Raven/Johnson Biology 8e
advertisement

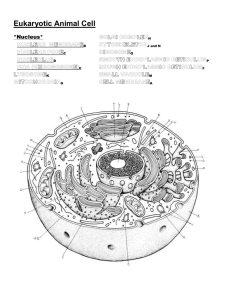
Raven/Johnson Biology 8e Chapter 04 - Answers 1. Which of the following statements is NOT part of the cell theory? a. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. b. Cells come from other cells by division. c. Cells are the smallest living things. d. Eukaryotic cells have evolved from prokaryotic cells. The correct answer is d— A. Answer a is incorrect. The cell theory states that all living things are composed of one or more cells. The correct answer is d— B. Answer b is incorrect. The idea that cells arise from preexisting cells is an important part of the cell theory. The correct answer is d— C. Answer c is incorrect. The cell theory states that cells are the smallest living things. The correct answer is d—Eukaryotic cells have evolved from prokaryotic cells. D. Answer d is correct. Although it may be correct that eukaryotic cells are derived from an ancestral prokaryotic cell, this evolutionary relationship is not part of the cell theory. 2. The most important factor that limits the size of a cell is— a. the amount of proteins and organelles that can be made by a cell b. the rate of diffusion c. the surface-area-to-volume ratio of the cell d. the amount of DNA in the cell The correct answer is c— A. Answer a is incorrect. As long as a cell has energy and raw materials it can make all the proteins and organelles that it needs. Size limitation is related to the ability of oxygen or other molecules to reach all parts of the cell. The correct answer is c— B. Answer b is incorrect. The ability of diffusion to carry materials efficiently decreases as the size of the cell increases. The rate of diffusion is the same, but the distance materials must travel has increased. The correct answer is c—the volume of the cell C. Answer c is correct. The surface-area-to-volume ratio of the cell is the limiting factor. As volume increases, the surface also increases, but by much less than the volume because surface area is a function of the square of the radius while volume is a function of the cube of the radius. As the volume of a cell increases, its energetic needs increase, but its relative ability to transport materials through the plasma membrane decreases. The correct answer is c— D. Answer d is incorrect. The amount of DNA in the cell is not related to its size. DNA in a cell is highly compacted, allowing a large amount of DNA to fit into a small area. Raven/Johnson Biology 8e Chapter 04 - Answers 3. What type of microscope would you use to examine the surface details of a cell? a. Compound light microscope b. Transmission electron microscope c. Scanning electron microscope d. Confocal microscope The correct answer is c— A. Answer a is incorrect. A compound light microscope is useful for examining the general size, shape, and even behavior of cells, but it lacks the resolution to examine the detailed surface of a cell. The correct answer is c— B. Answer b is incorrect. The transmission electron microscope is used to make highresolution images of the insides of cells or the relationship betweens cells and their environment. It cannot give you a view of the surface. The correct answer is c—Scanning electron microscope C. Answer c is correct. A scanning electron microscope is specially designed to scatter electrons off the surface of specially prepared samples. This technique provides a threedimensional view of the surface of a cell. The correct answer is c— D. Answer d is incorrect. A confocal microscope combines the technical precision of a laser with the optics of light microscope to provide a very clear image. Typically confocal microscopy is used to examine the insides of cells, not the surface. 4. All cells have all of the following except— a. plasma membrane b. genetic material c. cytoplasm d. cell wall The correct answer is d— A. Answer a is incorrect. All cells require a plasma membrane. The plasma membrane functions to create two spaces: everything inside the membrane (the intracellular contents) and everything outside the cell (the extracellular contents). The correct answer is d— B. Answer b is incorrect. All cells require genetic information. This information is used to make the proteins that cells need to survive. It is also the information that is transferred during replication. The correct answer is d— C. Answer c is incorrect. All cells have some internal space that holds the proteins, organelles, genetic material, and all the other molecules necessary for life. The correct answer is d—cell wall Raven/Johnson Biology 8e Chapter 04 - Answers D. Answer d is correct. Although all cells need a plasma membrane to separate “cell” from “not cell,” not all cells need a cell wall. The cell wall is a supporting structure that exists outside of the plasma membrane. 5. Eukaryotic cells are more complex that prokaryotic cells. Which of the following would you NOT find in a prokaryotic cell? a. Cell wall b. Plasma membrane c. Nucleus d. Ribosomes The correct answer is c— A. Answer a is incorrect. All prokaryotic cells have a cell wall. The chemical nature of the wall varies, especially between archaeal cells and bacterial cells, but the wall is there. The correct answer is c— B. Answer b is incorrect. All cells, prokaryotic or eukaryotic, must have plasma membrane. Without a plasma membrane there is nothing to separate the cell from its environment. The correct answer is c—Nucleus C. Answer c is correct. All cells must have genetic material, but how the genetic material is stored and organized can vary. The term nucleus refers to a separate membrane-enclosed compartment specialized for the storage of genetic material. Prokaryotes do not have separate membranous organelles in their cytoplasm. Instead, prokaryotes store their genetic material in a region of the cell called a nucleoid. The correct answer is c— D. Answer d is incorrect. All cells require ribosomes in order to make the proteins that help the cell function. The size of a ribosome differs between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, but they must be present. 