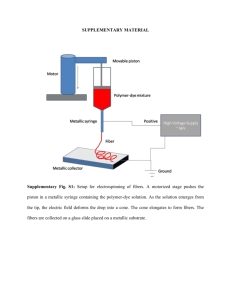
Supplementary data Microscopic study The presence of PHA
advertisement

Supplementary data Microscopic study The presence of PHA biopolymer was evidenced by the observation of cells under fluorescence microscope (Nikon TS 100 model) after staining with Nile blue A (Ostle and Holt 1982). A loopful of bacterial cells was heat- fixed and stained with 1% Nile Blue A, treated with 8% (v/v) acetic acid and observed by excitation at 460 nm to detect the presence of intracellular PHA granules. The granules were observed to possess yellowish orange fluorescence of different sizes bounded by the dye under the fluorescence microscope (100X) (Supplementary Fig. 1). Supplementary Fig. 1 Nile Blue staining of PHA under fluorescence microscope (1000X magnification) Supplementary data 1 Isolation of genomic DNA and PCR amplification of 16S r DNA of isolated Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolation of genomic DNA was carried out using the bacterial genomic DNA Isolation Kit (RKT09). Pure bacterial isolate of Pseudomonas spp. was identified by PCR amplification. The PCR product was sequenced bi-directionally using the forward, reverse and internal primer of the 16S rDNA. The PCR products (16S r DNA gene) were purified using gel extraction kit (Bangalore Genei) and sequenced with Big Dye Terminator version 3.1” Cycle sequencing kit and ABI 3500 XL Genetic Analyzer. The sequence data were aligned and compared with published sequences obtained from the Gen Bank database using Seq Scape v 5.2. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using ClustalW by distance matrix analysis and the neighbour-joining method. Result Phylogenetic analysis (Supplementary Fig. 2) indicated a comparative search for the sequence revealed 99.98% homology to the Pseudomonas aeruginosa P21(GenBank entry: HQ697283) 16S r DNA gene sequence. Further, a BLAST (NCBI) search showed 99% homology to other known P. aeruginosa 16S rDNA gene sequences and accordingly it was named as Pseudomonas aeruginosa BP C1 (GeneBank entry:JQ796859). Supplementary Fig. 2 Phylogenetic tree of 16S rDNA sequences related to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Supplementary Fig. 3 FTIR profiling of the PHA isolated from glucose a 2 a The FT-IR spectrum of the polymer revealed the presence of specific peaks at wave numbers 3,405-O-H bonding 2,923- bands of C-H stretching 1,730 cm-1 - strong absorption band of ester carbonyl C=O Weak peaks at 1,670 cm-1 and 3,085 cm-1 are indicative of the presence of –C=C and alkene C–H stretching in the polymer chain. Supplementary Fig. 4 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) thermograph of the PHA isolated from glucose 3 4