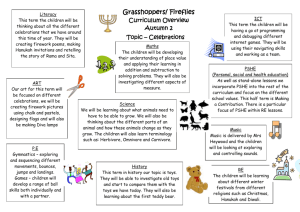
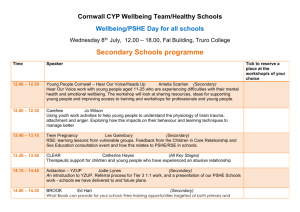
PSHE planning - Hampshire County Council
advertisement
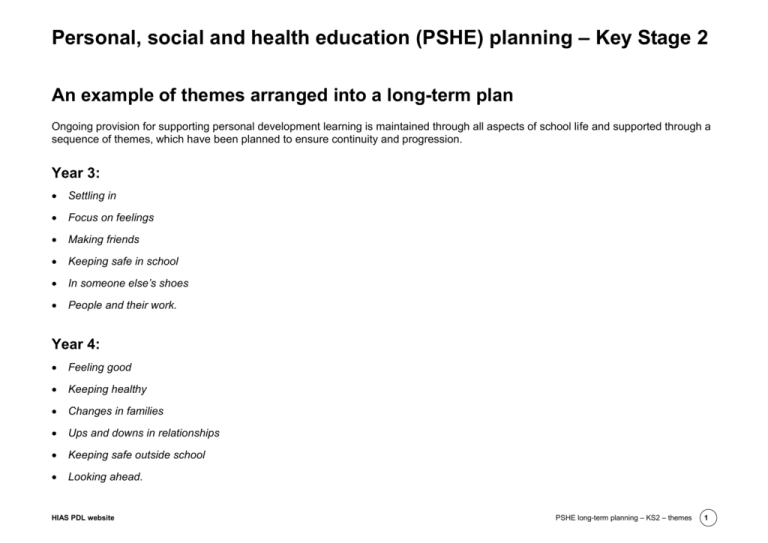
Personal, social and health education (PSHE) planning – Key Stage 2 An example of themes arranged into a long-term plan Ongoing provision for supporting personal development learning is maintained through all aspects of school life and supported through a sequence of themes, which have been planned to ensure continuity and progression. Year 3: Settling in Focus on feelings Making friends Keeping safe in school In someone else’s shoes People and their work. Year 4: Feeling good Keeping healthy Changes in families Ups and downs in relationships Keeping safe outside school Looking ahead. HIAS PDL website PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 1 Year 5: Who decides Risks and pressures We are all different It’s my body Being involved in my community Looking at the world. Year 6: Managing conflict The world of work Taking responsibility for my own safety Changing relationships Rights, responsibilities and the law Transition and managing change. 2 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Year 3 – Settling in Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 1c to face new challenges positively by collecting information, looking for help, making responsible choices, and taking action. enjoy life at school know the rules, and understand expectations for Key Stage 2 know where to get help in school recognise what is special about themselves and their abilities and interests co-operate, share and take turns. HIAS PDL website Introducing a partner – find out what they enjoy at school and introduce them to the class. Circle time – “I like it when ...”, “I enjoy school when ...”. Developing classroom charters. Discuss routines of junior school/Key Stage 2. Walk around school to introduce key members of staff. Route following. Children carrying out interviews with key staff and reporting back to class. Use of scenario cards to explore problem solving – where would you go/who would you see or ask? Making a personal page or a fact file. Self-analysis through using a questionnaire and personal work sampling. Co-operation activities through circle time and parachute games. contribute to making a classroom charter to enable children to enjoy school set own personal targets and write own personal page for report recognise and describe their own ability to share and co-operate demonstrate awareness of who to approach with a problem. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 3 Older children as visitors. The effect of transition on children. What experience of activities, such as circle time, have the children had at Key Stage 1. The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Books and stories. Problem-solving cards. School map. Games for wet play. Equipment to allow sharing. Parachute. Classroom charter. HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Own reporting, self-analysis, personal profile. Observation of use of problem-solving cards and drama scenarios. Links Every Child Matters Have you thought about? Resources Enjoy and achieve Ready for school. Achieve personal and social development and enjoy recreation. RRR Articles: 3 (adult involvement), 12 (opinions). Healthy Schools Emotional health and well-being 4 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes Provide opportunities for children to participate in school activities and responsibilities to build their confidence and self-esteem. HIAS PDL website Year 3 – Focus on feelings Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 1a to talk and write about their opinions, and explain their views, on issues that affect themselves and society develop the language of feelings recognise feelings in different situations be able to express feelings in different ways recognise the impact of feelings on others. 4a that their actions affect themselves and others, to care about other people’s feelings and to try to see things from their points of view. Have you thought about? Resources understand that people express feelings in different ways utilise appropriate and varied language to express ideas and feelings describe/state how they feel to a teacher or other adult speculate on emotional consequences. Children who have family problems, crises at home, are young carers or are vulnerable children.* Other agencies who could offer support. The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Books and stories – Misery Moo, by Jeanne Willis. Story – I’m bored!, by Brian Moses. Situation cards. Persona dolls (available from the County Religious Education Centre and/or Rights and Diversity Education Centre). Story – All in the family, by Tony Bradman. HIAS e-Profile CD. HIAS PDL website Brainstorm feelings. Cards with scenarios for role play. Art, music, dance and body language to explore expressing feelings. Writing to express feelings. Keeping a personal feelings log. Poetry and stories related to feelings, finishing a story or poem. Consequence diagram/tree. Use family decisions/dilemma type stories/poems/plays as a focus for family dilemma discussions.* Buddy systems. Role play. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 5 Assessment opportunities Links Every Child Matters Observation of role play. Speaking and writing about feelings. Be healthy Mentally and emotionally healthy. Stay safe Have security, stability and are cared for. Enjoy and achieve Achieve personal and social development and enjoy recreation. RRR Articles: 1 (rights of the Convention), 3 (adult involvement), 5 (family guidance), 12 (opinions), 16 (privacy), 37 (legal punishment). Healthy Schools Emotional health and well-being Have clear, planned curriculum opportunities for children to understand and explore feelings using appropriate learning and teaching styles. SEAL Getting on and falling out. *NB: To be aware that disclosures may occur during these discussions. Due to the sensitive nature of the subject matter, this should be handled carefully. For support and queries contact the school’s Child Protection Officer. 6 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Year 3 – Making friends Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 2f to resolve differences by looking at alternatives, making decisions and explaining choices think about being a friend know what we do that makes each other happy, sad and cross know what helps and hinders friendships consider ways of resolving differences be able to initiate friendships. 4a that their actions affect themselves and others, to care about other people’s feelings and to try to see things from their points of view 4c to be aware of different types of relationship, including marriage, and those between friends and families, and to develop the skills to be effective in relationships. Have you thought about? HIAS PDL website Circle time and interviewing in pairs on the qualities of a good friend. Poetry/non-consecutive writing – What makes a friend ...? Writing about friends – record what makes them happy, sad or cross about friends and pass round for discussion to show that we are all different. Role play to explore difficulties in friendships. Situation cards about situations in friendships to be acted out through role play – saying “No”, helping a friend, etc. Word banks created by children on what makes a friend? Mask making to extend language of feelings. Working in different groups, both in class and, if possible, across year groups. Role play. work with others for a variety of purposes identify personal qualities explain qualities which make a good friend describe difficulties which may arise in friendships know how to cope with some friendship problems. Access to appropriate vocabulary when discussing friendships and problems in friendships. Using/creating buddy schemes or equivalent. Sensitivity towards loner children and those who are not accepted by other children.* The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 7 Pictures of faces to show range of feelings. Persona dolls (available from the County Religious Education Centre and/or Rights and Diversity Education Centre). Books and stories. HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Children’s work/writing to exemplify where they are at that point (date and quote). Self-assessment of friendship skills. Links Every Child Matters Resources Make a positive contribution Engage in decision making and support the community and environment. Develop positive relationships and choose not to bully and discriminate. RRR Articles: 7 (name and nationality), 12 (opinions), 15 (joining groups). Healthy Schools Emotional health and well-being Have clear, planned curriculum opportunities for children to understand and explore feelings using appropriate learning and teaching styles. *NB: To be aware that disclosures may occur during these discussions. Due to the sensitive nature of the subject matter, this should be handled carefully. For support and queries contact the school’s Child Protection Officer. 8 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Year 3 – Keeping safe in school Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 2c to realise the consequences of anti-social and aggressive behaviours, such as bullying and racism, on individuals and communities 3g school rules about health and safety, basic emergency aid procedures and where to get help know about bullying, why it happens and the effects it has on people think about how to deal with bullying and how to stop it happening know school safety rules relating to medicines, alcohol, solvents and illegal drugs consider how they contribute to making the school environment a safe place know that discarded syringes and needles can be dangerous. Survey of playground – what we like/do not like about our playground. Circle time – “I don’t like it when ...”, “I think a bully is ...”, “I would help someone who was being bullied by ...”