6. The difference between a gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria is— a. the thickness of the peptidoglycan cell wall b. the type of polysaccharide present in the cell wall c. the type and amount of protein in the cell wall d. the layers of cellulose in the cell wall The correct answer is a—the thickness of the peptidoglycan cell wall A. Answer a is correct. The cell walls of bacteria are composed of peptidoglycan. Grampositive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan cell wall, but gram-negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan cell wall. The correct answer is a— B. Answer b is incorrect. Polysaccharide is a generic name of any polymer composed of carbohydrates. The bacterial cell wall is composed of a type of polysaccharide; however, the type of polysaccharide does not differ between gram-positive and gramnegative bacteria. The correct answer is a— Raven/Johnson Biology 8e Chapter 04 - Answers C. Answer c is incorrect. Amino acids are present in the cell wall of bacteria, but they are covalently bonded to another type of molecule. The correct answer is a— D. Answer d is incorrect. Cellulose is a type of polysaccharide. Cellulose is found in the cell walls of plants, not bacteria. 7. Which of the following is not true of bacterial flagella? a. Bacterial flagella rotate producing a spiral wave. b. Bacterial flagella are anchored to a basal body. c. Bacterial flagella are powered by a proton gradient. d. Bacterial flagella are composed of microtubules. The correct answer is d— A. Answer a is incorrect. The bacterial flagella rotate. The shape of the flagella acts like a propeller on a boat to cause the forward (or reverse) movement of the bacterial cell. The correct answer is d— B. Answer b is incorrect. The flagella must be anchored to the cell. The structure responsible for the anchoring of flagella in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic flagella is called a basal body. The correct answer is d— C. Answer c is incorrect. The movement of the bacterial flagella is powered by the difference in the concentration of protons across the plasma membrane. The correct answer is d— Bacterial flagella are composed of microtubules. D. Answer d is correct. A bacterial flagellum is composed of a single type of protein filament. Eukaryotic cilia and flagella are composed of microtubules. 8. All eukaryotic cells possess each of the following except— a. mitochondria b. cell wall c. cytoskeleton d. nucleus The correct answer is b— A. Answer a is incorrect. Mitochondria are found in all cells (plant and animal), where they contribute to the production of ATP energy for maintaining all the cellular processes required for life. The correct answer is b—cell wall B. Answer b is correct. A cell wall is a special feature of a subset of eukaryotic cells. Plants and fungi have cell walls. Don’t confuse a cell wall with a plasma membrane! All cells, whether eukaryotic or prokaryotic, must have a plasma membrane, but a cell wall is a special structure found outside the plasma membrane. The correct answer is b— Raven/Johnson Biology 8e Chapter 04 - Answers C. Answer c is incorrect. Different cells have different arrangements of cytoskeleton, giving rise to cellular diversity of shape and function; however, the cytoskeleton is a common feature of all eukaryotic cells. The correct answer is b— D. Answer d is incorrect. All eukaryotic cells contain a membrane-bounded nucleus that holds the genetic information for the cell. 9. Ribosomal RNAs are manufactured in which specific area of a eukaryotic cell? a. The nucleus b. The cytoplasm c. The nucleolus d. The chromatin The correct answer is c— A. Answer a is incorrect. The nucleus contains the genetic information required for the production of ribosomal subunits, however, a more specific answer is possible. The correct answer is c— B. Answer b is incorrect. Ribosomal subunits are derived from specific gene sequences with a cell’s DNA. Think about where you would expect to find DNA in a cell. The correct answer is c—The nucleolus C. Answer c is correct. The nucleolus is the specialized region within the DNA of a cell that contains the genes required to make ribosomal RNA. The correct answer is c— D. Answer d is incorrect. The term chromatin is used to describe strands of DNA with attached proteins and does not address the specific question of ribosome production. 10. Which of these organelles is NOT associated with the production of proteins in a cell? a. Ribosomes b. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) c. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) d. Golgi apparatus The correct answer is b— A. Answer a is incorrect. Ribosomes are directly involved in the assembly of amino acids into new proteins using the “instructions” provided by a molecule of messenger RNA. The correct answer is b—Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) B. Answer b is correct. