Foods II Vocabulary: Food Science Terms & Definitions
advertisement

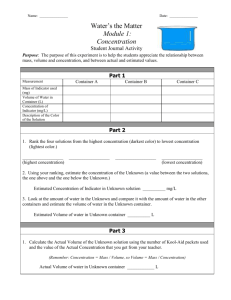
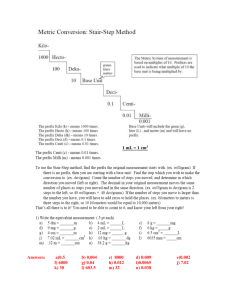
Foods II Vocabulary 1.01 1. Food Science – The study of the nature of food and the principles of its production, processing, preservation, and packaging. 2. Nutrition – A food component necessary to sustain life. 3. Proximate Analysis – quantitative analysis of a mixture (as food) to determine the percentage of components. Sometimes called product testing. 4. Objective Method – The first type of analytical method commonly used in the food industry. It involves the process of obtaining reliable and valid quantitative (or objective) data. 5. Science – The systematic knowledge of natural and physical phenomena. 6. Colorimeter – A device that measures the color of foods in terms of value, hue, and chroma. 7. Phenomenon – A fact, occurrence, circumstance, or process that can be observed. 8. Applied Science – The process of putting scientific knowledge to practical use. 9. Experiment – A controlled situation that allows a scientist or researcher to determine what causes a change to occur. 10. Formulation – The term for a recipe used in the food industry. 11. Replicable – Term used to describe an experiment that meets the scientific standard of being repeatable. 12. International System of Units (SI) – 13. Mass – A measure of the quantity of matter. 14. Gram (g) – The mass of 1 cubic centimeter (cm3) of water at 4°C (39°F). 15. Kilogram (kg) – The mass of 1 liter of water at 4°C (39°F). 16. Weight – The measure of the force of gravity between two objects. 17. Calibrate – The process of adjusting a measuring instrument to a standard. 18. Length – The distance between two points. 19. Meter (m) – The standard unit of length in the metric system. 20. Volume – The amount of space occupied by an object. 21. Liter (L) – A unit of fluid volume in the metric system, which equals the space in an area 1 decimeter high by 1 decimeter wide by 1 decimeter deep (1 cubic decimeter). 22. Beaker – A deep, wide-mouthed container with a pouring lip used to hold substances during experiments and take inexact volumes measurements. 23. Erlenmeyer Flask – A flat-bottomed, cone-shaped container used to mix and hold liquids and take inexact volume measurements. 24. Graduated Cylinder – A tall container used to accurately measure the volume of liquids to the nearest milliliter. 25. Burette – A graduated glass tube with a control valve at the bottom used to pour an accurate amount of liquid. 26. Meniscus – The curve at the surface of a liquid in a container. 27. Celsius degree – A unit of temperature equal to .01 of the difference between the boiling (100°C) and freezing points (0°C) of water. 28. Scientific Method – A system of steps used to solve problems. 29. Hypothesis – A possible solution to a problem based on available evidence. 30. Variable – A factor that is being changed in an experiment. 31. Control – The standard against which all changes in an experiment are measured. 32. Variation – Each change that is made in an experiment. 33. Data – Measurable facts that are collected during an experiment. 34. Conclusion – An analysis and application of data is an experiment that answers the question how, what, where, when, or why and describes what data and observations mean. 35. Meta-analysis – When the results of several individual studies are pooled to yield overall conclusions.