. Teacher-led explanations of how to report concerns/ incidents. What drugs are found in the home – sorting and drawing/ writing activities. Sort into everyday drugs such as alcohol, tobacco and medicines. Litter survey. Sequencing illustrated cards to explain what to do. describe their school safety rules describe the part they play in keeping themselves safe in school know who to tell if they experience or witness bullying understand the importance of sharing and telling if they are bullied or unhappy describe the risks of using alcohol and tobacco understand that some people need and use drugs for their own health and that all medicines are drugs. 4g where individuals, families and groups can get help and support. Have you thought about? Resources HIAS PDL website Inviting a visitor from your local district or borough council to talk about recycling. Finding out how much children already know about drugs. Cyberbullying.* Support/counselling for victims of bullying and bullies. The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Community police officer to support drug education. Anti-bullying Week. Books and stories. Hampshire primary drug planning handbook (HIAS). PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 9 HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Observation of children asking for help in role play situations. Links Every Child Matters Be healthy Healthy lifestyles. Choose not to take illegal drugs. Stay safe Safe from bullying and discrimination. RRR Articles: 3 (adult involvement), 12 (opinions), 24 (health care), 33 (protection from drugs), 39 (restoring self-respect). Healthy Schools PSHE Have up-to-date policies in place – developed through wide consultation, implemented and monitored and evaluated for impact, covering sex and relationship education, drug education and incidents, safeguarding and confidentiality. Emotional health and well-being Have explicit values underpinning positive emotional health which are reflected in practice and work to combat stigma and discrimination. Have a clear policy on bullying, which is owned, understood and implemented by the whole school community. *NB: Due to the sensitive nature of the subject matter, this should be handled carefully. 10 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Year 3 – In someone else’s shoes Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 4a that their actions affect themselves and others, to care about other people’s feelings and to try to see things from their points of view 4f that differences and similarities between people arise from a number of factors, including cultural, ethnic, racial and religious diversity, gender and disability. Have you thought about? Resources HIAS PDL website be able to recognise their own and someone else’s feelings recognise the views of their peers, parents, teachers and people of different faiths and cultures understand that there are many social groups in society in terms of culture, religion, age, etc know that people live their lives in different ways and that different cultures may have different life patterns respect other people’s feelings, decisions, rights and bodies. Consolidation of previous work on feelings through circle time, story or poetry. Use of drama strategies to explore relevant views – role play, hot-seating, for example, on permission to go to a disco, vegetarianism, choice of clothes. Decision-making games. Value of different cultures modelled, for example, through literacy or collective worship involving visitors. Use of film/DVD of different life patterns. Finishing a story or poem. Circle time for reflection on: How do you think they felt ...?, using stories, poems and photographs as triggers for this. show a willingness to explain and listen to the views of others demonstrate a concern for fairness appreciate that diversity and variety is an essential part of life. Visiting the HCC Rights and Diversity Education Centre to find resources. Parents’/carers’ religious views. Dealing with racism or stereotyping in the classroom or playground. The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Visitors. Stories from Holy Books. Books and stories about feelings and opinions. Films or DVDs. School Library Service. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 11 United Nations RRR posters. Choice cards. HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Observation of participation in group work or a debate – ability to listen and/or to state an opinion. Links Every Child Matters Stay safe Safe from bullying and discrimination. Make a positive contribution Develop positive relationships and choose not to bully and discriminate. RRR Articles: 2 (equality), 3 (adult involvement), 8 (government respect), 12 (opinions), 22 (refugees), 23 (disability), 30 (home language), 38 (military service). Healthy Schools Emotional health and well-being Have clear, planned curriculum opportunities for children to understand and explore feelings using appropriate learning and teaching styles. Have explicit values underpinning positive emotional health which are reflected in practice and work to combat stigma and discrimination. SEAL 12 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes Good to be me. HIAS PDL website Year 3 – People and their work Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 1e about the range of jobs carried out by people they know, and to understand how they can develop skills to make their own contribution in the future. know the range of jobs and work roles carried out by people they know and what they like/dislike about their work identify ways in which different types of work are similar or different to each other explore and compare how adults feel about their work understand how work involves a variety of different tasks, undertaken by people with different roles. Have you thought about? HIAS PDL website A questionnaire for people at home. Find examples of paid, voluntary, self-employed, domestic and other forms of work. Survey of all the jobs and work done in school, and interviews with adults in school or visitors. Use of local maps and newspapers to identify work in the district. Make a wall map plotting residential and work places. Plan a visit to a workplace and discuss the different tasks people do and what would happen if certain tasks were not done; observing and talking to people. Write or draw about a day in the life of ... – someone in their visited workplace. Following a visit, work in a team to design and make a product related to that particular workplace. Drama to illustrate and guess the job. show an awareness of what a job involves, and the different roles undertaken in a work context understand the importance of team work in relation to work work in a team to complete an agreed task. Inviting parents to talk about their work. Gender issues in relation to work and home roles.* The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 13 Books and stories. Visitors. Contact with local employers. Newspapers. Websites. Careers education and guidance – First impressions. Make it real game (Prospects Educational Resources). What money means (www.hants.gov.uk/education/hias/pdl/financial-capability.htm). HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Participation in team activity. Writing about particular work roles. Links Every Child Matters Resources Achieve economic well-being Ready for employment (understanding different job roles). RRR Articles: 3 (adult involvement), 8 (government respect), 12 (opinions), 30 (home language), 32 (protection from unsafe work), 37 (legal punishment). Healthy Schools PSHE Involve professionals from appropriate external agencies to create specialist teams to support PSHE delivery and to improve skills and knowledge, such as a school nurse, sexual health outreach workers and drug education advisers. *NB: To be aware that disclosures may occur during these discussions. Due to the sensitive nature of the subject matter, this should be handled carefully. For support and queries contact the school’s Child Protection Officer. 14 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Year 4 – Feeling good Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 1a to talk and write about their opinions, and explain their views on issues that affect themselves and society appreciate home and school values make “I” statements about their interests and feelings express positive things about themselves and others recognise and be sensitive to the needs and feelings of others clarify what is important to them form reasoned opinions. 1b to recognise their worth as individuals by identifying positive things about themselves and their achievements, seeing their mistakes, making amends and setting personal goals. Have you thought about? Resources HIAS PDL website Generating class rules and understanding school’s positive behaviour rules. Circle time to raise self-esteem, make positive “I” statements, and talk about “I am responsible for ...”. Circle time, making positive statements about each other “I appreciate ... because …”. Celebration assemblies. Identify personal priorities and treasures. Use of personal diary/log to record targets and achievements. Working to support a charity or appeal. Debate, discussion, role play on a relevant issue. Writing a letter to a newspaper. Story – It’s not fair! name and describe positive qualities about themselves demonstrate a positive self-image recognise and name positive qualities in others express an opinion listen to other people’s points of view. Supporting those children with low self-esteem. Possible dichotomy between home and school values. The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Books and stories. Stories – It’s not fair, by Bel Mooney. Local newspapers. Materials from a charity or appeal. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 15 HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Written work – “I feel good when ...”