Canada Climate & Ecosystems Worksheet
advertisement

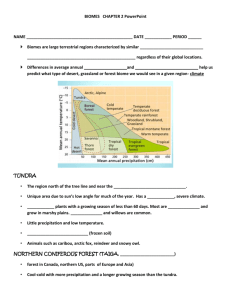
1 5 2 6 3 7 4 7 7 Climate Region 1 Arctic Climate Region Characteristics *small amount of precipitation (< 350mm) * Very long winters (10 months) & short, cold summers * too cold for trees Ecosystem Tundra * Maritime climate 2 West Coast * Mild winter temperatures, above freezing West Coast Forest * Cooler summers 3 Mountain 4 Boreal 5 Prairie * Variety of climate condition experienced caused by differences in elevation and aspect. * Windward slopes receive precipitation * Leeward slopes are dry (rain shadow) * Largest regions with continental climate, located mostly interior * winter, cold & 6 months + & Summer is short, cool * Precipitation mostly in summer & mostly convectional * Experiences continental climate * Climate is rather dry, the little precipitation that does occur, occurs during summer. * Large temperature ranges Cordilleran Forest Boreal Forest Grassland / Parkland Ecosystem Characteristics * Permafrost (frozen soil); only thin top layer thaws * plants bloom, mature and seed very quickly (very short summer) * No trees, only small shrubs mosses & lichens * Large, tall trees flourish here * mild climate and large amounts of precipitation are excellent for trees of this forest * Douglas fir, western hemlock and red cedar are some trees of this forest * Vegetation varies greatly because climate varies greatly! *Grasses and cacti grow I dry parts, while forests grow in wetter parts. * higher elevations = smaller plants similar to the tundra, even higher NO vegetation (rocks, snow & ice) * below the treeline; longer growing season and more precipitation. * To the north = needle-leaf trees (spruce pine, fir) * to the south = broad leaved trees (poplar & birch) * driest areas = short grasses & cacti * more precipitation = taller grasses * transition zone of grasslands with sporadic clumps of trees. (northern parts) Climate Region 6 7 Southeastern East Coast Climate Region Characteristics Ecosystem Ecosystem Characteristics * Affected by both the Atlantic Ocean and Great Lakes * experiences mostly continental climate but maritime climates experienced in some areas * Winter is cool-cold and summer is warm – hot. * maritime climate, nearness o the ocean * mixture of needle-leaved and broad leaved trees. Acadian Forest * transition zone between boreal / Broad leaved forest and broad-leaved forest. * near coast, harsher climate = small forest shrubs or trees. * winters not too cold, nor summers very hot Mixed Forest / Boreal * > 1000 mm precipitation * mixture of needle-leaved and broad leaved trees. * transition zone between boreal forest and broad-leaved forest. * small tracks of forest remain, most land used for farming because of hot summers and lots of precipitation. Climate Regions Arctic Boreal East Coast Prairie Southeastern West Coast Mountain Climate Region Descriptions * winters not too cold, nor summers very hot * very long winters (10 months) & short, cold summers * maritime climate * largest regions with continental climate, located mostly interior * experiences continental climate * mild winter temperatures, above freezing * variety of climate condition experienced caused by differences in elevation and aspect. * large temperature ranges * windward slopes receive precipitation * winter, cold & 6 months + & summer is short, cool * experiences mostly continental climate but maritime climates experienced in some areas * precipitation mostly in summer & mostly convectional * leeward slopes are dry (rain shadow) * climate is rather dry, the little precipitation that does occur, occurs during summer. * cooler summers * affected by both the Atlantic Ocean and Great Lakes * too cold for trees * winter is cool-cold and summer is warm – hot. * maritime climate, nearness o the ocean *small amount of precipitation (< 350mm) * > 1000 mm precipitation Ecosystems / Vegetation Regions Tundra Mixed Forest / Boreal Forest Boreal Forest Acadian Forest / Broadleaved forest West Coast Forest Cordilleran Forest Grassland / Parkland Vegetation Region Descriptions * transition zone between boreal forest and broad-leaved forest. * plants bloom, mature and seed very quickly (very short summer) * large, tall trees flourish here * transition zone between boreal forest and broad-leaved forest. * driest areas = short grasses & cacti * to the north = needle-leaf trees (spruce pine, fir) * mild climate and large amounts of precipitation are excellent for trees of this forest * vegetation varies greatly because climate varies greatly! * more precipitation = taller grasses * higher elevations = smaller plants similar to the tundra, even higher no vegetation (rocks, snow & ice) *grasses and cacti grow in dry parts, while forests grow in wetter parts. * to the south = broad leaved trees (poplar & birch) * Douglas Fir, Western Hemlock and Red Cedar are some trees of this forest * transition zone of grasslands with sporadic clumps of trees. (northern parts) * mixture of needle-leaved and broad leaved trees. * no trees, only small shrubs mosses & lichens * below the treeline; longer growing season and more precipitation. * near coast, harsher climate = small shrubs or trees. * mixture of needle-leaved and broad leaved trees. * permafrost (frozen soil); only thin top layer thaws * small tracks of forest remain, most land used for farming because of hot summers and lots of precipitation.