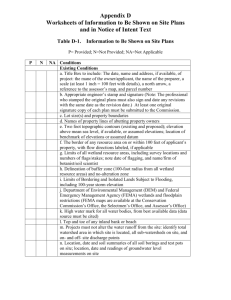
English
advertisement

October 6, 1999 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 PROJECT DESCRIPTION ...............................................................................................................................5 1.1 DESCRIPTION OF ACTIVITIES FOR THE EVALUATION TEAM ...............................................................................5 1.2 FOCUS AREAS AND TOPICS................................................................................................................................6 1.3 MITIGATION MEASURES ....................................................................................................................................7 1.4 REGULATORY AND INSTITUTIONAL SETTING ....................................................................................................8 2 ENVIRONMENTAL SITUATION ANALYSIS ..............................................................................................9 2.1 LAND USE AND POPULATION PRESSURES..........................................................................................................9 2.2 CLIMATE ......................................................................................................................................................... 10 2.3 GEOLOGY ........................................................................................................................................................ 10 3 ANALYSIS OF ALTERNATIVES ................................................................................................................. 12 3.1 BASELINE STUDY ............................................................................................................................................ 12 3.2 LAND VALUATION .......................................................................................................................................... 13 3.3 ANALYZING THE ALTERNATIVE OF DEVELOPING LARGER SITES .................................................................... 13 3.4 WETLAND USES FOREGONE ............................................................................................................................ 13 3.5 UPLAND IMPACTS FOREGONE ......................................................................................................................... 13 4 WATER MANAGEMENT .............................................................................................................................. 15 4.1 LAND DRAINAGE ............................................................................................................................................. 17 4.2 WATER DIVERSION ......................................................................................................................................... 18 4.3 EXPOSURE TO FLOOD RISK.............................................................................................................................. 19 4.3.1 On-Site Flooding Issues ......................................................................................................................... 19 4.3.2 Downstream Flooding Issues ................................................................................................................. 20 4.3.3 Flood Mitigation Measures ................................................................................................................... 21 4.4 WATER CONSERVATION IMPACT ..................................................................................................................... 21 5 LAND DEVELOPMENT ................................................................................................................................. 23 5.1 LAND TENURE AND OTHER SOCIAL ISSUES ..................................................................................................... 23 5.2 LAND CLEARING AND LEVELING..................................................................................................................... 24 5.3 EROSION .......................................................................................................................................................... 25 5.4 SOIL AND RICE PRODUCTIVITY LOSS FACTORS ............................................................................................... 26 6 5.4.1 Poor Water Control ............................................................................................................................... 27 5.4.2 Poor Weed Control ................................................................................................................................ 28 5.4.3 Excessive Turnaround Time ................................................................................................................... 29 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH ...................................................................................................................... 30 6.1 MALARIA ........................................................................................................................................................ 31 6.2 SCHISTOSOMIASIS ........................................................................................................................................... 31 6.3 NUISANCES ..................................................................................................................................................... 32 6.4 HAZARDOUS WASTE ....................................................................................................................................... 32 7 BIODIVERSITY AND ECOLOGY ................................................................................................................ 33 7.1 DISRUPTION OF NATIVE FLORA AND FAUNA ................................................................................................... 34 7.2 INTEGRATED NATURAL SYSTEMS ................................................................................................................... 34 7.3 FERTILIZER USE .............................................................................................................................................. 