2003-04
2003-04
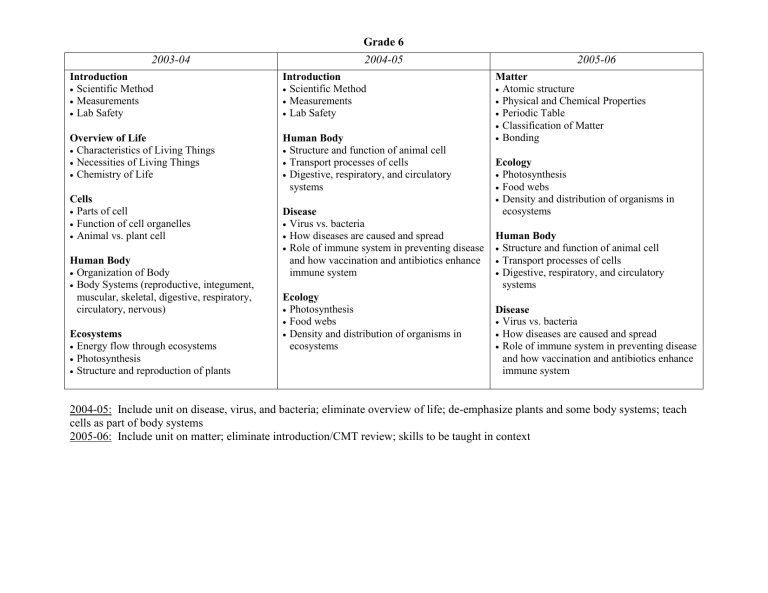
Grade 6
2004-05 2005-06
Introduction
Scientific Method
Measurements
Lab Safety
Overview of Life
Characteristics of Living Things
Necessities of Living Things
Chemistry of Life
Cells
Parts of cell
Function of cell organelles
Animal vs. plant cell
Human Body
Organization of Body
Body Systems (reproductive, integument, muscular, skeletal, digestive, respiratory, circulatory, nervous)
Ecosystems
Energy flow through ecosystems
Photosynthesis
Structure and reproduction of plants
Introduction
Scientific Method
Measurements
Lab Safety
Human Body
Structure and function of animal cell
Transport processes of cells
Digestive, respiratory, and circulatory systems
Disease
Virus vs. bacteria
How diseases are caused and spread
Role of immune system in preventing disease and how vaccination and antibiotics enhance immune system
Ecology
Photosynthesis
Food webs
Density and distribution of organisms in ecosystems
Matter
Atomic structure
Physical and Chemical Properties
Periodic Table
Classification of Matter
Bonding
Ecology
Photosynthesis
Food webs
Density and distribution of organisms in ecosystems
Human Body
Structure and function of animal cell
Transport processes of cells
Digestive, respiratory, and circulatory systems
Disease
Virus vs. bacteria
How diseases are caused and spread
Role of immune system in preventing disease and how vaccination and antibiotics enhance immune system
2004-05: Include unit on disease, virus, and bacteria; eliminate overview of life; de-emphasize plants and some body systems; teach cells as part of body systems
2005-06: Include unit on matter; eliminate introduction/CMT review; skills to be taught in context
2003-04
Introduction
Scientific Method
Measurements
CMT preparation
Matter
Physical vs. chemical properties
Physical vs. chemical changes
Periodic Table and the atom
Heat and Temperature
Temperature scales
Specific heat
Heat Transfer
Effects of heat on matter (phases and phase changes)
Chemical Reactions
Bonding
Law of Conservation of Mass
Types of Chemical reactions
Balancing Chemical Equations
Endothermic vs. Exothermic
Waves
Characteristics of waves
Electromagnetic spectrum
Sound vs. noise
Composition of light
Grade 7
2004-05
Introduction
Scientific Method
Measurements
CMT preparation
Chemistry
Describing matter
Classification of matter
Periodic Table and the atom
Bonding
Law of Conservation of Mass
Types of Chemical reactions
Forces and Motion
How forces change the velocity of an object
(speed up, slow down, stop, change
direction)
Newton’s Laws of Motion
Energy and Work
Relationship between force, distance, and work
Simple machines and how simple machines are used to make everyday tasks easier to do
Conservation of energy (potential and kinetic)
How energy is used to do work
2005-06
Forces and Motion
How forces change the velocity of an object
(speed up, slow down, stop, change
direction)
Newton’s Laws of Motion
Energy and Work
Relationship between force, distance, and work
Simple machines and how simple machines are used to make everyday tasks easier to do
Conservation of energy (potential and kinetic)
How energy is used to do work
Weather and Climate
How Sun’s energy affects air pressure and influences weather
Composition of atmosphere and how atmosphere protects Earth
Climate (and effects of atmospheric temperature and oceanic temperature
Dynamic Earth
Layers of the Earth
Role of water cycle on rock cycle
Plate tectonics: how earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountains are formed
Effect of plate tectonics on rock cycle
2004-05: Include units on force and motion, energy and work; synthesize and streamline chemistry units
2005-06: Include units on weather and climate, dynamic Earth; eliminate introduction/CMT review; skills to be taught in context
2003-04
Grade 8
2004-05 2005-06
Introduction
Scientific Method
Measurements
CMT preparation
Meteorology
Wind patterns
Weather vs. Climate
Air pressure
Humidity
Geology
Types of rocks
Mineral identification
Rock cycle
Plate tectonics
Astronomy
Heliocentric vs. Geocentric
Star formation and life cycle
Galaxies
Earth-Moon-Sun system (tides, moon phases, eclipses)
Planets/Solar system
Introduction
Scientific Method
Measurements
Lab Safety
Meteorology
Wind patterns
Weather vs. Climate
Air pressure
Humidity
Life in Outer Space
Characteristics of planets
Space program exploration
Necessities of life and potential to sustain life on other planets
How technology might help humans sustain life in outer space/other planets
Plate Tectonics
Radioactivity (overview)
Convection and circulation in mantle
Plate movement
Earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain building
Motion on Earth and in the Solar System
Application of Newton’s Laws to motion in solar system
Measuring and calculating average speed and illustrating motion with graphs of distance vs. time
Effects of gravity on Earth and in space
Sun-Earth-Moon relationships (phases, tides, eclipses)
Life in Outer Space
Characteristics of planets
Space program exploration
Necessities of life and potential to sustain life on other planets
How technology might help humans sustain life in outer space/other planets
Reproduction and Nutrition
Nutritional needs of humans (how food is transformed into energy to sustain life)
Sexual vs. asexual reproduction
Benefits of sexual reproduction
Inheritance of traits (genotype vs. phenotype, dominant vs. recessive, sex determination)
Plate Tectonics
Radioactivity (overview)
Convection and circulation in mantle
Plate movement
Earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain building
2004-05: Include unit on disease, virus, and bacteria; eliminate overview of life; de-emphasize plants and some body systems; teach cells as part of body systems
2005-06: Include unit on matter; eliminate introduction/CMT review; skills to be taught in context