. Positive writing and comments about another child. Links Every Child Matters Be healthy Mentally and emotionally healthy. Make a positive contribution Develop self-confidence and successfully deal with significant life changes and challenges. RRR Articles: 5 (family guidance), 7 (name and nationality), 12 (opinions), 15 (joining groups), 16 (privacy), 24 (health care), 27 (financial stability), 31 (relaxation and play), 37 (legal punishment). Healthy Schools Emotional health and well-being Have clear, planned curriculum opportunities for children to understand and explore feelings using appropriate learning and teaching styles. Provide opportunities for children to participate in school activities and responsibilities to build their confidence and self-esteem. SEAL 16 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes Good to be me. HIAS PDL website Year 4 – Keeping healthy Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 3a what makes a healthy lifestyle, including the benefits of exercise and healthy eating, what affects mental health, and how to make informed choices 3b that bacteria and viruses can affect health and that following simple, safe routines can reduce their spread. Have you thought about? Resources HIAS PDL website accept responsibility for personal cleanliness handle food safely know that bacteria and viruses can affect health and that transmission may be reduced when simple safe routines are used know about different cultural practices in health and hygiene understand the important and beneficial role which drugs have played in society know some of the options open to them in developing a healthy lifestyle now and in the future know about the positive effects of exercise. Looking at toiletries, advertisements, packaging, DVDs. Visit from school cook, school nurse, a worker who works with food. Quiz on food hygiene. Washing hands – visit from environmental health professional with testing dye. Link to religious education and practices of different religions and cultures. World of drugs – who needs drugs to keep healthy? How do people manage asthma and diabetes medication? Interviews. Physical education, lunchtime games, clubs; importance of warm-up and cool-down exercises. Survey of exercise taken by class members. take responsibility for personal cleanliness demonstrate an understanding about healthy eating demonstrate an understanding about other things taken into their bodies, accidentally and on purpose, and how their bodies react to them demonstrate an understanding that germs are bacteria and viruses understand that all medicines are drugs but not all drugs are medicines describe how they can take care of their bodies understand what happens to their bodies when they exercise. Cultural differences.* Gender issues.* Tactful handling of home background.* The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Books and stories. Primary Care Trust resources. Toiletries. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 17 Health education collection (Channel 4 DVD). Local environmental health department. Visit from a dentist or nurse. HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Draw and write activities at start and end of the unit of work (or the year or key stage). True/false questionnaire. Links Every Child Matters Be healthy Physically healthy. Healthy lifestyles. RRR Articles: 3 (adult involvement), 6 (right to life), 24 (health care), 27 (financial stability), 31 (relaxation and play). Healthy Schools Healthy eating Have whole-school food policy – developed through wide consultation, implemented, monitored and evaluated for impact. Involve children and parents/carers in guiding food policy and practice within the school, enabling them to contribute to healthy eating and act on their feedback. Physical activity Have whole-school physical activity policy – developed through wide consultation, implemented, monitored and evaluated for impact. Provide opportunities for all children to participate in a broad range of extra-curricular activities that promote physical activity. *NB: Due to the sensitive nature of the subject matter, this should be handled carefully. 18 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Year 4 – Changes in families Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 3c about how the body changes as they approach puberty 4c to be aware of different types of relationship, including marriage, and those between friends and families, and to develop the skills to be effective in relationships. develop understanding of different types of relationships and families understand what families are, and what members expect of each other know the different changes that take place in human life develop skills needed for relationships, such as listening, supporting, showing care. Have you thought about? HIAS PDL website Drawing a network of special people; illustrating relationships in diagrammatic form; identifying different family members. Roles in relationships – grandparent, teacher, parent/ carer, school nurse, friend – group presentations to explore similarities and differences between roles. Family celebrations and occasions – clarifying expectations – making a set of guidelines. Poetry, stories, plays, etc, related to family decisions/ dilemmas.* Visits from/interviews with older people – reminiscences; visit of mother and baby – human life cycle. Role play on situations where you need to listen or be listened to – what helps and hinders good communication? Pair work to practise listening skills. Class/school initiative, eg: tea party for senior citizens. understand that different groups of people have different ways of living understand the human life cycle demonstrate awareness of the needs of babies and older family members recognise their own and other people’s feelings demonstrate a willingness to care for others. Stereotyping. Children being playground helpers/friends. Buddy support mechanisms with either older or younger class. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 19 The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Books and stories – Heartbeat. School Library Service. HIAS e-Profile CD. Story – All in the family, by Tony Bradman. Assessment opportunities Jottings by teacher of skills displayed during discussions and/or pair work. Links Every Child Matters Resources Be healthy Sexually healthy (relationships with friends and families). Stay safe Have security, stability and are cared for. Make a positive contribution Develop positive relationships and choose not to bully and discriminate. RRR Articles: 2 (equality), 3 (adult involvement), 5 (family guidance), 8 (government respect), 9 (staying with parents), 10 (movement between countries), 12 (opinions), 14 (own beliefs), 18 (parental responsibilities), 19 (protection from violence/abuse), 21 (adopted children), 27 (financial stability). Healthy Schools Emotional health and well-being Have clear, planned curriculum opportunities for children to understand and explore feelings using appropriate learning and teaching styles. SEAL Changes. *NB: Due to the sensitivities around changes in family situations, this should be handled carefully. 20 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Year 4 – Ups and downs in relationships Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 3f that pressure to behave in an unacceptable or risky way can come from a variety of sources, including people they know, and how to ask for help and use basic techniques for resisting pressure to do wrong Resources Assessment opportunities HIAS PDL website 4c to be aware of different types of relationship, including marriage, and those between friends and families, and to develop the skills to be effective in relationships. Have you thought about? know that there are many different patterns of friendship understand the meaning of friendship and loyalty be able to be honest know where to get help in school and through helplines when facing problems. Diamond 9 activity – What is a friend? Circle time “A friend is someone who ...”, “I am a good friend when ...”. Stories to initiate discussion about friendship. Designing an advertisement/ application for a friend. Role play on different situations with friends, practising saying “No”. Circle time – When is it OK to say “No” to your friends? How can you tell a friend the truth? Scenarios to explore what happens next, feelings, choices and decisions. demonstrate the skills of friendship understand that they are a role model for younger children understand that pressures to behave in unacceptable or risky ways may come from friends say “No” to friends if they are unhappy about what is planned understand that in risky or dangerous situations that it is better to tell someone about it than threaten to tell. Sources of support and help for children. The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Diamond 9 template. Books and stories – Best friends, by Jacqueline Wilson. Stories – Pimple-head and Curly, by Ian Bore. HIAS e-Profile CD. Making a statement about when it is OK to say “No” to friends. Writing about being a friend, or making friends. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 21 Links Every Child Matters Be healthy Choose not to take illegal drugs. Stay safe Safe from crime and anti-social behaviour in and out of school. Make a positive contribution Engage in decision making and support the community and environment. RRR Articles: 5 (family guidance), 8 (government respect), 9 (staying with parents), 10 (movement between countries), 12 (opinions), 13 (share information), 15 (joining groups), 16 (privacy), 18 (parental responsibilities), 19 (protection from violence/abuse), 21 (adopted children), 30 (home language), 37 (legal punishment), 39 (restoring self-respect). Healthy Schools PSHE Involve professionals from appropriate external agencies to create specialist teams to support PSHE delivery and to improve skills and knowledge, such as a school nurse, sexual health outreach workers and drug education advisers. Have arrangements in place to refer children to specialist services who can give professional advice on matters such as contraception, sexual health and drugs. SEAL Relationships. *NB: Due to sensitivities around changes in relationships, this should be handled carefully. 