Extra-corporeal Extraction + Intoxication
advertisement
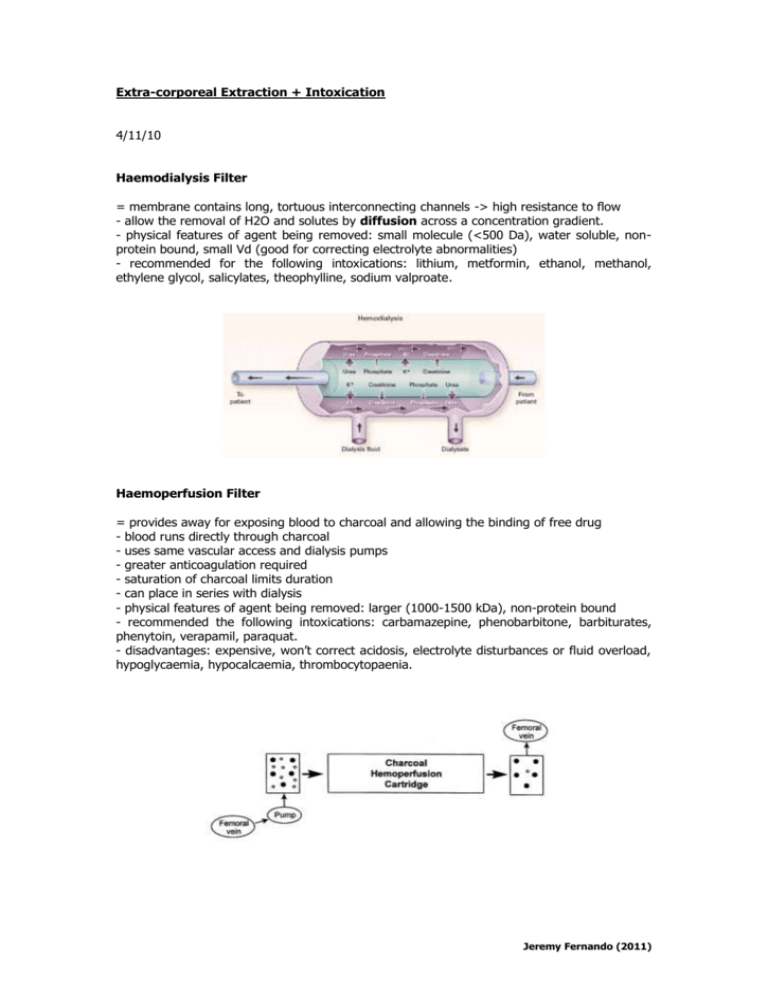
Extra-corporeal Extraction + Intoxication 4/11/10 Haemodialysis Filter = membrane contains long, tortuous interconnecting channels -> high resistance to flow - allow the removal of H2O and solutes by diffusion across a concentration gradient. - physical features of agent being removed: small molecule (<500 Da), water soluble, nonprotein bound, small Vd (good for correcting electrolyte abnormalities) - recommended for the following intoxications: lithium, metformin, ethanol, methanol, ethylene glycol, salicylates, theophylline, sodium valproate. Haemoperfusion Filter = provides away for exposing blood to charcoal and allowing the binding of free drug - blood runs directly through charcoal - uses same vascular access and dialysis pumps - greater anticoagulation required - saturation of charcoal limits duration - can place in series with dialysis - physical features of agent being removed: larger (1000-1500 kDa), non-protein bound - recommended the following intoxications: carbamazepine, phenobarbitone, barbiturates, phenytoin, verapamil, paraquat. - disadvantages: expensive, won’t correct acidosis, electrolyte disturbances or fluid overload, hypoglycaemia, hypocalcaemia, thrombocytopaenia. Jeremy Fernando (2011) Haemofiltration Filter = membrane consists of relatively straight channels of every increasing diameter -> low resistance to flow - recommended for the following intoxications: methotrexate, procanamide Jeremy Fernando (2011)