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for the production of new phospholipids and for the detoxification of the cell. The correct answer is b— C. Answer c is incorrect. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is the site of synthesis of proteins that are to be exported out of the cell, inserted into the plasma membrane, or transferred to the lysosomes. Raven/Johnson Biology 8e Chapter 04 - Answers The correct answer is b— D. Answer d is incorrect. The Golgi apparatus is the “next step” for proteins synthesized on the rough endoplasmic reticulum. 11. Proteins can move from the Golgi apparatus to— a. the extracellular fluid b. transport vesicles c. lysosomes d. all of the above The correct answer is d— A. Answer a is incorrect. Proteins present in the extracellular matrix originally were made inside cells. The Golgi apparatus is part of the endomembrane system that allows for the movement of proteins out of the cell. The correct answer is d— B. Answer b is incorrect. Transport vesicles are, like their name suggests, the membranous organelles responsible for moving proteins made on the rough endoplasm reticulum to the Golgi apparatus and from there to the protein’s final destination. The correct answer is d— C. Answer c is not correct. Lysosomes are organelles that contain hydrolytic enzymes. The lysosomal enzymes are synthesized on the rough endoplasmic reticulum and then travel to the Golgi apparatus where they are sorted and packaged into special membrane-bounded organelles. The correct answer is d—all of the above D. Answer d is correct. The Golgi apparatus is uniquely placed to sort proteins to each of the previously listed locations. 12. Lysosomes function to— a. carry proteins to the surface of the cell b. add short-chain carbohydrates to make glycoproteins c. break down organelles, proteins, and nucleic acids d. remove electrons and hydrogen atoms from hydrogen peroxide The correct answer is c— A. Answer a is incorrect. Proteins are carried from the Golgi apparatus to the cell’s plasma membrane using small transport vesicles. The correct answer is c— B. Answer b is incorrect. The addition of carbohydrates to newly synthesized proteins occurs first in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and to a greater extent in the Golgi apparatus. The correct answer is c—break down organelles, proteins, and nucleic acids C. Lysosomes are specialized organelles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that are capable of breaking down cellular contents. The correct answer is c— Raven/Johnson Biology 8e Chapter 04 - Answers D. Answer d is incorrect. The ability to convert hydrogen peroxide to water using the enzyme catalase is a property associated with peroxisomes, not lysosomes. 13. What do chloroplasts and mitochondria have in common? a. Both are present in animal cells. b. Both have an outer membrane and an elaborate inner membrane. c. Both are present in all eukaryotic cells. d. Both organelles function to produce glucose. The correct answer is b— A. Answer a is incorrect. Mitochondria are present in animal cells, however chloroplasts are only found in plants. The correct answer is b—Both are present in plant cells. B. Answer b is correct. Mitochondria and chloroplasts both have a complex structure consisting of an outer membrane and an elaborate inner membrane. In mitochondria it is folded into cristae, and in chloroplasts it is organized into thylakoid disks. The correct answer is b— C. Answer c is incorrect. Mitochondria are present in all eukaryotic cells; however, chloroplasts are only found in cells that use photosynthesis. The correct answer is b— D. Answer d is incorrect. Chloroplasts use light energy to produce glucose; however, mitochondria use the energy stored in the chemical bonds of glucose to make ATP energy. 14. Eukaryotic cells are composed of three types of cytoskeletal filaments. How are these three filaments similar? a. They contribute to the shape of the cell. b. They are all made of the same type of protein. c. They are all the same size and shape. d. They are all equally dynamic and flexible. The correct answer is a—They contribute to the shape of the cell. A. Answer a is correct. A eukaryotic cell’s cytoskeleton functions to organize both the cytoplasm and the plasma membrane, thereby giving a cell its particular shape. The correct answer is a— B. Answer b is incorrect. Each of the three different filaments is composed of specific protein monomers, or subunits. Actin microfilaments are composed of the protein actin, and microtubules are composed of the protein tubulin. Intermediate filaments can be composed of various proteins including vimentin and keratin. The correct answer is a— C. Answer c is incorrect. The cytoskeletal filaments differ in their diameter, ranging from the smallest (actin microfilaments) to the largest (microtubules). Each filament also takes on a unique three-dimensional shape as a result of the way the monomers assemble. Raven/Johnson Biology 8e Chapter 04 - Answers The correct answer is a— D. Answer d is incorrect. Whereas actin microfilaments and microtubules are very dynamic; capable of growing and shrinking, intermediate filaments are very stable. 