22 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Year 4 – Keeping safe outside school Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 2c to realise the consequences of anti-social and aggressive behaviours, such as bullying and racism, on individuals and communities 3d which commonly available substances and drugs are legal and illegal, their effects and risks 4d to realise the nature and consequences of racism, teasing, bullying and aggressive behaviours, and how to respond to them and ask for help HIAS PDL website 4e to recognise and challenge stereotypes. Have you thought about? identify hazards from substances at home and at school know about the range of legal drugs encountered in everyday life, including over-the-counter drugs such as aspirin, drugs which are prescribed as medicines, tea, coffee, alcohol and tobacco have some understanding of the effects of these drugs and associated risks and some of the costs to society of drug misuse think about risks and hazards in the environment and where to go for help understand that it is wrong for children to be bullied or abused by other children or adults. Looking at pictures and containers – reading the instructions, identifying hazards. Group work on true/false statements about smoking and alcohol. Brainstorm on drugs to inform starting point for work on illegal drugs. Case studies/scenario cards – What happens next? Role play on saying “No” when being persuaded to try cigarettes, alcohol or an illegal drug. Visit from a road safety officer, railway worker, fire brigade, community police officer. Photographs to identify safe places to play. Study of anti-social behaviour in the school neighbourhood – consider problems and suggestions for solutions. Language work – debate and talk on school or wider issues, eg: bullying.* know about people who need and use drugs for their health understand that some people use drugs to appear grown-up and confident know the effects these drugs can have on friendships and relationships talk about their feelings about the world of drugs develop a sense of responsibility and concern recognise that there are times when they should tell about a secret demonstrate a raised awareness and understanding of community issues. Risk of frightening children. Attending HCC drug education conferences/forums. Need to start from where children are at and use strategies such as brainstorm, draw and write. Checking own knowledge of school policy and procedures on bullying, child protection, drugs, cyberbullying.* Have any of the children experienced being/feeling unsafe out of school?* PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 23 The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Books and stories. Visitors. Health education collection (Channel 4 DVD). Royal Society for the Prevention of Accidents. Photography. Community police officer. Hampshire Fire and Rescue Service. HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Sorting activity to identify risks. Designing a Keeping safe guidebook. Links Every Child Matters Resources Be healthy Choose not to take illegal drugs. Stay safe Safe from bullying and discrimination. Make a positive contribution Engage in decision making and support the community and environment. RRR Articles: 19 (protection from violence/abuse), 24 (health care), 32 (protection from unsafe work), 33 (protection from drugs), 34 (protection from sexual abuse), 35 (ensure not abducted/sold), 36 (protection from harmful activities). Healthy Schools PSHE 24 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes Have up-to-date policies in place – developed through wide consultation, implemented and monitored and evaluated for impact, covering sex and relationship education, drug education and incidents, safeguarding and confidentiality. HIAS PDL website Emotional health and well-being Have a clear policy on bullying, which is owned, understood and implemented by the whole school community. *NB: To be aware that disclosures may occur during these discussions. Due to the sensitive nature of the subject matter, this should be handled carefully. For support and queries contact the school’s Child Protection Officer. HIAS PDL website PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 25 Year 4 – Looking ahead Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 1a to talk and write about their opinions, and explain their views, on issues that affect themselves and society 1b to recognise their worth as individuals by identifying positive things about themselves and their achievements, seeing their mistakes, making amends and setting personal goals look forward to new situations assess positive things about themselves and set personal goals record information about current events and choices they will make in the future have realistic aspirations when target setting think about financial implications of future needs and wants. Looking back and looking forward, brainstorming, making a record sheet. Circle time to share positive qualities and talents. Filling in a personal and academic target-setting card. Personal journal, New Year resolutions. Pair work on setting short-term, manageable, precise targets. Confirming targets with teacher and personal recording. Identifying future needs and wants, and researching real costs and advantages of saving to meet future needs. demonstrate a positive self-image describe new situations they expect to encounter participate in realistic self-assessment, identifying appropriate and achievable targets describe personal and social targets, as well as those to do with their work. 1c to face new challenges positively by collecting information, looking for help, making responsible choices, and taking action 1f to look after their money and realise that future wants and needs may be met through saving. Have you thought about? 26 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes The importance of children understanding appropriate targets. The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. HIAS PDL website Resources Assessment opportunities Links Books and stories. School system of recording and record keeping. Resources about saving from banks and building societies. HIAS e-Profile CD. What money means (www.hants.gov.uk/education/hias/pdl/financial-capability.htm). Self-assessment, peer assessment, and/or negotiation with teacher. Work sampling. Writing a self-assessment for their report. Every Child Matters Enjoy and achieve Achieve personal and social development and enjoy recreation. Make a personal contribution Develop self-confidence and successfully deal with significant life changes and challenges. RRR Articles: 12 (opinions), 28 (right to an education), 29 (developing personal talents), 41 (international laws). Healthy Schools Emotional health and well-being Provide opportunities for children to participate in school activities and responsibilities to build their confidence and self-esteem. SEAL HIAS PDL website Changes, Going for goals!, New beginnings. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 27 Year 5 – Who decides Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 1a to talk and write about their opinions, and explain their views, on issues that affect themselves and society 2i to appreciate the range of national, regional, religious and ethnic identities in the United Kingdom describe what is important to them form and express reasoned opinions be able to put themselves in someone else’s shoes value the diversity of lifestyles recognise that actions have consequences for oneself and others challenge the opinions and actions of others know how advertising can influence them recognise and challenge stereotypes. 2k to explore how the media presents information 4d to realise the nature and consequences of racism, teasing, bullying and aggressive behaviours, and how to respond to them and ask for help A self-portrait – All about me, values and beliefs. Reading, discussing and responding to letters from papers and magazines. Taking a newspaper story and putting it into first person. Religions and cultures, jobs – identifying similarities and differences. Stories and poetry – You, me and us, as a resource; role play. A class, year or school debate, eg: school uniforms, tuck shop, bedtimes, homework. Advertisements – looking for the hidden persuaders. Gender issues linked to advertisements. Story – Bill’s new frock. express an opinion, give their reasons, and reflect on why they feel this way be willing to explain their own views and listen to the views of others describe the possible consequences of actions demonstrate an ability to empathise with others show tolerance and understanding describe similarities and differences between faiths. 4e to recognise and challenge stereotypes. Have you thought about? 28 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes Sensitivity to home and upbringing.* The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. HIAS PDL website Resources Assessment opportunities Newspaper articles and letters, magazines, news. You, me and us, Citizenship Foundation. Books and stories – Bill’s new frock, by Anne Fine. Stories – Matilda, by Roald Dahl. Local Democracy Week (October). HIAS e-Profile CD. Writing on: – things I decide – things that are decided for me – what I would like to decide. Observation of participation in a class debate. Links Every Child Matters Make a positive contribution Engage in law-abiding and positive behaviour in and out of school. Develop positive relationships and choose not to bully and discriminate. RRR Articles: 3 (adult involvement), 12 (opinions), 13 (share information), 14 (own beliefs), 25 (looked after children), 40 (the law). Healthy Schools Emotional health and well-being Have clear, planned curriculum opportunities for children to understand and explore feelings using appropriate learning and teaching styles. Have explicit values underpinning positive emotional health which are reflected in practice and work to combat stigma and discrimination. SEAL Good to be me. *NB: Due to the sensitive nature of the subject matter, this should be handled carefully. HIAS PDL website PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 29 Year 5 – Risks and pressures Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 1c to face new challenges positively by collecting information, looking for help, making responsible choices, and taking action 3f that pressure to behave in an unacceptable or risky way can come from a variety of sources, including people they know, and how to ask for help and use basic techniques for resisting pressure to do wrong. Have you thought about? Resources 30 develop a positive approach and self-motivation towards personal safety and risk taking identify decisions they may need to make explore attitudes about different drugs and the people who use or misuse them exercise basic techniques for resisting pressure from friends, particularly in relation to smoking learn to be assertive, especially in the face of pressure from others – saying “No”. Risk assessment activities, situation cards/pictures to discuss and understand risk and challenge. Case studies and scenarios to explore decisions and choices. Brainstorm – Why do people take risks? Revisit work on what makes a friend, responsibility, trust, being sensible, knowing when to tell even if a friend does not want you to.