior to others and therefore were destined to rule over inferior peoples and cultures Reasons Americans Embraced Social Darwinism “Manifest Destiny” “Our Country”-Josiah Strong-picked up a religious theme to “Manifest Destiny” “The Significance of the Frontier in American History” –Frederick Jackson Turner-now that the frontier had closed discontent ambitious Americans could pursue their fortunes and secure a fresh start U.S. Power Grows in the Pacific 1853-Commodore Mathew Perry sailed into present day Tokyo Bay, Japan “Giant Dragons Puffing Smoke” Result-Perry negotiated a treaty that opened Japan to trade with America Seward Purchases Alaska 1867-Secretary of State, William Seward bought Alaska from Russia for 7.2 million “Seward’s Folly” or “Seward’s Icebox” The “Icebox” turned out to be rich in timber, oil, and other natural resources Alaska greatly expanded America’s reach across the Pacific U.S. Influence in Latin America Grows Businessmen saw Latin America as a natural place to expand their trade and investments First Pan-American Conference Pan-American highway linked the U.S. to Central and South America The United States Acquires Hawaii Americans invested in Sugar Cane plantations 1887-Hawaii amends the constitution so that voting rights were limited to only wealthy landowners American Planters Increase Power 1890’s American Planters faced two obstacles. 1. New U.S. Tariff law imposed duties on previously duty-free Hawaiian sugar 2. 1891-Queen Liliuokalani-”Hawaii for Hawaiian’s” American Planters Increase Power in Hawaii John L. Stevens, U.S. Minister to Hawaii ordered U.S. Marines on shore 1893-rebels overthrow the Queen New government led by Sanford B. Dole asks President Benjamin Harrison to annex, senate didn’t get it approved before Cleveland took office. The United States Annexes Hawaii Grover Cleveland becomes President Cleveland’s investigation revealed the majority of Hawaii’s were against annexation. Cleveland refused to sign the agreement “flagrant wrong-doing” 1897-new President William McKinley favored the annexation of Hawaii 1898-Congress proclaimed Hawaii an official U.S. Territory