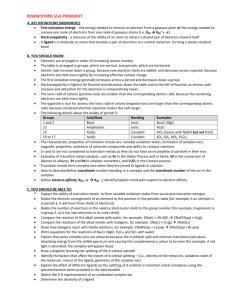
Ion Formation Notes

Name: __________________________________________________________ Date __________________________________ Period ___________
Ion Formation Notes
(Unit 5.1)
MANY ELEMENTS ARE UNSTABLE
Many elements do not exist all by themselves in nature.
They _____________________ with other elements and form ______________________.
This is because their neutral form is _________________________.
In other words, they have A LOT of chemical potential energy.
Having a lot of chemical potential energy is like a pencil standing on its point.
Eventually it will fall to a lower energy position.
Everything in the universe tends towards as ____________ an energy state as possible, so elements will do what they need to do to be more _____________________.
HOW DO ELEMENTS BECOME MORE STABLE?
Many elements are unstable because they have _____________________ electron configurations.
The most stable electron configuration is having 8 electrons in the highest energy level (a full ______________).
Unstable elements will ________________ or lose valance electrons to achieve a full octet.
Then they will have an overall _____________________ and will be known as ___________________.
Elements will gain or lose valance electrons to be like the closest _________________________ gas.
Example: Fluorine 9p + and 9e -
e configuration: ______________________________
It has ______ valance electrons.
It will gain one more electron and its electron configuration would be the same as Neon’s:
___________________________.
It would have an overall charge of ___________. Why?_________________________________
ANIONS
Once fluorine gains its electron it is now known as a _____________________ ion which is represented with the symbol: ____
Negative ions like fluorine are known as _______.
Other ___________________ like Cl and Br will also form anions with ____________ charges.
Why? ________________________________________
Since other non metals also have high ________________________ they will also gain electrons and form
_______________________.
Group 16 elements will gain ______valance electrons and will end up with a _______ charge.
Name: __________________________________________________________ Date __________________________________ Period ___________
Group 15 elements will gain __________ valance electrons and will end up with a ____ charge.
CATIONS
______________ tend to ___________ electrons to become stable.
Example: Sodium 11p + and11e -
› e configuration:_________________
›
It has _______ valance electron.
›
It is easier to lose 1 valance electron then to gain _______.
›
So its electron configuration will end up the same as Neon’s: _________________.
›
It would have an overall charge of ________. Why?
Once sodium loses its electron it is now known as a sodium ion which is represented with the symbol: ______
Positive ions like Na+ are known as _____________.
Other alkali metals like Li and K will also form cations with ______ charges.
Why? ________________________
Since other metals also have low ______________________________ they will also ____________ electrons and form _____________.
Group 2 elements will lose ______ valance electrons and will end up with a ______ charge.
Aluminum will lose 3 valance electrons and will end up with a _________ charge.
TRANSITION METALS AND GROUPS 3A AND 4A
Tranistion metals and some of the group 3A and 4A elements don’t lose or gain enough electrons to have a completely ___________ octet.
In fact many of the transition metals can form __________ than one ____________ ion.
For example, Fe can lose two electrons to become _____ or it can lose three electrons to become ________
Name: __________________________________________________________ Date __________________________________ Period ___________
NAMING IONS
When __________ like sodium become __________ they keep their names.
When nonmetals like _________________ become
______________ their names change to have ___________at the end.
2 MORE THINGS
When atoms become ions they no longer have the same
________________ as their _____________ atom.
Also, ions usually take on the electron configuration of the nearest noble gas but they do not actually ________________ that noble gas.
For example _____________ has the same electron configuration as Ne but it still has 11p+ so it doesn’t behave like _______.
FYI
You should be able to list the charges of the following ions just by looking at their location on the periodic table:
Alkali metals: H, Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs
Alkali Earth metals: Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba
Group 13: Al
Group 15: N, P
Group 16: O, S, Se
Group 17: F, Cl, Br, I