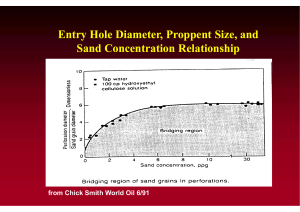
Exam 3
advertisement

Phys24-001, Spring 2003 Exam 3 Name _____________________________ PID: __________________ Sequence Number: 101 Honor Pledge and signature: I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination. _____________________ Instructions: This exam is closed book, closed notes. However, you may use a calculator. Mark your answers to the multiple-choice questions on a Scantron answer sheet. If you do not find your answer, write your solution on these pages and mark option 5. You may write on these test papers, but partial credit will not be given on the multiple-choice section. Turn in your Scantron answer sheet and these test papers at the end of the hour. Equations and conversion factors that may be useful: x xo vox t 12 a x t 2 o t 12 t 2 v vo at 0 t t vt r v 2 vo2 2ax 2 o2 2 Ei E f dp dt dL I dt m1 m2 Fg G 2 r F ma Elasticmodulus PE mgh Fd L I KEr 12 I 2 PE s 12 kx 2 I disk 12 MR 2 I sphere 52 MR 2 f s s n, f k k n P m F P P Po gh P 12 v 2 gy const. V A 9 TF 5 TC 32 L Lo T A Ao T V Vo T 1 2 mv 2 32 k B T W PV water 1000 kg/m 3 cglass 837 J/kg C Q mcT Q mL P Weng Qh Qc x A cos( 2ft ) T 2 c water 4186 J/kg C c Al 900 J/kg C e M Earth 5.98 10 24 kg T 2 c Fe 448 J/kg C 2 1 m/s 2.24 mi/h REarth 6.38 10 6 m Vcylinder = r2h Qh 1 Qc Qh L g Asphere = 4r2 ec 1 f 1 T 1 12 ML2 A1v1 A2 v 2 PV nRT Q T T kA 2 1 t L cice 2090 J/kg C Po 1 atm 1.013 10 5 N/m 2 (or Pa) 14.70 lb/in 1 mi 1.61 km m k Weng W Fv t I rod 13 ML2 or ρ k 2 (A x2 ) m Acircle = r2 vt2 r 2 r W ( F cos )d Wnet KE f KEi KEt 12 mv 2 N P 23 ( 12 mv 2 ) V 1 m 3.28 ft. ac p mv T TC 273.15 v Ft p I hoop MR 2 stress strain U Q W t at rα P AeT 4 Tc Th S v f Qr T v F Lf (water) 3.33 10 J/kg 5 brass 19 x 10 -6 C -1 air 1.29 kg/m 3 1 cal 4186 J 1 lb. 4.45 N 1 Btu 252 cal 1 hp 0.746 kW G 6.67 10 11 N m 2 /kg 2 Vsphere = (4/3) r3 1 Cal 1 kcal g 9.80 m/s 2 = 5.67 x 10-8 W/m2 K4 2 1. What is the buoyant force acting on a rock that is resting at the bottom of a pond? 1. mg – Fn 2. Fn – mg 3. Fb + Fn – mg 4. zero 2. Blood flows through a coronary artery that is partially blocked by deposits along the artery wall. In which part of the artery is the blood pressure the greatest? 1. The pressure is highest in the constricted region. 2. The pressure is highest in the wide region. 3. The pressure is the same throughout the artery. 3. A 12-lb bowling ball has a diameter of 23 cm. Will this bowling ball float in water? 1. yes 2. no 3. not enough information to determine 4. A deflated rubber balloon is placed on a digital balance and found to have a mass of 5.0 g. It is inflated with air to a diameter of 30 cm, and placed on the same balance, which now shows a reading of 5.7 g. What is the magnitude of the buoyant force acting on this inflated round balloon? 1. 0.0069 N 2. 0.056 N 3. 0.14 N 4. 0.18 N 5. A Grandfather clock is controlled by a swinging brass pendulum that is 0.90 m long and accurately keeps time at a temperature of 25 C. How much time will this clock gain or loose over the course of one day if the temperature is at 15 C? 1. 8.2 s 2. 9.1 s 3. 16 s 4. 3.5 min 6. A Grandfather clock uses a swinging brass pendulum to keep time. As the room temperature rises, will the clock run fast or slow? 1. fast 2. slow 3. neither 7. Equal masses of water, sand, and iron filings are heated by identical Bunsen burners. Rank the order of the temperatures of the samples after they have each been heated 2.0 minutes under the same conditions. 