Homework #1 - LaGuardia ePortfolio
advertisement

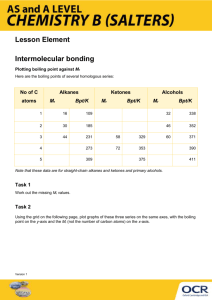
Dr. Ivan Rivera-Torres LaGuardia Community College Name: Cherub Ami Ruiz Spring 2009 SCC 202.1760 Homework #1(10pts.) Due March 18, 2009 1. The types of intermolecular forces present in each of the following substances and the highest boiling point in each pair are as follows: a) C6H14 is a non polar molecule; thus the intermolecular force present is London Dispersion Force. C8H18 is also a non polar molecule with London Dispersion intermolecular forces. However, due to the greater molecular weight of C8H18, it will have stronger intermolecular forces thus its boiling point will be higher than C6H14. b) C3H8 is a hydrophobic molecule with London Dispersion intermolecular forces. CH3OCH3 is a polar molecule with dipole-dipole and London Dispersion intermolecular forces. These bonds will cause the CH3OCH3 molecule to have a much higher boiling point than C3H8 because more of the heat energy will go into breaking all the bonds. c) HOOH is a polar molecule with dipole-dipole bonds, London dispersion forces and hydrogen bonds as its intermolecular forces. HSSH is also a polar molecule with both dipole-dipole bond and London dispersion forces but lacks the hydrogen bonds. Therefore, HOOH will have higher boiling point than HSSH because it takes greater heat energy to break up hydrogen bonds. d) NH2NH2 is a polar molecule with dipole-dipole bonds, London dispersion forces and hydrogen bonds as its intermolecular forces. CH3CH3 is a Cherub Ruiz Page 1 2/16/20161 hydrophobic molecule with London Dispersion intermolecular forces. Therefore, NH2NH2 will have a higher boiling point than CH3CH3. e) CH3CH2OH is hydrophilic with dipole-dipole bonds, London dispersion forces and hydrogen bonds as its intermolecular forces. Although, CH3OCH3 is a polar molecule with dipole-dipole and London Dispersion intermolecular forces, it will have a lower boiling point as compared to CH3CH2OH. Therefore the hydrogen bond in CH3CH2OH will cause it to have a higher boiling point. 2. A particular refrigerator cools by evaporating liquefied chlorodiflouromethane, CCl2F2. How many kilograms of this liquid must be evaporated to freeze a tray of water at 0°C to ice at 0°C? The mass of water is 525g, the heat of fusion (melting) of ice in 6.01kJ/mol, the heat of vaporization of chlorodiflouromethane is 17.4kJ/mol. Hint: apply a negative sign to the heat of fusion of ice, since heat energy is taken away from water. Cherub Ruiz Page 2 2/16/20162