15. Animal cells connect to the extracellular matrix through— a. glycoproteins b. fibronectins c. integrins d. collagen The correct answer is c— A. Answer a is incorrect. Glycoproteins are present on the cell’s plasma membrane and as part of the extracellular environment; however, they are not involved in anchoring the cell. The correct answer is c— B. Answer b is incorrect. Fibronectins are a type of glycoprotein that can help the cell form an attachment to the extracellular matrix, but they are not directly connected to the cell. The correct answer is c—integrins C. Answer c is correct. Integrins are proteins that function to anchor cells to the extracellular matrix by forming connections between the cell’s cytoskeleton and the proteins of the extracellular matrix. The correct answer is c— D. Answer d is incorrect. Collagen is an important protein fiber that fills the extracellular matrix around eukaryotic cells. Challenge Questions 1. Eukaryotic cells are typically larger than prokaryotic cells (refer to Figure 4.2). How might the difference in the cellular structure of a eukaryotic versus a prokaryotic cell help to explain this observation? Answer—Eukaryotic cells possess internal organelles and endomembrane systems that create subcompartments within the cytoplasm. Both eukaryotes and prokaryotes use diffusion to move materials within the cell, but for eukaryotes, the effective distances are smaller. 2. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is the site of synthesis of the phospholipids that make up all the membranes of a cell—especially the plasma membrane. Use the diagram of an animal cell (Figure 4.6) to trace a pathway that would carry a phospholipid molecule from the SER to the plasma membrane. What endomembrane compartments would the phospholipids travel through? How can a phospholipid molecule move between membrane compartments? Answer—Your diagram should start at the SER and then move to the RER, Golgi apparatus, and finally to the plasma membrane. Small transport vesicles are the mechanism that would carry a Raven/Johnson Biology 8e Chapter 04 - Answers phospholipids molecule between two membrane compartments. Transport vesicles are small “membrane bubbles” composed of a phospholipid bilayer. 3. Use the information provided in Table 4.3 to develop a set of predictions about the properties of mitochondria and chloroplasts if these organelles were once free-living prokaryotic cells. How do your predictions match with the evidence for endosymbiosis? Answer—Based on the properties of prokaryotes listed in Table 4.3, you might predict that mitochondria and chloroplasts would have a cell wall, ribosomes, circular DNA, and possibly cilia or flagella. In fact it has been shown that mitochondria and chloroplasts do indeed have their own DNA and their own ribosomes. Their ribosomes are of the kind found in prokaryotes, not eukaryotes, and their DNA is circular. In some species, there appear to be remnants of a cell wall surrounding the organelle. Other evidence for the endosymbiotic theory described in this chapter includes the observation that both mitochondria and chloroplasts are enclosed in two or more membranes, the organelles are about the same size as modern prokaryotes, the genes encoded within the DNA or the organelles are similar to those of bacteria, and the organelles replicate like modern-day bacteria. 4. In evolutionary theory, homologous traits are those with a similar structure and function derived from a common ancestor. Analogous traits represent adaptations to a similar environment, but from distantly related organisms. Consider the structure and function of the flagella found on eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Are the flagella an example of a homologous or analogous trait? Defend your answer. Answer—The prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella are examples of an analogous trait. Both flagella function to propel the cell through its environment by converting chemical energy into mechanical force. The key difference is in the structure of the flagella. The bacterial flagellum is composed of a single protein emerging from a basal body anchored within the cell’s plasma membrane and using the potential energy of a proton gradient to cause a rotary movement. In contrast, the flagellum of the eukaryote is composed of many different proteins assembled into a complex axoneme structure that uses ATP energy to cause an undulating motion. 5. The protist, Giardia lamblia, is the organism associated with water-borne diarrheal diseases. Giardia is an unusual eukaryote because it seems to lack mitochondria. Explain the existence of a mitochondria-less eukaryote in the context of the endosymbiotic theory. Answer—Eukaryotic cells are distinguished from prokaryotic cells by the presence of a system of internal membrane compartments and membrane-bounded organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts. As outlined in Figure 4.19, the first step in the evolution of the eukaryotic cell was the infolding of the plasma membrane to create separate internal membranes such as the nuclear envelope and the endoplasmic reticulum. The origins of mitochondria and chloroplasts are hypothesized to be the result of a bit of cellular “indigestion” where aerobic or photosynthetic prokaryotes were engulfed, but not digested by the larger ancestor eukaryote. Given this information, there are two possible scenarios for the origin of Giardia. In the first scenario, the ancestor of Giardia split off from the eukaryotic lineage after the evolution of the nucleus, but before the acquisition of mitochondria. In the second scenario, the ancestor of Giardia split off after the acquisition of mitochondria, and subsequently lost the mitochondria. At present, neither Raven/Johnson Biology 8e Chapter 04 - Answers of these two scenarios can be rejected. The first case was long thought to be the best explanation, but recently it has been challenged by evidence for the second case.