* Brainstorm drugs, true or false questionnaires. Assertiveness activities – speaking and listening, practising skills through drama strategies. demonstrate a range of responses to use in difficult situations such as “No – I will not take the risk, I will ask”, “No, it is not for me” explain what might make a situation risky for them or children like them demonstrate a range of strategies to deal with pressure describe how their bodies and health are their responsibility. Attending HCC drug education conferences/forums (see HTLC website). Visits from people who need drugs to keep healthy, such as a person with diabetes. That some parents/carers may be smokers, drink heavily or use illegal drugs.* Cyberbullying.* The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Local community police officer. Primary Care Trust resources. Case studies from You, me and us, Citizenship Foundation. Photographs/pictures. Books and stories. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Hampshire primary drug planning handbook (HIAS). HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Poster and art work to represent healthy lifestyles. Contribution to class display. Links Every Child Matters Be healthy Physically healthy. Mentally and emotionally healthy. Healthy lifestyles. Choose not to take illegal drugs. Make a positive contribution Engage in law-abiding and positive behaviour in and out of school. RRR Articles: 5 (family guidance), 6 (right to life), 8 (government respect), 12 (opinions), 24 (health care), 32 (protection from unsafe work), 33 (protection from drugs), 34 (protection from sexual abuse), 39 (restoring self-respect). Healthy Schools PSHE Have up-to-date policies in place – developed through wide consultation, implemented and monitored and evaluated for impact, covering sex and relationship education, drug education and incidents, safeguarding and confidentiality. Involve professionals from appropriate external agencies to create specialist teams to support PSHE delivery and to improve skills and knowledge, such as a school nurse, sexual health outreach workers and drug education advisers. *NB: Due to the sensitive nature of the subject matter, this should be handled carefully. HIAS PDL website PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 31 Year 5 – We are all different Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 2e to reflect on spiritual, moral, social and cultural issues, using imagination to understand other people’s experiences 4b to think about the lives of people living in other places and times, and people with different values and customs 4d to realise the nature and consequences of racism, teasing, bullying and aggressive behaviours, and how to respond to them and ask for help know that differences between people are caused by different genes and different environments know that people’s responses to ideas and events may be determined by age, religion or culture value cultural background of self and others know that different people live their lives in different ways and that different cultures may have different life patterns contrast work in different cultures and at different times demonstrate and promote tolerance, understanding, respect and acceptance of difference understand that bullying is an unacceptable response to difference. Studying data – physical differences, populations, environment. Current event – seeing it through different points of view, eg: a pop concert, a flood, sporting event – through eyes of teenager, police, parent, grandparent, neighbour, etc. Playmaking. Personal topic and/or research into different cultures and links with cross-curricular topics. Developing an equal opportunities policy to be displayed in the classroom and/or school. Assembly focused on celebration of differences. Circle time to explore feelings associated with, and perceptions about, bullying and why it happens. show increased knowledge and respect for other cultures explore assumptions, such as variations in lifestyle recognise the importance of equal opportunities demonstrate concern for others and describe initial thoughts on human rights. 4e to recognise and challenge stereotypes. Have you thought about? 32 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes Use of the Internet to make links with other schools. The HCC Rights and Diversity Education Centre. Anti-bullying Week. Involving children in Rock Challenge. Equal opportunities policy and practice in your school. The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. HIAS PDL website Resources drawn from other curricular areas. Books and stories. HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Participation in a whole-class activity, such as an assembly. Links Every Child Matters Resources Make a positive contribution Engage in decision making and support the community and environment. Engage in law-abiding and positive behaviour in and out of school. Develop positive relationships and choose not to bully and discriminate. RRR Articles: 2 (equality), 7 (name and nationality), 8 (government respect), 12 (opinions), 14 (own beliefs), 23 (disability), 26 (financial support), 30 (home language), 37 (legal punishment). Healthy Schools Emotional health and well-being HIAS PDL website Have clear, planned curriculum opportunities for children to understand and explore feelings using appropriate learning and teaching styles. Have explicit values underpinning positive emotional health which are reflected in practice and work to combat stigma and discrimination. Have a clear policy on bullying, which is owned, understood and implemented by the whole school community. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 33 Year 5 – It’s my body Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 1d to recognise, as they approach puberty, how people’s emotions change at that time, and how to deal with their feelings towards themselves, their family and others, in a positive way be able to discuss and choose the healthy options in relation to food, exercise, rest, etc know how changes at puberty affect the body in relation to hygiene know how to cope with periods in school know that body changes are a preparation for sexual maturity be able to discuss and ask questions about changing bodily needs. 3a what makes a healthy lifestyle, including the benefits of exercise and healthy eating, what affects mental health, and how to make informed choices Draw and write activity – what I do to keep healthy. Food groups – food label survey. Healthy lunch box project. Survey of exercise taken by all members of school. Jump rope or other initiatives. Exercise/healthy lifestyles guides and leaflets for 9 to 11-year-olds. Group work to develop a healthy decisions checklist and poster display. Puberty quiz or true/false questionnaire to establish starting points. BBC and Channel 4 schools programmes. Visit from school nurse. demonstrate an understanding about healthy eating, and what happens to their bodies when they exercise describe the changes their bodies will go through at puberty understand that puberty will have an impact on themselves, their emotions and relationships explain how to care for their bodies, including the importance of personal hygiene. 3c about how the body changes as they approach puberty. Have you thought about? 34 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes Attending HCC health and well-being conferences/forums (see HTLC website). School provision to support menstruation.* Cultural differences/gender issues.* The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. HIAS PDL website Primary Care Trust resources. School nurse. Models, leaflets and posters from health promotion departments. Collection of foods to show labeling. British Heart Foundation Jump rope initiative. Books and stories. HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Self/peer assessment of understanding of healthy lifestyle. Naming and labeling of body parts/systems. Links Every Child Matters Resources Be healthy Physically healthy. Mentally and emotionally healthy. Sexually healthy. Healthy lifestyles. Choose not to take illegal drugs. RRR Articles: 3 (adult involvement), 12 (opinions), 32 (protection from unsafe work), 33 (protection from drugs), 34 (protection from sexual abuse), 35 (ensure not abducted/sold), 36 (protection from harmful activities), 39 (restoring self-respect). Healthy Schools PSHE Have up-to-date policies in place – developed through wide consultation, implemented and monitored and evaluated for impact, covering sex and relationship education, drug education and incidents, safeguarding and confidentiality. Healthy eating HIAS PDL website Have whole-school food policy – developed through wide consultation, implemented, monitored and evaluated for impact. Ensure that children have opportunities to learn about different types of food in the context of a balanced diet (using the Balance of Good Health) and how to plan, budget, prepare and cook meals, understanding the PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 35 need to avoid the consumption of food high in salt, sugar and fat, and increase the consumption of fruit and vegetables. Physical activity Have whole-school physical activity policy – developed through wide consultation, implemented, monitored and evaluated for impact. Encourage children and parents/carers to walk or cycle to school under safe conditions, utilising the school travel plan. *NB: Due to the sensitive nature of the subject matter, this should be handled carefully. 