Cell Division and Genetics Study Guide
advertisement

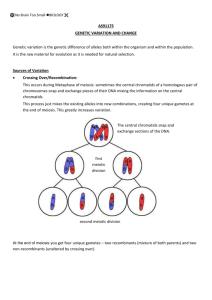
Study Guide – Cell division and Genetics (The cell division portion of this study guide will be useful for your quiz too!) Cell Cycle and Cancer: - know the phases of the cell cycle, what happens in each phase - Why and when must a cell divide? - Discuss how the cell regulates cell division and what happens when this regulation is disrupted o Differentiate between cyclins, oncogenes and tumor surpressors Chromosomes: - know what they are, when they appear, how many we have - Understand difference between homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids - Understand the difference between crossing over and translocations - Understand non-disjuction and how it causes loss of chromosomes - Be able to explain how we diagnose chromosomal mutations and the different types that exist Mitosis and Meiosis: - be able to draw and recognize all phases and list key events that happen in each phase - Compare and contrast the two processes and discuss the significance of each difference - Discuss all mechanisms that lead to genetic diversity in sexually reproducing species and why this is important. - Differentiate between oogenesis and spermatogenesis Embryology: - Describe the steps that occur following fertilization - Differentiate between how fraternal and identical twins are formed - Explain differentiation Vocabulary: if they aren’t in your notes LOOK THEM UP Cyclin interphase Replication Organelle Mitosis Meiosis Somatic cell Gamete Crossing-over Translocation Monosomy Trisomy Diploid Haploid Gene Genome Homologous chromosomes Microtubules Centromere Sister chromatids Cytokinesis Cell Plate Gap 2 (G1) Tetrad polar body G0 (rest) phase Gap 1 (G2) Non-disjunction S Phase Mitotic Spindle Centriole Cleavage Furrow Additional Recommendations: Use our resources. There are many good review games and quizzes including multiple choice questions! Genetics: Be able to answer genetics problems with the following inheritance patterns: 1. complete dominance 2. incomplete dominance 3. co-dominance 4. X-linked 5. Test Cross 6. Polygenic traits 7. Multiple alleles (not really an inheritance pattern, but you are responsible for knowing the alleles for human blood type and how they interact together) Know the difference between genotypes and phenotypes - be able to identify a person’s genotype or phenotype base on a description Know how to find the allele combinations present in gametes for dihybrid crosses, be able to identify the genotype of a dihybrid phenotype; be able to construct or interpret a dihybrid cross Know the meaning of any genetics related word in your note packet or assignments and be able to use them properly Know who Mendel was and what his contributions were - KNOW HIS THREE LAWS!!!!! This does not mean be able to recite them. Understand what he was saying. Be able to identify the significance of each and explain how they happen. This means relating them to events in meiosis. Think about what would happen if one of his first two laws fails. How does the law of independent assortment fail if genes are linked? Know what each part of the punnett square means as well as being able to fill it out. Know how many alleles we have for each gene, how many we pass down to each child. Be able to differentiate between genes and alleles. Formation of gametes - briefly review of meiosis o how are gametes made? How many chromosomes? o How is independent assortment and segregation demonstrated in meiosis o Can linked genes ever be separated? If so how… what makes separation more or less likely? Pedigrees - know what shape is what - how to interpret a pedigree and determine the inheritance pattern by looking for clues - be able to draw a pedigree if given a verbal description - understand that if two inheritance patterns are possible, pick the one that is most likely (ex: if every spouse that marries in has to be a carrier in order for it to work out to be autosomal dominant, then it is probably something else) Variation: WHY is there so much emphasis on making us different? Why is this beneficial to the species?