35 7.4 PESTICIDE USE ................................................................................................................................................ 35 7.5 PEST MANAGEMENT........................................................................................................................................ 36 7.6 ENCROACHING ON PROTECTED AREAS............................................................................................................ 38 8 MONITORING AND EVALUATING ........................................................................................................... 39 APPENDIX 1. EVALUATION TEAM MEMBERS AND KEY CONTACTS .................................................... 41 APPENDIX 2. REFERENCE SOURCES ............................................................................................................... 42 APPENDIX 3. ORGANIZATIONS CONSULTED ................................................................................................ 43 APPENDIX 4. MITIGATION MEASURES FOR ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS OF WETLAND DEVELOPMENT ...................................................................................................................................................... 44 APPENDIX 5. WETLAND ENVIRONMENT CHECKLIST ............................................................................... 47 APPENDIX 6. SAMPLE MEMORANDUM OF UNDERSTANDING ................................................................ 51 APPENDIX 7. LIST OF PROTECTED SPECIES AND AREAS IN LIBERIA.................................................. 53 APPENDIX 8. MONITORING PLAN FOR ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES OF WETLAND DEVELOPMENT ...................................................................................................................................................... 57 1 PROJECT DESCRIPTION These guidelines are part of an effort by the participating organizations to improve their project planning related to wetland development activities. The purpose of these guidelines is to ensure that environmental factors and conditions are considered in the project proposal phase. The material contained herein serves as a resource for agencies planning agricultural programs that may include wetland environments. It covers the potential environmental effects from wetland development activities. Both beneficial and detrimental effects are discussed. The environmental consequences of project activities can now be considered prior to approval and appropriate mitigation activities can be clarified. The three organizations that contributed logistical support and funding for these guidelines are: Catholic Relief Services (CRS) World Vision (WV) Lutheran World Federation / World Service (LWF/WS). The environmental issues discussed in this report are often encountered in wetland development projects, and were of significant concern for the projects visited. Attention is drawn to what should have been done in addition to – and at times contrary to – what has been done. Recommended practices are given to address common negative impacts. It is intended that this document will provide guidance in developing agricultural programs for wetlands in an environmentally friendly manner. NGOs generally must comply with donor environmental guidelines and procedures in planning, design, implementing and monitoring of all activities proposed herein except where standards set by the Government of Liberia would be more stringent. 1.1 Description of Activities for the Evaluation Team The study commenced on 13 September and was completed by 7 October, 1999. The team of experts (see Appendix 1) assembled for this evaluation performed the following tasks: Reading and review of relevant documentation (see Appendix 2). Interviews with key persons/institutions in Liberia (see Appendix 3). Field visits and information gathering at representative sites in the NGO’s project areas. Preparation of these guidelines. Debriefing with NGO technicians and project managers. Public consultation was an integral part of this evaluation process. The team carried out consultations with national NGOs (for example, for nature protection), scientific experts, and government agencies. This consultation process helped ensure public support for - and input to the final sector program. Finally, a workshop was conducted to debrief other interested organizations and individuals. The list of organizations and contact person consulted during the D:\533566517.doc 5 evaluation process is given in Appendix 3. After the field-visit phase of the evaluation, the consultant team met with the project managers from each NGO to summarize the findings and recommendations, and to present this report. This team also examined the Liberia Forest Development Authority’s recommendation that the best way to prevent forest degradation by slash and burn practices is to encourage the use of wetlands for permanent farming. Natural resource values have not been overlooked in this analysis. 1.2 Focus Areas and Topics The areas examined during this review team visit to Liberia are given in Table 1. A national map indicating the sites visited is attached to this document. Table 1. Counties of Liberia in which the NGOs are actively promoting wetland development. The number of sites visited by the review team in each county is given in parentheses. Organization Catholic Relief Services World Vision Liberia County 1999 Total Population [1000s] 1998 Developed Wetland Area [1000s ha] Montserrado 844 Margibi Developed Wetlands Proposed Area [ha] # Sites 5 11 3 180 219 8 24 8 480 Sinoe 79 5 36 10 600 Bong (3) 300 37 10 3 180 Grand Bassa (4) 215 19 30 10 600 Rivercess (3) 38 4.5 18 6 360 Lofa 351 25 190 7 45* Bong (3) 300 37 32 2 22* Cape Mount (4) 120 6 21 1 351 25 20 4 80 114 4 15 3 60 339 36 10 2 40 Lutheran (Lower) Lofa World Bomi (7) Federation / World Services Nimba (1) # Participants * Only the number of communities is known. Wetland development activities related to environmental issues and discussed in these guidelines consist of the following: Site selection D:\533566517.doc 6 