TEKS 5
advertisement

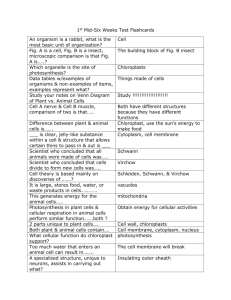
TEKS 7.12F Recognize that according to cell theory all organisms are composed of cells and cells carry on similar functions such as extracting energy from food to sustain life. Used to see CELLS! What is cell theory? Until the 1600s, no one knew cells existed because there was no way to see them. Around 1590, the invention of the first microscope allowed people to look at very small objects. A microscope is an instrument that makes small objects look larger. Over the next 200 years, this new technology revealed that cells came in many shapes and sizes, depending on their function in an organism. Also, depending on what organism was under study, cells had different organelles. But despite these differences, scientists determined that cells had many things in common. These studies led to the development of cell theory. Cell Theory The cell theory is a widely accepted explanation of the relationship between cells and living things. The cell theory states the following: • All living things are composed of cells. (1 or more cells) unicellular or multicellular • Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. • All cells are produced from other cells. Living things differ greatly from one another, but all are made of cells. The cell theory holds true for all living things, no matter how big or how small. Because cells are common to all living things, cells can provide clues about the functions that living things perform. And because all cells come from other cells, scientists can study cells to learn about growth and reproduction. 1.Recognize According to the cell theory, what are all organisms composed of? cells ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ All cells can… Cells and Function An organism’s functions are the processes that enable it to live, grow, and reproduce. Those functions include obtaining oxygen, food, and water and getting rid of wastes. Cells are involved in all these functions. For example, cells in your digestive system absorb food. The food provides your body with energy and materials needed for growth. Cells in your lungs help you get oxygen. Your body’s cells work together, keeping you alive. How do cells carry out their functions? In order for each cell to stay alive, it must carry out many of the same functions as the entire organism. Recall that the organelles carry out functions inside a cell. Each organelle is specialized for processes such as consuming water and food, changing food into energy for the cell, eliminating wastes, and exchanging gases. Function of substances Water The cell membrane controls movement of water into and out of a cell. Water moves from areas of higher concentration to those of lower concentration. Ideally, a cell stays in a state of equilibrium with the same number of water molecules entering and leaving the cell at any given time. aka: Homeostasis – Obtaining Food Organisms that have chloroplasts in their cells make their own food through maintain balance photosynthesis. Sugar molecules produced Example: your body regulates by this process are then processed temperature by by mitochondria in the cell to provide Function sweat/shiver energy. Organisms that do not have chloroplasts cannot perform photosynthesis. Instead, small food particles pass through their cell membranes into the cell. Some food particles are too large to cross the cell membrane. Enter In a process called endocytosis (ehn doh sigh TOH sihs), the cell membrane changes shape and engulfs the particle. The image shows an amoeba consuming food by endocytosis. 2.Define What is endocytosis? How cell membrane surrounds and consumes food ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Using Food Some form of sugar is the basic food for all cells, whether it comes from photosynthesis or from food particles. In animals, lysosomes (LY suh sohmz) break down large food particles into simple Function sugars and other nutrients. Mitochondria release the energy stored in sugar through a process called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration uses oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. Breathing 3.Recognize Which organelles extract energy from sugar to sustain the life of a cell? … Function Mitochondria ________________________________________________________________________________________ Function in animal cells. They also break down Handling Wastes Lysosomes digest more than just food particles old cell parts into substances that can be used again. Vacuoles store wastes that the cell cannot use. These waste-filled vacuoles fuse with the cell membrane and release wastes from the cell through exocytosis (ehk soh sigh TOH sihs), which is the reverse of endocytosis. Small waste products can leave a cell by Exit passing directly out through the cell membrane. Plant cells produce few wastes. The wastes they do produce are stored in their vacuoles, released as a gas into the air, or leach out of roots or leaves. Gas Exchange Plant cells must obtain carbon dioxide to perform photosynthesis, and they must eliminate the excess oxygen that photosynthesis produces. The cell membrane allows passage of carbon dioxide into and oxygen out of the plant’s cell. Animal cells have opposite needs for exchanging gases. Animal cells must obtain oxygen for cellular respiration and must rid themselves of the carbon dioxide they produce. As in plants, the cell membrane allows these gases to pass into and out of the cell. 4.Recognize What cell part controls the movement of life-sustaining gases into and out of a cell? Cell membrane ______________________________________________________________________________________ Lesson Check 1.Recognize According to cell theory, which organisms are composed of cells? All living organisms _____________________________________________________________________________ 2.Identify Name three basic needs that organisms and cells share. Oxygen, water, energy, and to get rid of wastes (any 3) ______________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3.Infer Complete the analogy. An organelle is to a cell_________ as an organ is to an organism. 