Handout 2.9 Issues i..
advertisement

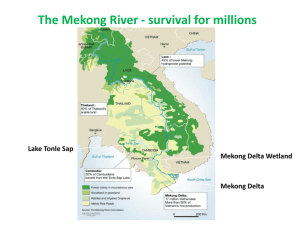
Handout 2.9 Issues in Southern Floodplains and the Delta Implications for Basin Planning in Southern Floodplains and Delta Basin planning on the Cambodian floodplains Whilst there is land available for irrigation, the costs of irrigation are high and the risks are high. Opportunities to exploit the capture fishery are also limited by low incomes (which mean people cannot afford boats or fishing gear). As a result the annual flood and the size of the flood is extremely important – it brings the fish onto the floodplain, it provides water for the crops and it gets rid of the rats. The river and Tonle Sap are important transport routes. Goods are transported without regulation and pollutants are carried across Tonle Sap (such as petrol). Any spill in Tonle Sap would have significant implications for the fishery which would have impacts beyond just those living around the lake. Basin Planning on the Vietnamese Delta The Mekong delta is densely populated and that population will increase substantially (even though growth rates are low for the Mekong region). Changes in land use on the floodplain (urbanisation and the move toward permanent crops rather than rice) will have implications for flooding by changing flood flows and exposing more people to flooding. Aquaculture is very important in the delta and sustainable expansion of aquaculture will be necessary to provide protein for a growing population and to take the pressure off the capture fishery. Sustainable expansion of aquaculture is a challenge. Aquaculture production can potentially put a lot of pollutants into waterways but there is work being done by research institutes such as in Can Tho on sustainable aquaculture/rice rotations. Overall, there are some major other issues for further discussion in the basin planning. These are: Because of over population, increasing water demand in all sectors, irrigated intensification and intensive land use with increasing use of chemicals, this sub-area is facing natural resource degradation. These include declining of fish population, deforestation and completing demand on water leading water shortage in dry season Topographical limitations to increase production such as salinity intrusion, acidity, erosion of river bank, Handout 2.9 Issues in Southern Floodplains and the Delta sedimentation, flood and inundation and imbalance water flow in dry and wet season. All people in the sub-areas both direct and indirect clients, the ecology per se, and the bio-diversity are affected by the degradation of the Mekong. The landless, rural poor and ethnicities in the areas are the first groups who would suffer from the declining of the resources. Planning issues on the shared resources of the Delta are taken consideration the limits to growth perspective.