36 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Year 5 – Being involved in my community Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 1c to face new challenges positively by collecting information, looking for help, making responsible choices, and taking action 2d that there are different kinds of responsibilities, rights and duties at home, at school and in the community, and that these can sometimes conflict with each other. value opportunities for new experiences in and out of school, including opportunities to meet adults other than teachers take a constructive interest in their local community and begin to take on a wider sense of social responsibility know what they are good at and how it can help a group perform a task appreciate the aesthetic qualities of their surroundings understand how they and others can cause changes for better or for worse, both in their immediate surroundings and in the wider community contribute to a discussion and put their own views forward clearly and appropriately. Have you thought about? HIAS PDL website Inviting and working with visitors representative of the local community, or making visits; use of digital camera or other multi-media device to produce a record of the community. Survey of leisure time and positive benefits of the activities chosen. Leaflet about opportunities available in their community. School monitors, mentors, buddies and mediators, and opportunities to work in a range of different groups and pairs. Group investigation into a local issue – eg: by-pass, traffic calming, new housing development, making links with the local council. Group projects to suggest improvements for an area of the school grounds or local area, eg: safety in the school grounds discussion leading to action. Circle time, school council. Creation of charter of rights for a community – real or imaginary. explain the concept of community and environment describe how their responsibilities increase with age and as their community widens understand that they have the ability to influence the quality of their environment demonstrate a willingness to explain and listen to the views of others appreciate that the strength or weakness of a group depends on the ability of members to co-operate, negotiate, collaborate and compromise to complete a group task contribute to a group task. A whole-day event on our community to involve a wide range of visitors. Involving children in Rock Challenge. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 37 Cyberbulling.* Setting up a school council if you do not have one in place. Internet links with schools in differing environments. Pen pals. The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Visitors – community police officer, Hampshire Fire and Rescue Service, vicar, school nurse, parents/carers, elderly people, governors, local council. Internet. Local democracy week (October). Books and stories. HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Self, peer and group assessment of group work skills. Teacher observation of participation in a group. Links Every Child Matters Resources Enjoy and achieve Achieve personal and social development and enjoy recreation. Make a positive contribution Engage in decision making and support the community and environment. RRR Articles: 2 (equality), 4 (government responsibilities), 12 (opinions), 30 (home language), 39 (restoring self-respect), 41 (international laws). Healthy Schools PSHE Have mechanisms in place to ensure children’s views are reflected in curriculum planning, teaching and learning, and in the whole-school environment, including those with SEN and specific health conditions, as well as disaffected children and young carers. *NB: Due to the sensitive nature of the subject matter, this should be handled carefully. 38 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Year 5 – Looking at the world Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 2a to research, discuss and debate topical issues, problems and events 2f to resolve differences by looking at alternatives, making decisions and explaining choices 2j that resources can be allocated in different ways, and that these economic choices affect individuals, communities and the sustainability of the environment. know the variety of communities to which they simultaneously belong – family, school, local, national, European and worldwide – and the interdependence of individuals, groups and communities know about public service provision, locally and nationally and that this is not free know the benefits and costs of personal spending decisions on themselves, the local community, the local economy and on people in other parts of the world research information and identify relevant issues use different modes of communication to express personal and group views about social and environmental issues show a willingness to move on a personal position after considering new information or perspectives. HIAS PDL website Use activities such as card sort, brainstorm or values continuum to explore beliefs about the world. Circle time – what rights, what responsibilities do I/we have locally, nationally, internationally? District or borough council visitor to be interviewed/ questioned about local service provision, council tax expenditure, etc. Exploring data on world debt. Review of financial report of international charity such as Oxfam. Study of a global issue, eg: war, refugees, a natural disaster. Playmaking with news item as stimulus material. Support for a personal, class or school charity, participation in an appeal, writing letters, presenting an assembly. A news diary over a week, with recording of personal views and responses to share in a group. demonstrate an increased knowledge of rights and responsibilities within a society show an awareness of the idea of collective and individual responsibility to find solutions participate and show concern for their community. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 39 Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development Debate of current world issue or simulation of protest hearing with whole class in role, voting on the issues before and after the debate/simulation. A map, directory or photographic display to show community facilities, services, employers and school. Financial capability, eg: pfeg (see: www.hants.gov.uk/education/hias/pdl/financial-capability.htm). The Internet. The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Books and stories. Visitors. Internet. Oxfam and UNICEF materials. What money means (www.hants.gov.uk/education/hias/pdl/financial-capability.htm). HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Expression of personal views in circle time. Links Every Child Matters Have you thought about? Resources Make a positive contribution Engage in decision making and support the community and environment. Achieve economic well-being Ready for employment. (Life skills) RRR Articles: 4 (government responsibilities), 11 (forceably removed), 12 (opinions), 27 (financial stability), 29 (developing personal talents), 35 (ensure not abducted/sold), 36 (protection from harmful activities), 38 (military service), 41 (international laws). 40 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Healthy Schools PSHE Have mechanisms in place to ensure children’s views are reflected in curriculum planning, teaching and learning, and the whole-school environment, including those with SEN and specific health conditions, as well as disaffected children and young carers. Emotional health and well-being HIAS PDL website Have clear, planned curriculum opportunities for children to understand and explore feelings using appropriate learning and teaching styles. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 41 Year 6 – Managing conflict Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 2f to resolve differences by looking at alternatives, making decisions and explaining choices 2k to explore how the media presents information 4a that their actions affect themselves and others, to care about other people’s feelings and to try to see things from their points of view 4d to realise the nature and consequences of racism, teasing, bullying and aggressive behaviours, and how to respond to them and ask for help talk about their own feelings and reactions read and express non-verbal messages recognise that one’s actions have consequences for themselves and others manage a range of emotions such as excitement, anger, jealousy develop strategies to avoid conflict in situations, including bullying negotiate and resolve conflict peacefully resolving problems and conflicts democratically using discussion recognise stereotyping in attitudes in the media and the impact of the media in reinforcing equal opportunities develop a sense of fair play in their dealings with peers and others. 4e to recognise and challenge stereotypes. 42 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes Circle time work on feelings, sentence stems, appreciations, complaints and recommendations. Drama strategies to explore feelings – frozen pictures, body on the wall. Artwork, looking at artists’ work, music to explore language of feelings and emotions. Newspaper photographs and pictures as triggers to discuss body language, emotions, conflict situations and consequences. Exploring different ways of resolving conflict through drama and role play. Language work through debate and talk on school or wider issues. School council as model for democracy, voting and compromising. Use of television, magazine and hoarding advertisements to explore, persuasion, target group and equal opportunities. name positive feelings about themselves, others in class and school, community, media and wider world recognise and describe a range of emotions manage their emotions positively and effectively most of the time consider how they are perceived by others demonstrate the ability to negotiate and compromise describe and demonstrate a variety of ways of resolving conflict. Presentation of issues in a range of media. HIAS PDL website Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development Making a DVD, CD or photograph display to communicate class views on an issue such as bullying, racism or disability. Class or school newspaper articles. Stories and poetry. Learning and practising mediation skills. Children training to become playground mediators. Attending HCC peer mentoring conference (see HTLC website). Cyberbullying.