Lesson 5 Assignment - Rocky View Schools Moodle 2
advertisement
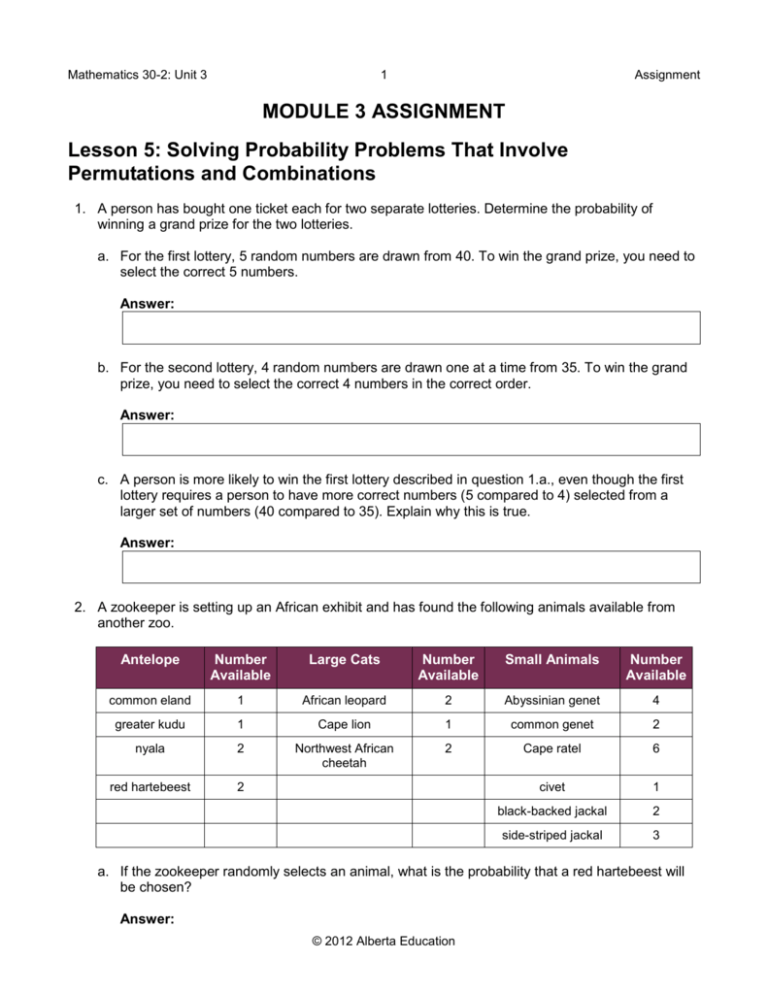
Mathematics 30-2: Unit 3 1 Assignment MODULE 3 ASSIGNMENT Lesson 5: Solving Probability Problems That Involve Permutations and Combinations 1. A person has bought one ticket each for two separate lotteries. Determine the probability of winning a grand prize for the two lotteries. a. For the first lottery, 5 random numbers are drawn from 40. To win the grand prize, you need to select the correct 5 numbers. Answer: b. For the second lottery, 4 random numbers are drawn one at a time from 35. To win the grand prize, you need to select the correct 4 numbers in the correct order. Answer: c. A person is more likely to win the first lottery described in question 1.a., even though the first lottery requires a person to have more correct numbers (5 compared to 4) selected from a larger set of numbers (40 compared to 35). Explain why this is true. Answer: 2. A zookeeper is setting up an African exhibit and has found the following animals available from another zoo. Antelope Number Available Large Cats Number Available Small Animals Number Available common eland 1 African leopard 2 Abyssinian genet 4 greater kudu 1 Cape lion 1 common genet 2 nyala 2 Northwest African cheetah 2 Cape ratel 6 red hartebeest 2 civet 1 black-backed jackal 2 side-striped jackal 3 a. If the zookeeper randomly selects an animal, what is the probability that a red hartebeest will be chosen? Answer: © 2012 Alberta Education Mathematics 30-2: Unit 3 2 Assignment b. If the zookeeper randomly selects 8 animals, what is the probability that a cheetah or a jackal will not be chosen? Answer: c. If the zookeeper randomly selects 4 small animals, what is the probability that at least 1 Abyssinian genet will be chosen? Answer: d. If the zookeeper asked for 4 antelope or large cats, what is the probability that both the eland and the kudu would be received? Answer: 3. a. Suppose you wrote the following message using the pigpen cipher from the beginning of the lesson. What is the probability that an interceptor would correctly guess the message on the first try if the interceptor assumed each symbol corresponded to a letter of the alphabet? Answer: b. What is the probability of the person correctly guessing the following message on the first try if that person knew was an s? (Hint: You can assume that if you guess the first correctly, you will also guess the second correctly.) Answer: © 2012 Alberta Education Mathematics 30-2: Unit 3 3 Submit your completed Lesson 5 Assignment to your teacher for assessment. © 2012 Alberta Education Assignment