1. water > sand > iron 2. iron > sand > water 3. iron > water > sand 4. water > iron > sand 3 8. A rectangular steel plate has a hole drilled through its center. What happens to the hole as the plate is heated in a furnace? 1. the diameter of the hole increases 2. diameter of the hole decreases 3. the diameter of the hole remains the same 4. the hole becomes distorted and is no longer circular 9. A cylindrical diving bell that is 2.0 m tall and 2.0 m in diameter with an open bottom is submerged to a depth of 25 m in a fresh-water lake. The surface temperature is 25 C, and the temperature 25 m down is 10 C. How high does the water rise in the bell? 1. 56 cm 2. 79 cm 3. 121 cm 4. 144 cm 10. The surfaces of a Dewar flask are silvered for the purpose of minimizing heat transfer by what process? 1. conduction 2. radiation 3. convection 4. vaporization 11. Estimate the efficiency of a microwave oven rated at 750 W if a cup of water (250 mL) at room temperature boils in 3.0 minutes on high. 1. 40% 2. 50% 3. 60% 4. 70% 12. The surface temperature of the Sun is about 5 800 K and its radius is 6.96 x 108 m. Calculate the total energy radiated by the Sun each second. (Assume emissivity = 0.965) 1. 1.1 x 1019 W 2. 9.5 x 1025 W 3. 3.8 x 1026 W 4. 7.9 x 1030 W 13. Suppose a heat engine can operate in different modes. Which mode will yield the highest efficiency? Mode A: Th = 900 K, Tc = 600 K Mode B: Th = 600 K, Tc = 300 K 1. Mode A 2. Mode B 3. both modes have the same theoretical efficiency 4 14. According to the first law of thermodynamics, the sum of the heat gained by a system and the work done on that system is equivalent to which of the following? 1. change in entropy 2. change in internal energy 3. change in temperature 4. specific heat 15. Which of the following is true for the entropy change of a system that undergoes a reversible, adiabatic process? 1. dS < 0 2. dS = 0 3. dS > 0 16. One mole of an ideal gas undergoes an adiabatic expansion where it does 20 J of work on its environment. How much heat is received by the system? 1. -20 J 2. + 20 J 3. + 5 J 4. zero 17. A child rides on a swing that oscillates at its natural frequency. What will happen to this natural frequency if two children ride on this swing? 1. The natural frequency will increase. 2. The natural frequency will decrease. 3. The natural frequency will stay the same. 18. Which of the following is NOT affected by increasing the amplitude of a simple harmonic oscillator? 1. frequency 2. maximum acceleration 3. maximum speed 4. total energy 19. Doubling the tension in a guitar string will result in changing the fundamental frequency of the string by what factor? 1. 2.0 2. 1.4 3. 0.7 4. 0.5 20. A mass of 400 g is suspended from a spring that is 45 cm long with a spring constant of 80 N/m. The mass is raised 10 cm above the equilibrium point and released from rest. What is the speed of the mass as it passes through the equilibrium point? 1. 3.4 m/s 2. 2.0 m/s 3. 1.4 m/s 4. zero 5 Answer Key: 1–1 2–2 3–1 4–4 5–1 6–2 7–2 8–1 9–4 10 – 2 11 –3 12 – 3 13 – 2 14 – 2 15 – 2 16 – 4 17 – 3 18 – 1 19 – 2 20 – 3