Text S1. Detailed description of A. nidulans strain constructions. We
advertisement

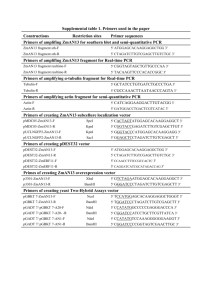
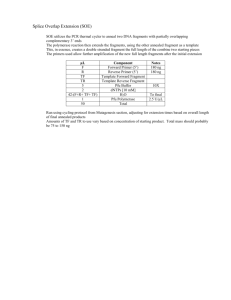
1 Text S1. Detailed description of A. nidulans strain constructions. 2 We constructed the pkcA-ts mutants as follows. A 4.4-kb fragment containing the 3 coding region of an N-terminus of PkcA was amplified from the total DNA of the A26 4 strain using primers, 5pkcAF and pkcA-plR. A 1.0-kb fragment containing the coding 5 region of a C-terminus of PkcA and a downstream of pkcA was amplified from the total 6 DNA of the A26 strain using primers pkcA-plF and 3pkcA518R-friboB. A 2.1-kb 7 fragment containing riboB was amplified from the total DNA of the A26 strain using 8 primers, riboBF and riboBR. A 0.9-kb fragment containing a downstream of pkcA was 9 amplified from the total DNA of the A26 strain using primers, 3pkcA518F-friboB and 10 3pkcA1405R. These amplified fragments were fused by the fusion PCR using primers, 11 5npkcAF and 3pkcA1405R-n. The A1145 strain was transformed with the fused 12 fragment. The total DNA of the transformants was extracted as described previously [1] 13 and Southern blot analysis was performed as described previously [2]. The three 14 transformants in which a single copy of the transformed fragment was integrated into 15 the pkcA locus confirmed by Southern blot analysis were designated pkcA-ts-2, 16 pkcA-ts-3, and pkcA-ts-5 (Fig. S6A and B). 17 We constructed strains in which pkcA was expressed under the control of alcA(p) as 18 follows: A 1.1-kb fragment containing the upstream of pkcA was amplified from the 19 total DNA of the A26 strain using primers 5pkcAF and 5pkcAR-friboB. A 2.1-kb riboB 20 fragment was amplified from the total DNA of the A26 strain using primers riboBF and 21 riboBR. A 1.4-kb fragment, in which a coding region of the 5’ terminus of pkcA was 22 fused to the alcA(p), was amplified from pPAALP (Ichinomiya et al., 2007) using 1 23 primers, ALpkcAF-friboB and pkcA1020R. These amplified fragments were fused by 24 the fusion PCR using primers 5npkcAF and pkcA1020R-n. The A1145 strain was 25 transformed with the fused fragment. The two transformants in which a single copy of 26 the transformed fragment was integrated into the pkcA locus confirmed by Southern blot 27 analysis were designated alcA(p)-pkcA-3, and alcA(p)-pkcA-4 (Fig. S6C and D). 28 We constructed the bckA deletion mutants as follows: The A1149 strain was 29 transformed with a 6.2-kb HindIII-SpeI fragment of pbckA::pyroA. The two 30 transformants in which wild-type bckA was replaced with a single copy of the 31 bckA::pyroA fragment at the bckA locus confirmed by Southern blot analysis were 32 designated ΔbckA-1 and ΔbckA-2 (Fig. S6E and F). 33 We constructed the mpkA deletion mutants as follows: A 1.2-kb fragment containing 34 the upstream of mpkA was amplified from the total DNA of the A26 strain using primers 35 5mpkAF and 5mpkAR-fpyrG. A 2.0-kb fragment containing pyrG was amplified from 36 the total DNA of the A26 strain using primers pyrG-481 and pyrG-r-new. A 1.1-kb 37 fragment containing the downstream of mpkA was amplified from the total DNA of the 38 A26 strain using primers 3mpkAF-fpyrG and 3mpkAR. These amplified fragments 39 were fused by the fusion PCR using primers 5mpkAF-n and 3mpkAR-n. The A1149 40 strain was transformed with the fused fragment. The three transformants in which a 41 single copy of the fragment was integrated into the mpkA locus confirmed by Southern 42 blot analysis were designated ΔmpkA-1, ΔmpkA-2 and ΔmpkA-8 (Fig. S6G and H). 