* Buddying or mentor schemes to support younger children. A presentation to a younger age group. The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Newspaper photographs. Pictures, artists’ work – paintings, sculpture, music CDs, television clips. Books and stories. HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Problem-solving activities to assess learning about conflict resolution. Links Every Child Matters Have you thought about? Resources Be healthy Mentally and emotionally healthy. Make a positive contribution HIAS PDL website Develop positive relationships and choose not to bully and discriminate. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 43 RRR Articles: 7 (name and nationality), 12 (opinions), 39 (restoring self-respect). Healthy Schools Emotional health and well-being Have clear, planned curriculum opportunities for children to understand and explore feelings using appropriate learning and teaching styles. SEAL Getting on and falling out. *NB: Due to the sensitive nature of the subject matter, this should be handled carefully. 44 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Year 6 – The world of work Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 1c to face new challenges positively by collecting information, looking for help, making responsible choices and taking action 1e about the range of jobs carried out by people they know, and to understand how they can develop skills to make their contribution in the future 3a what makes a healthy lifestyle, including the benefits of exercise and healthy eating, what affects mental health, and how to make informed choices. interview adults to find out about job roles and responsibilities know that certain skills can be used for different tasks know the range of knowledge, skills and personal qualities required for different types of work respect other people’s work and career choices act confidently understand what affects mental health, eg: the balance between work and leisure, positive relationships. HIAS PDL website Visitors or visit to local employers. Investigation of work-related skills through review of job details in local press, and develop a checklist of skills. Presentation through role play of jobs, demonstrating skills, success criteria, experience challenges. Information and communication technology in workplace – survey of school systems which support school as a workplace. Teams for work, class, school, families, sport, workplace – comparing to investigate skills of team work – what makes an effective team? Write a personal statement about own strengths, skills, ambitions and aspirations. Interview situations – role play of real situations in school, eg: for positions of responsibility, monitors, buddies, school council membership. Learning and practising relaxation skills. work independently or in a group to research information show an understanding of the different roles undertaken in the work context identify and demonstrate various skills such as co-operation, communication skills, information and communication technology skills and teamwork understand the value of keeping healthy demonstrate understanding of the importance of balance between work and leisure, and the value of positive relationships make choices and describe their reasons. Pupils discuss aspects of jobs and paid employment. Study job advertisements. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 45 Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development Create imaginary job descriptions/adverts/ application forms. Role play job interviews. Pupils develop a questionnaire to find out what people actually do in their jobs. Use a story involving a variety of job roles, eg: Postman Pat – identify all jobs in the story and compare to local jobs. Appreciation of parent/carer skills, as well as workplace skills. Employment status of parents/carers. Children’s awareness of support for those not in work.* The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Books and stories. School staff. Visitors. Local employers. Make it real game (Prospects Education Resources). What money means (www.hants.gov.uk/education/hias/pdl/financial-capability.htm). HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Written or oral realistic personal person specification. Links Every Child Matters Have you thought about? Resources Enjoy and achieve Achieve stretching national educational standards at primary school. Achieve economic well-being 46 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes Ready for employment. HIAS PDL website Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development RRR Articles: 2 (equality), 4 (government responsibilities), 6 (right to life), 11 (forceably removed), 12 (opinions), 32 (protection from unsafe work), 35 (ensure not abducted/sold), 36 (protection from harmful activities), 37 (legal punishment), 38 (military service). Healthy Schools Emotional health and well-being Provide opportunities for children to participate in school activities and responsibilities to build their confidence and self-esteem. *NB: Due to the sensitive nature of the subject matter, this should be handled carefully. HIAS PDL website PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 47 Year 6 – Taking responsibility for my own safety Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 3d which commonly available substances and drugs are legal and illegal, their effects and risks 3e to recognise the different risks in different situations and then decide how to behave responsibly, including sensible road use, and judging what kind of physical contact is acceptable or unacceptable 3f that pressure to behave in an unacceptable or risky way can come from a variety of sources, including people they know, and how to ask for help and use basic techniques for resisting pressure to do wrong 3g school rules about health and safety, basic emergency aid procedures and where to get help 48 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes be able to express positive things about themselves and their values take responsibility for their bodies and behaviour know that some substances are illegal and have some understanding of their effects and the associated risks understand that the pressure to take harmful or illegal substances may come from people they know such as friends, relatives, neighbours recognise that some role models for young people take drugs, eg: in sports, and explore feelings about them choose the right decision-making approach in a real or simulated situation, including being assertive recognise the need to ask for support sometimes, know who to ask and how to find out more. Personal profile/fact file. Circle time – “I am responsible for ...”. Brainstorming, quizzes, true or false questionnaires, risk continuum. Card sort on drugs, effects and the law. Scenarios relating to persuasion, and practising strategies to say “No!”. Newspaper, news items, photographs. Problem pages, case studies – What is happening? What happens next? Finishing a story or writing stories. Role play, playmaking around decision-making situations. Home fire safety plans, basic first aid. Creating a help list for a friend experiencing difficulties. Accessing helplines, and making emergency 999 calls. describe the effects of substances and drugs on the body and how they affect how you feel describe the risks of misusing prescribed and over-thecounter medicines, solvents and illegal drugs, as well as alcohol and tobacco explain the effect substance misuse can have on friendship and family relationships understand the nature of role models, and that they are role models for younger children talk about their feelings about drugs and issues such as drugs in sport, drug-related news items demonstrate assertiveness and self-confidence to make decisions for themselves demonstrate an awareness of sources of help, in school, helplines, other adults, and know how to ask for help know that it is better to tell someone about a situation than to threaten to tell. HIAS PDL website Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development 4g where individuals, families and groups can get help and support. Families with drug problems.* Children and family members who rely on drugs to keep healthy.* Involving the community police officer. The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Community police officer, fire officer, St John Young Lifesaver programme, Red Cross. Helpline information, eg: Childline, National Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Children. Book and stories. What money means (www.hants.gov.uk/education/hias/pdl/financial-capability.htm). HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Observation of participation in role play and playmaking. Draw and write as summative evaluation. Links Every Child Matters Have you thought about? Resources Be healthy Choose not to take illegal drugs. Stay safe Safe from crime and anti-social behaviour in and out of school. Make a positive contribution Engage in decision making and support the community and environment. RRR Articles: 2 (equality), 12 (opinions), 24 (health care), 33 (protection from drugs), 39 (restoring self-respect), 40 (the law). HIAS PDL website PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 49 Healthy Schools PSHE Have up-to-date policies in place – developed through wide consultation, implemented and monitored and evaluated for impact, covering sex and relationship education, drug education and incidents, safeguarding and confidentiality. SEAL Good to be me. *NB: To be aware that disclosures may occur during these discussions. Due to the sensitive nature of the subject matter, this should be handled carefully. For support and queries contact the school’s Child Protection Officer. 