4.Compare Complete the Venn diagram to compare and contrast the cell functions of exocytosis and endocytosis. Exocytosis How substances exit Both Moving substances Endocytosis How substances enter 5.Recognize According to cell theory, what do all cells have in common? A They are the same size. B They have the same organelles. C They carry on similar functions to live. D They have about the same shape. 6.Recognize All cells must have a way of extracting energy from food to sustain life. a. How do plant cells obtain the energy they need to live? Photosynthesis/sun/chloroplast (any option) ________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ b. How do animal cells obtain the energy they need to live? Eat food/ mitochondria release energy from food ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ c. Which organelle present in both plants and animals is responsible for transforming simple sugars into the energy cells need to sustain life? mitochondria _____________________________________________________________________________________ Lesson Review 7.12F: Cell Theory TEKS Check 1.Recognize What are the three components of cell theory? All living things are composed of cells. • Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. • All cells are produced from other cells. 2.Recognize Like organisms, cells must exchange gases with the environment. a. Identify the gases that both plant and animal cells use for life processes. Oxygen (animals) and carbon dioxide (plants)________________________________________________ b. Describe the movement and use of these gases in a plant cell. Include the terms cell membrane, photosynthesis, and cellular respiration in your description. Plant cells must obtain carbon dioxide to perform photosynthesis, and they must eliminate the excess oxygen that photosynthesis produces. The cell membrane allows passage of carbon dioxide into and oxygen out of the plant’s cell. Mitochondria perform cellular respiration to release the energy from the sugar made during photosynthesis. c. Describe the movement and use of these gases in an animal cell. Include the terms cell membrane and cellular respiration in your description. Animal cells must obtain oxygen for cellular respiration and must rid themselves of the carbon dioxide they produce. The cell membrane allows these gases to pass into and out of the cell. 3.Identify Mitochondria are present in all plant and animal cells. In which cell process are mitochondria important? A gas exchange B production release of energy C getting food D waste elimination 4.Recognize Recognize that cells carry on similar functions to sustain life. a. Identify the role of lysosomes in two different functions within an animal cell. Lysosomes digest food particles in animal cells. They also break down old cell parts into substances that can be used again. b. Which function of lysosomes is carried out by vacuoles in plant cells? Vacuoles store wastes that the cell cannot use. These waste-filled vacuoles fuse with the cell membrane and release wastes from the cell. TEKS in Context 5.Compare You have read that cells and organisms have similar functions that meet similar needs. For each life function listed below, make a checkmark in the correct column to indicate whether it is a need of cells or organisms or both. Meeting Needs Need a. Gas exchange b. Getting food and water c. Changing food into energy d. Eliminating wastes In Cells? In Organisms? In Both? X X X X Cell Theory The discovery of the cell was made possible by the invention of the microscope, which was made possible by improved lens-grinding techniques. Antoni van Leeuwenhoek (16321723), a Dutch tradesman, learned to grind lenses and Invented modern, 1668microscopes. His contemporary assemble them into simple Robert Hooke (1635-1703) used such an instrument to observe spaces in cork, sketches of which appeared in his 1665 publication "Micrographia.” Hooke is responsible for naming these spaces in the cork “cells” – Latin for “little rooms.” Inspired by Hooke's work, Leeuwenhoek began making microscopic examinations of his own. In 1678, he reported to the Royal Society that he had discovered "little animals" -- bacteria and protozoa -- in various samples of pond scum. The society asked Hooke to confirm Leeuwenhoek's findings, and he did. This paved the way for wide acceptance that a hidden world existed just beyond the limits of human vision and encouraged many scientists to take up the microscope in their investigations. One such scientist was German botanist Matthias Jakob Schleiden (1804-1881), who looked at numerous plant 1838 samples. Schleiden was the first to recognize that all plants, and all the different parts of plants, are composed of cells. While having dinner with zoologist Theodor Schwann (1810-1882), Schleiden mentioned his idea. Schwann, who came to similar conclusions while studying animal tissues, quickly saw the implications of their work. In 1839, he published "Microscopic Investigations on the Accordance in the Structure and Growth of Plants and Animals," which included the first statement of the cell theory: All living things are made up of cells. Then, in 1858, Rudolf Virchow (1821-1902) extended the work of Schleiden and Schwann by proposing that all living cells must rise from preexisting cells. This was a radical idea at the time because most people, scientists included, believed that nonliving matter could spontaneously generate living tissue. List the parts of the Cell Theory, and name the scientists who are credited. 1. All living things are composed of cells. Scientists: Schleiden & Schwann 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function for living things. Scientists: Schleiden & Schwann 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. Scientist: Virchow Create a Cell Theory Timeline. 1668 Anton van Leeuwenhoek Invented the modern microscope 1665 Robert Hooke Discovered and named CELLS while looking at cork 1839 Theodor Schwann Discovered all animals are made of cells (credited with 1st two parts of cell theory) 1858 1838 Rudolf Virchow Matthias Schleiden Discovered all cells Discovered all plants come from existing are made of cells st cells. (3rd pert of cell (credited with 1 two theory) parts of cell theory)