Chapter 1 - TamAPChemistryHart
advertisement
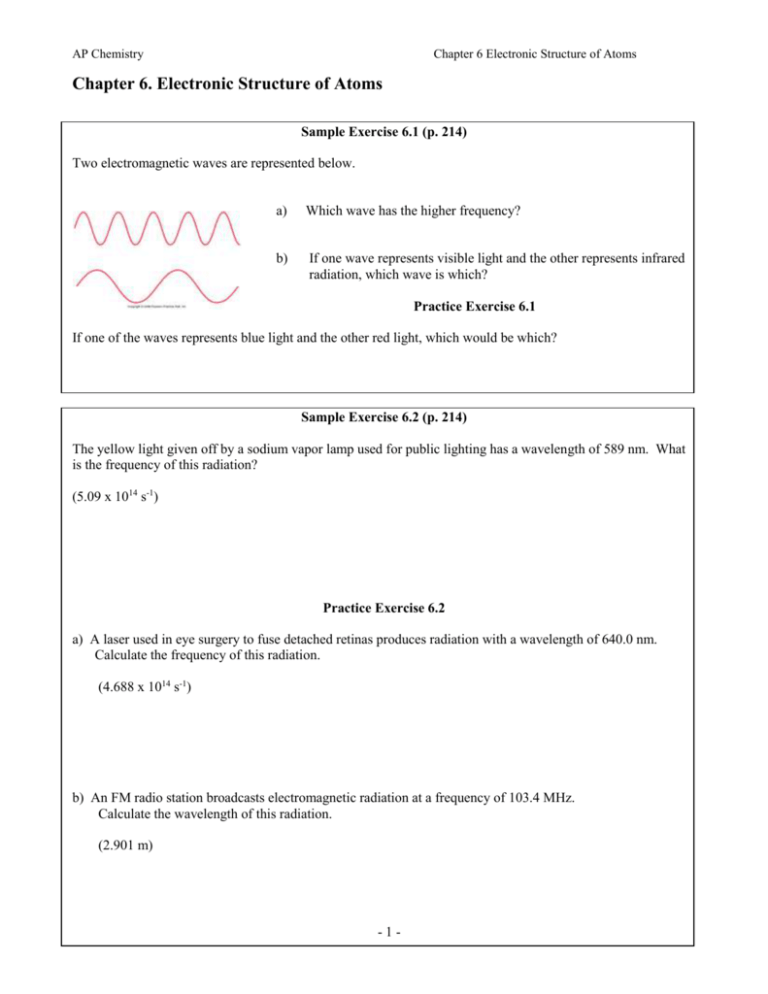
AP Chemistry Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms Chapter 6. Electronic Structure of Atoms Sample Exercise 6.1 (p. 214) Two electromagnetic waves are represented below. a) Which wave has the higher frequency? b) If one wave represents visible light and the other represents infrared radiation, which wave is which? Practice Exercise 6.1 Figure 06.05-01UN If one of the waves represents blue light and the other red light, which would be which? Sample Exercise 6.2 (p. 214) The yellow light given off by a sodium vapor lamp used for public lighting has a wavelength of 589 nm. What is the frequency of this radiation? (5.09 x 1014 s-1) Practice Exercise 6.2 a) A laser used in eye surgery to fuse detached retinas produces radiation with a wavelength of 640.0 nm. Calculate the frequency of this radiation. (4.688 x 1014 s-1) b) An FM radio station broadcasts electromagnetic radiation at a frequency of 103.4 MHz. Calculate the wavelength of this radiation. (2.901 m) -1- AP Chemistry Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms Sample Exercise 6.3 (p. 217) Calculate the energy of one photon of yellow light whose wavelength is 589 nm. (3.37 x 10-19 J) If one photon of radiant energy supplies 3.37 x 10-19 J, then how many photons will one mole of these photons supply? (2.03 x 105 J/mol) Note: this amount is the magnitude at which chemical reactions take place. Radiation break bonds, i.e. photochemical reactions. Practice Exercise 6.3 a) A laser emits light with a frequency of 4.69 x 1014s-1. What is the energy of one photon of the radiation from this laser? (3.11 x 10-19 J) b) If the laser emits a burst or pulse of energy containing 5.0 x 1017 photons of this radiation, what is the total energy of that pulse? (0.16 J) c) If the laser emits 1.3 x 10-2 J of energy during a pulse, how many photons are emitted during the pulse? (4.2 x 1016 photons) -2- AP Chemistry Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms Sample Exercise 6.4 (p. 222) Predict which of the following electronic transitions produces the longest wavelength spectral line: n = 2 to n = 1, n = 3 to n = 2, or n = 4 to n = 3. (See textbook, Figure 6.14 on p. 220.) Practice Exercise 6.4 Indicate whether each of the following electronic transitions emits energy or requires the absorption of energy: a) n = 3 to n = 1; b) n = 2 to n = 4. Sample Exercise 6.5 (p. 223) OPTIONAL Note: You will need the following conversion factor: 1 J = kg m2 s2 What is the wavelength of an electron with a velocity of 5.97 x 106 m/s? (0.122 nm or 1.22 Å) Practice Exercise 6.5 Calculate the velocity of a neutron whose de Broglie wavelength is 500. pm. (mass of a neutron = 1 amu = 1.66053873 x 10-24 g) (799 m/s) -3- AP Chemistry Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms Note new alternate notation for s,p,d,f – pp. 226, 227 Sample Exercise 6.6 (p. 228) a) Without referring to Table 6.2, predict the number of subshells in the fourth shell, that is, for n = 4. b) Give the label for each of these subshells. c) How many orbitals are in each subshell? Practice Exercise 6.6 a) What is the designation for the subshell with n = 5 and l = 1? b) How many orbitals are in this subshell? c) Indicate the values of ml for each of these orbitals. Sample Exercise 6.7 (p. 237) Draw the orbital diagram representation for the electron configuration of oxygen, atomic number 8. How many unpaired electrons does an oxygen atom possess? Practice Exercise 6.7 a) Write the electron configuration of phosphorus, element 15. b) How many unpaired electrons does a phosphorus atom possess? -4- AP Chemistry Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms Sample Exercise 6.8 (p. 241) What is the characteristic valence shell electron configuration of the group 7A elements, the halogens? Practice Exercise 6.8 What family of elements is characterized by having an ns2np2 outer-electron configuration? Sample Exercise 6.9 (p. 241) a) Write the complete electron configuration for bismuth, element number 83. b) Write the condensed electron configuration for this element, showing the appropriate noble-gas core. c) How many unpaired electrons does each atom of bismuth possess? Practice Exercise 6.9 Use the periodic table to write the condensed electron configurations for the following atoms: a) Co (atomic number 27) b) Te (atomic number 52) -5- AP Chemistry Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms Integrative Exercise 6 (p. 243) Boron, atomic number 5, occurs naturally as two isotopes, 10B and 11B, with natural abundances of 19.9% and 80.1% respectively. a) In what ways do the two isotopes differ from each other? Does the electronic configurations of 10B differ from that of 11 B? b) Draw the orbital diagram for an atom of 11B. Which electrons are the valence electrons (the ones involved in chemical reactions)? c) Indicate three major ways in which the 1s electrons in boron different from the 2s electrons. d) Elemental boron reacts with fluorine to form BF3, a gas. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction of solid boron with fluorine gas. f) When BCl3, also a gas at room temperature, comes into contact with water, it reacts to form hydrochloric acid and boric acid, H3BO3, a very weak acid in water. Write a balanced net ionic equation for this reaction. -6-