SNC 2P NAME________________________________________
advertisement

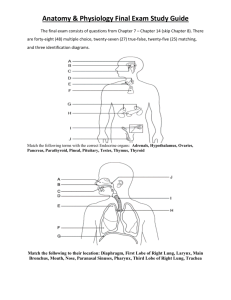
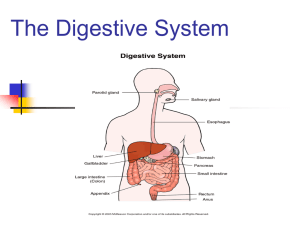
SNC 2P NAME________________________________________ Final Exam- PRACTICE EXAM Part 2: Multiple Choice Portion 50 minutes All questions must be answered on the Scantron card provided. You must fill in your answer using pencil. Identify the following chemical reactions (#1- #4) as one of the following: (a) SYNTHESIS (b) DECOMPOSITION (c) COMBUSTION (d) NEUTRALIZATION Fill in your answer on your Scantron © card. 1. C + O2 CO2 2. H2O2 H2 + O2 3. acid + base salt + water 4. CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O 5. The compound “NaOH” is: a. an acid b. a base c. neither an acid nor a base 6. This substance turns blue litmus paper red: a. an acid b. a base c. neither an acid nor a base 7. This substance tastes sour. a. an acid b. a base c. neither an acid nor a base 8. This substance feels slippery. a. an acid b. a base c. neither an acid nor a base 9. An ionic compound is formed from the combination of: a. two metals b. two non-metals c. a metal and a non-metal d. two semi-metals 10. The alkali metals take on an ionic charge of: a. +2 b. -2 c. +1 d. -1 11. A characteristic or description of a substance that may help you to identify it is called a: a. chemical reaction c. physical property b. physical reaction d. chemical property 12. The smallest particle of an element that is still considered to be whole is a(n): a. molecule c. atom b. neutron d. proton 13. Which of the following does not describe a typical metal? a. a shiny lustre c. brittle b. malleable d. conducts heat well 14. Which of the following does not indicate that a chemical change has taken place? a. a change in state c. a change in colour b. the formation of a new gas d. the formation of a new solid 15. The elements that are in Group One on the Periodic Table (the first vertical column) are: a. the halogens c. the alkali metals b. the noble gases d. the alkaline earth metals 16. Food travels through the digestive tract in the following order: a. mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum b. mouth, esophagus, stomach, large intestine, small intestine, rectum c. mouth, stomach, esophagus, small intestine, large intestine, rectum d. mouth, stomach, esophagus, large intestine, small intestine, rectum 17. What happens to the unusable materials that are left over after digestion takes place? a. it goes to the pancreas to await disposal. b. it goes to the right ventricle to await disposal c. it goes to the large intestine to await disposal d. it goes to the small intestine to await disposal 18.What structure prevents food from entering our windpipe (trachea)? a. The uvula b. The tongue c. The epiglottis d. The teeth 19.What happens to the trachea before it reaches the lungs? a. It branches in two directions b. It branches in three directions c. It vibrates to create sounds d. It closes up so that oxygen can’t escape 20.Which of the following events takes place in the lungs? a. Food is digested b. Liquid waste is filtered from the blood c. Oxygen is delivered into the blood stream d. Carbon dioxide is delivered into the blood stream 21. What is another name for the THROAT? a. Lungs b. Larynx c. Pharynx d. Trachea 22.What is another name for the VOICE-BOX? a. Lungs b. Larynx c. Pharynx d. Trachea 23.What is the purpose of the little hairs inside the nose? a. To fight disease b. They serve no purpose c. Nose hairs just look great d. They keep dust and particles from entering the airway 24.The preferred entrance for air into the human body is through: a. The mouth b. The nose c. The skin d. The ear holes 25. a. b. c. d. What is the organ that pumps blood throughout the human body? The lungs The heart The kidneys The blood vessels and capillaries 26. a. b. c. d. What is the function of the blood vessels? They pump blood to the heart They filter impurities from the blood They carry blood to all parts of the body They carry messages from the brain to the muscles 27. a. b. c. d. What type of blood vessel is only one cell thick in diameter? Arteries Veins Capillaries All of the above are only one cell thick 28. a. b. c. d. What type of blood vessel is thick and muscular? Arteries Veins Capillaries All of the above 29. a. b. c. d. What type of blood vessel carries blood back to the heart? Arteries Veins Capillaries All of the above 30. a. b. c. d. What is the straw-coloured, fluid part of the blood called? Red blood cells White blood cells Plasma Platelets 31. What is precipitation? a. water that falls over landmasses only b. snow falling over temperate areas c. water that falls over lakes only d. any water that falls over Earth, in any form 32. Which of the following tells us the amount of water vapour in the air? a. humidity b. temperature c. barometric pressure d. dew point 33. What is relative humidity? a. a measure of the amount of water vapour in the air as a percentage of the minimum amount of water vapour the air could hold at that temperature b. the same as humidity c. like the chill factor for cold weather d. a measure of the amount of water vapour in the air as a percentage of the maximum amount of water vapour the air could hold at that temperature 34. The temperature at which dew forms is called the: a. saturation point b. the dry point c. the wet point d. the dew point 35. What is produced if the fast rising air from a thunderstorm begins to spin? a. a hurricane b. El Nino c. A tornado d. Lightning strikes 36. Which of the following is NOT a greenhouse gas? a. carbon dioxide b. water vapour c. sulphur dioxides d. oxygen 37. Which of the following gives evidence from the past of climate change? a. change in season length b. tree rings c. the daily weather report d. a person getting a sunburn 38. Which is an example of a natural event that can cause long-term climate change? a. the loss of trees from deforestation b. a major volcanic eruption c. an El Nino event d. a change in the position of Earth’s land areas 39. Which activity contributes the MOST to Canada’s greenhouse gas emissions? a. transportation b. heating c. agriculture d. electrical generation 40. Which of the following might be caused by an increase in greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere? a. rising temperatures b. formation of new ice sheets c. expansion of Arctic sea ice d. reduced use of fossil fuels For the following table, match the correct term to the proper definition by filling in the right letter on your Scantron card. TERM DEFINITION 41. opaque a. the production of light by living things 42. translucent b. doesn’t allow light to pass through 43. bioluminescence c. when light waves bounce off a surface 44. reflection d. allows scattered light to pass through 45. In a beam of light, the light rays are: a. reversed b. parallel c. perpendicular d. bent For the following table, match the correct term to the proper definition by filling in the right letter on your Scantron card. TERM DEFINITION 46. diverging a. may be real or virtual 47. incident ray b. curved inward 48. Law of Reflection c. incoming ray 49. image d. curved inward 50.converging e. the incident ray is equal to the reflected