Global Dam Reoptimization Initiative
advertisement

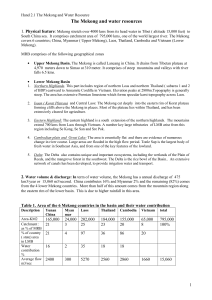
The Mekong River - survival for millions Lake Tonle Sap Mekong Delta Wetland Mekong Delta CLIMATE RESILIENT MEKONG: MAINTAINING THE FLOWS THAT NOURISH LIFE With the Support of Partners and Cooperating Agencies: National Governments: Ministry of Water Resources and Meteorology, Cambodia Department of Water Resources, Thailand Institute of Meteorology, Hydrology and Environment, Vietnam Water Resources & Environment Administration, Lao PDR [Invited, but not confirmed] Major Initial Funder: International NGOs: Consvervation International World Wide Fund The Nature Conservancy Natural Heritage Insitute [Project Coordinator] Cooperating Agency: Expected Effects of Climate Change in Mekong Basin Precipitation & River Flow: • Precipitation and runoff increase of 13.5 % predominantly from wet season increases • Increase in dry season precipitation in northern catchments and decrease in southern catchments. • Increase in Mekong River flow in both wet and dry seasons – Wet season increase = 15% above PP – Dry season increase =30% in upper portions • Increase in total annual runoff of 21% + increase in flooding Greater Mekong/ Lancang Area Inundated in the Mekong Delta (Sea Level Rise = 1m) (Source: MRC Technical Paper No. 24, September 2009) Maintaining the Flows that Nourish • Water • Sediment • Nutrients • Information River erosion due to reduction in sediment Objective To inform decisions on siting, design and operation of dams to: • Counteract the effects of climate change • Maintain water and sediment flows to preserve ecosystem health and food production • At any level or pace of development Sediment Capture will have High Impact • On the most biologically productive features of the river system – – – – – • Floodplains—84,000 km2 Wetlands –e.g. Tonle Sap Deep pools—400 mapped Delta—most endangered Near shore ocean—nutrient dependent On the economic value of reservoir depends on maintaining storage capacity Project Premise • At any level of development, there are better and worse choices in – Siting – Design – Operation • To move sediment through dams and reduce impacts on food/ecosystem productivity We need to learn about Sediment Good for Us and Good for Them