43 We constructed strains in which Lifeact-EGFP was expressed under the control of the 44 alcA(p) as follows: The A1149 strain and the pkcA-ts-2 mutant were transformed with a 2 45 3.0-kb fragment that was amplified from ppyrGLA using primers pyrG5 and pyrGRn. 46 The two transformants of the wild-type strain, in which a single copy of the amplified 47 fragment was integrated into the pyrG locus confirmed by Southern blot analysis, were 48 designated A1149LA-1 and A1149LA-2 (Fig. S5I and J). The two transformants of the 49 pkcA-ts mutant, in which a single copy of the amplified fragment was integrated into the 50 pyrG locus confirmed by Southern blot analysis, were designated pkcA-tsLA-1 and 51 pkcA-tsLA-2. 52 We constructed the bckA deletion mutants in which Lifeact-EGFP was expressed 53 under the control of the alcA(p) as follows: The A1149LA-1 strain was transformed 54 with the 6.2-kb HindIII-SpeI fragment of pbckA::pyroA. The two transformants in 55 which wild-type bckA was replaced with a single copy of the bckA::pyroA fragment at 56 the bckA locus confirmed by Southern blot analysis were designated ΔbckALA-1 and 57 ΔbckALA-2. 58 We constructed strains in which MpkA-FLAG was expressed from its own promoter 59 as follows: A 1.5-kb fragment containing mpkA was amplified from pMPKA-pyroA 60 using primers mpkA5 and 3FLAG-mpkA. A 3xFLAG fragment was amplified from 61 p3xFLAG-myc-CMV-26 (Sigma) using primers 3xFLAGF and 3xFLAGR. A 4.5-kb 62 fragment containing pyroA and the downstream region of mpkA was amplified from 63 pMPKA-pyroA using primers mpkA3 and 5mpkA-FLAG. These amplified fragments 64 were fused by the fusion PCR using primers mpkA5 and mpkA3. The A1149 strain and 65 the pkcA-ts-2 mutant were transformed with the fused fragment. The two transformants 66 of the wild-type strain, in which a single copy of the fused fragment was integrated into 3 67 the mpkA locus confirmed by Southern blot analysis, were designated A1149/MF-1 and 68 A1149/MF-2. The two transformants of the pkcA-ts mutant, in which a single copy of 69 the fused fragment was integrated into the mpkA locus confirmed by Southern blot 70 analysis, were designated pkcA-ts/MF-1 and pkcA-ts/MF-2. 71 We constructed wild-type strains, which were auxotrophic for pyrimidine as follows: 72 The A1149 strain was transformed with the 2.0-kb EcoRV-PstI fragment of ppyrG+750 73 containing pyrG (Yamazaki H., Ohta A., Horiuchi H., unpublished). The three 74 transformants in which a single copy of the fragment was integrated into the pyrG locus 75 confirmed by Southern blot analysis were designated A1149/pyrG-1, A1149/pyrG-2 and 76 A1149/pyrG-8. 77 We constructed the heterokaryons containing both wild-type and pkcA-deleted nuclei 78 as follows: A 2.1-kb fragment containing riboB was amplified from the total DNA of 79 the A26 strain using primers, riboBF and riboBR. The 1.1-kb upstream and 1.1-kb 80 downstream fragment of the pkcA coding region was amplified from the total DNA of 81 the A26 strain using primers, 5pkcAF and 5pkcAR-friboB, and 3pkcAF-friboB and 82 3pkcAR respectively. These amplified fragments were fused by the fusion PCR using 83 primers, 5npkcAF and 3pkcAR. The A1145 strain was transformed with the fused 84 fragment. 85 untransformed-pkcA alleles confirmed by Southern blot analysis, were designated 86 ΔpkcA-h1, ΔpkcA-h2, ΔpkcA-h3. The three transformants, which 87 4 contain both transformed- and 88 References 89 1. Oakley CE, Weil CF, Kretz PL, Oakley BR (1987) Cloning of the riboB locus of 90 Aspergillus nidulans. Gene 53: 293-298. 91 2. Horiuchi H, Fujiwara M, Yamashita S, Ohta S, Takagi M (1999) Proliferation of 92 intrahyphal hyphae caused by disruption of csmA, which encodes a class V chitin 93 synthase with a myosin motor-like domain in Aspergillus nidulans. J Bacteriol 181: 94 3721-3729. 5