Population Ecology Notes
advertisement

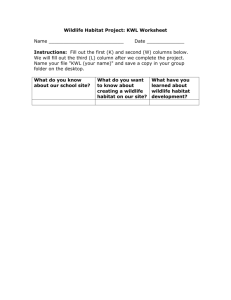
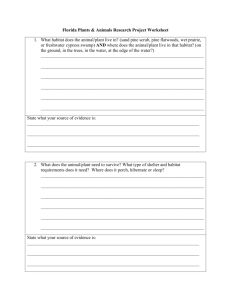
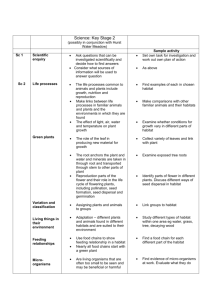
Population Ecology Branch of ecology that studies the structure and dynamics of populations What is a population? Collection of the same species living in the same area Methods for Determining a Population Count What is the female population in the room? What is the white-tailed deer population in Blair County? Not necessarily the best or easiest method Census: Including all members of a population Random Sampling Estimating a population by counting the individuals in a small portion of a specific area (density) Makes a lot of assumptions Yearly counts can be used to track population growth or decline Example: Turkeys in a field Count the number of turkeys in half the field and double it If there are 24 turkeys in the field, how many can be in the entire field Random Sampling Example Sample vs. Census Lower cost relative to census. If the budget is small, take a sample, if large take a census. Time needed. If short, sample. If large, census. Population size Capture - Recapture 1st – Capturing, marking/tagging and releasing Keep a count of the number captured and tagged 2nd – Capture a number and count the number with tags Equation Equation m=M n N What Can Change a Population? Increase Births (B) Immigration (I) Decrease Deaths (D) Emmigration (E) Limiting Factors Disease/parasites Starvation Predators Pollution Accidents Old Age Hunting Loss of Habitat Population Equation N = starting population 100 Elk N +1 = population during the next year N + 1= B – D + 1 – E Answer? Population & Habitat A habitat is where an organism lives. What does it provide? Are those things in endless supply? Carrying Capacity (K) The number of individuals that the resources of a habitat can support. Often decreases in winter when less food and cover is available. If there are more individuals in an area than the habitat can support, some will have to die or leave. Carrying Capacity (K) Carrying Capacity (K) Population Graphs Linear – constant increase Exponential – population increases without limit on resources or is adversely affected Population Management Strategies What techniques can be used to control populations? Increase? Decrease? Keep it the same? What can be done if the population exceeds the carrying capacity of the habitat? Population Management Studies Hunting Removal (plants) Trap and Transfer Reproduction Studies Species Introduction Habitat Restoration Wildlife Management Agencies PA Game Commission http://www.pgc.state.pa.us/ PA Fish and Boat Commission http://sites.state.pa.us/PA_Exec/Fish_Boat/mpag1.htm