50 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Year 6 – Changing relationships Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 3c about how the body changes as they approach puberty 3e to recognise the different risks in different situations and then decide how to behave responsibly, including sensible road use, and judging what kind of physical contact is acceptable or unacceptable 4c to be aware of different types of relationship, including marriage and those between friends and families, and to develop the skills to be effective in relationships. think about making new relationships as they get older understand about parenthood know about human sexuality and that it is expressed in different ways, understand what it means and have some words to describe it appreciate different ways of loving and its importance to a range of relationships know ways of coping with difficult emotions, fears and worries decide who has access to their bodies. Have you thought about? HIAS PDL website Identify types of relationships – brainstorm, stories, television programmes. Group work to develop a fact file on parents/carers. Agreeing ground rules. Word bank of vocabulary for relationships, sexuality, and sexual activity, which is agreed as appropriate. Sex education DVDs. School nurse, health visitor, pregnant mother, and/or mother and baby visit. Question box before work and review at end. Comparison of access to bodies at different times, eg: as a baby, a patient, an elderly person, a person with a disability, in friendships, in sexual relationships in the future.* Different sorts of touch – talking about comfortable and uncomfortable feelings.* Circle time to promote self-esteem and self-worth. describe the changes the body goes through at puberty understand that body changes are a preparation for sexual maturity understand that there are different types of relationships and patterns of friendships show awareness of the importance of loving, responsibility and honesty in relationships describe the importance of good parenting demonstrate an awareness of the difference between secrets which make people happy and secrets which can hurt or frighten people decide who has access to their bodies and demonstrate an understanding that some physical contact is unacceptable. School sex and relationship education (SRE) policy, including consultation and involvement of parents/carers. Attending HCC health and well-being conferences/forums (see HTLC website). Child protection procedures.* Support for vulnerable children.* PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 51 The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Assessment opportunities School nurses. Primary Care Trust resources. Sex education programmes and materials – BBC and Channel 4. Classroom’s own anonymous questions/worries box. Books and stories. Hampshire teenage pregnancy website (www.hants.gov.uk/childrens-services/families/teenage-pregnancy.htm). HIAS e-Profile CD. Writing or group presentation on What makes a good parent/carer? Links Every Child Matters Resources Be healthy Mentally and emotionally healthy. Sexually healthy. Stay safe Safe from accidental injury and death. RRR Articles: 3 (adult involvement), 12 (opinions), 17 (mass media), 24 (health care), 30 (home language), 37 (legal punishment). Healthy Schools PSHE Have up-to-date policies in place – developed through wide consultation, implemented and monitored and evaluated for impact, covering sex and relationship education, drug education and incidents, safeguarding and confidentiality. Emotional health and well-being Have clear, planned curriculum opportunities for children to understand and explore feelings using appropriate learning and teaching styles. *NB: To be aware that disclosures may occur during these discussions. Due to the sensitive nature of the subject matter, this should be handled carefully. For support and queries contact the school’s Child Protection Officer. 52 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Year 6 – Rights, responsibilities and the law Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 2b why and how rules and laws are made and enforced, why different rules are needed in different situations and how to take part in making and changing rules 2d that there are different kinds of responsibilities, rights and duties at home, at school and in the community, and that these can sometimes conflict with each other 2g what democracy is, and about the basic institutions that support it locally and nationally 2h to recognise the role of voluntary, community and pressure groups 2j that resources can be allocated in different ways and that these economic choices affect individuals, communities and the sustainability of the environment. HIAS PDL website know their individual rights and responsibilities at home, in school and in the community gain simple knowledge about the law and understand that rules and the law are designed to protect appreciate the positive impact of human beings on plants, animals and the environment think about decisions that need to be made about the use of scarce resources, evaluating information about priorities for spending demonstrate that their reasoning is informed and considered use varied and appropriate language to express their ideas be able to manage money, budgeting and accounting. Compiling a rights and responsibilities list, looking at the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child. Use short case studies to illustrate laws which children must maintain or are protected by. Survey local, natural and built environments to identify changes. Interviews with older people – those who have seen change in their community. Drawing up a project plan to improve a local area, writing to local council, involving a planner as a visitor. Presenting their case for change through a range of approaches such as persuasive writing, poetry, newspaper articles, leaflet material. Working in a group to plan and cost a project to raise funds, such as cooking and selling the product, making greetings cards, and keeping and balancing a budget. demonstrate an awareness of the idea of individual and collective responsibility to find solutions explain a basic understanding of the meaning of democracy, rights, respect and responsibility show respect for others and a concern for fairness and rights choose an appropriate decision in a real or imaginary situation about the use of resources, including their own money. Set up a school council with elections and real power, eg: over a budget. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 53 Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development Research how Parliament operates and about democracy. Talk to local police officers about laws and how they are enforced. A mock election, producing manifestoes. A Children’s Rights Day. Involving a visitor from your local district or borough council. Involving the community police officer to develop case studies. The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. UN Convention on the Rights of the Child and UNICEF. Visitors. Polling station booths/ballot boxes – hire from local district or borough council office. Website for Houses of Parliament: www.parliament.uk. Books and stories. Local democracy week (October). What money means (www.hants.gov.uk/education/hias/pdl/financial-capability.htm). HIAS e-Profile CD. Assessment opportunities Observation of presentations. Participation in a group activity. Links Every Child Matters Have you thought about? Resources Make a positive contribution Engage in law-abiding and positive behaviour in and out of school. RRR Articles: All – 1 (rights of the Convention) to 42 (knowledge of Convention). 54 PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Healthy Schools PSHE HIAS PDL website Have mechanisms in place to ensure children’s views are reflected in curriculum planning, teaching and learning, and the whole-school environment, including those with SEN and specific health conditions, as well as disaffected children and young carers. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 55 Year 6 – Transition and managing change Skills, knowledge and understanding Objectives Suggested activities Outcomes for personal and social development The National Curriculum framework for PSHE and citizenship teachers in England, DCSF/QCA Children should have opportunities to: Children can: Pupils should be taught: 1b to recognise their worth as individuals by identifying positive things about themselves and their achievements, seeing their mistakes, making amends and setting personal goals 1c to face new challenges positively by collecting information, looking for help, making responsible choices, and taking action. Have you thought about? Resources Assessment opportunities 56 understand about the nature of change look forward and cope with the transition to secondary school review personal experiences as a basis for setting new targets develop simple vocabulary for describing personal effectiveness and setting personal goals know what affects positive mental health present themselves confidently and positively. Brainstorm change. Circle time to celebrate achievements, identify challenges and anxieties about transition, offer each other support. Writing personal description of skills and experiences, making a class year book/record of achievement. Practising stress management skills, such as relaxation and breathing. Drama strategies to explore perceptions of new school, such as the playground. Visit to secondary school. Visit from secondary school pupils. express their expectations and feelings about transfer to a new school name positive qualities about themselves celebrate their own and others’ achievements and strengths review achievements and set realistic targets demonstrate a range of appropriate behaviours for a range of situations. Visits from secondary school pupils. e-Profile/personal profile. The breadth of opportunity required to support children’s personal development learning. Exploring the possibility of productive links with other curriculum areas. Secondary school liaison – staff and pupils. Books and stories. HIAS e-Profile CD. HIAS e-Profile CD. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes HIAS PDL website Links Every Child Matters Be healthy Mentally and emotionally healthy. Enjoy and achieve Ready for school. Achieve personal and social development and enjoy recreation. RRR Articles: 5 (family guidance), 8 (government respect), 12 (opinions). Healthy Schools Emotional health and well-being Provide opportunities for children to participate in school activities and responsibilities to build their confidence and self-esteem. SEAL HIAS PDL website Changes. PSHE long-term planning – KS2 – themes 57