Distribution of plots to community members Hydrologic assessment for water management Field-level irrigation design, construction and scheduling norms Clearing and leveling of fields Plant variety selection Environmental health management Pest management 1.3 Mitigation Measures Useful mitigation measures noted throughout the text are summarized in Appendix 4. Additional information such as site selection can be found implicitly in these guidelines, but the reader is also encouraged to review the general wetland development guidelines of Brewer (1984). Training Considerations: Training in methods to improve the overall understanding of wetland cultivation is suggested. It should be stressed that extension agents are the most appropriate targets for this level of training, and that they should be transferring environmental awareness to the farmer communities. The technological level of the interventions should not surpass the level of comprehension of farmers for unsupervised replication. The West African Rice Development Association (WARDA) and the Central Agricultural Research Institute (CARI) are institutes for rice cultivation and training. Training courses can be arranged for extension staff of the three projects jointly to cover the following areas: Technical (existing development technologies and transfer in packages that are interpretable and practical) LNGO and CBO staff – organization and management training Farmers participation training through demonstrations Community education and sensitization training (women and youths) Micro-enterprise development and marketing (women groups and youths). This intervention should be done in collaboration with the Department of Regional, Research and Extension, Ministry of Agriculture with facilitation from CARI, UNDP/FAO and the Environmental Foundation for Africa (EFA) cognizant of the comparative advantages. The Environmental Foundation for Africa (EFA) conducts environmental awareness training. FAO is also planning to conduct technical workshops for environmental issues related to agricultural projects. A general consideration is the eventual transfer of responsibility of the wetland and surrounding watershed. Local farmers must be trained in the use of simple monitoring, accounting, and D:\533566517.doc 7 irrigation system operation tools. Also, the work of canal maintenance, crop scheduling, agricultural training, and other functions require local expertise. 1.4 Regulatory And Institutional Setting The government of Liberia has yet to develop substantial legal and policy guidelines for development activities related to the environment. The Ministry of Agriculture is responsible for providing follow-up extension advice to farmers for crop rotation, green manure, water management, and soil fertility. The Liberian Forest Development Agency is responsible for environmental monitoring. But in fact, few extension agents or materials are available at the present time. The National Environment Committee (NEC) will be working this year with a technical advisory committee to develop a plan of action for environmental issues. This effort is in response to Agenda 21, which the country is in the process of ratifying. D:\533566517.doc 8 2 ENVIRONMENTAL SITUATION ANALYSIS Wetlands are the most physically and chemically heterogeneous of all the major aquatic ecosystems in Liberia. They act as sinks for silt particles and soluble inorganic nutrients but sources for dissolved and particulate organic matter. The wetlands are typically environmentally fragile, requiring some intervention to maintain an ecological balance and sustainable agricultural production. Wetlands referred to as “inland valley swamps” are the subject of the majority of lowland agricultural development activities being promoted in Liberia. These valleys are formed on the uppermost part of the watershed base relief and extend up to 25 km downstream. The watershed areas above them are generally greater than 2 km2. Widths vary from 10 m to 250 m in lower stretches. Stream-wise slopes are generally 2-5%. FAO is planning to develop an agricultural database as a national repository of data, but that level of information is not presently available. No climate data is being collected by anyone in Liberia, although the European Commission plans to begin next year by installing 24 climate stations around the country. A checklist used to develop an environmental situation analysis is given in Appendix 5. The sections indicate the types of data that should be collected when evaluating potential sites for agricultural development. Below are several general remarks on the wetland environmental situation. 2.1 Land Use and Population Pressures Of the small valleys in West Africa, those in the humid Tropical Forest Zone (within which the entirety of Liberia lies) are most suitable for rice cultivation. Of the 2.2 million km2 within this zone and the Guinea Savanna Zone, about 10% consist of small valleys (Oosterbaan et al. 1988). Thus, there are approximately 0.2 million km2 of wetland area in this zone. Present (1998 estimates) rice paddy yields totaled 210,000 tonnes on 162,000 ha, indicating an average yield of 1.3 tonnes/ha. For the 1995 estimated total population of 2.4 million and a total land area of 97,750 km 2, estimates and assumptions are that*: Approximately 200,000 farming families (~6 members per family) are currently active. Approximately 30% of land area is considered arable (=29,325 km2). Less than 20% of the potential lowland area for rice cultivation are presently being exploited (=19,550 km2). Less than 4% of utilized wetland cultivation utilizes some form of water control (<800 km2). * source: Ministry of Agriculture D:\533566517.doc 9 Assuming that only 5% of the land can be characterized as a wetland-type environment, almost 5,000 km2 of wetland is available for development. Based on the estimate that a family of six would need to cultivate 0.22 ha of wetland for adequate nutrition in an entire year (based on a double crop yielding 2.5 tons/ha), just 430 km2 would be adequate. Thus, potentially ten times the existing population could be fed from lowland production in Liberia if fully exploited. Even the currently exploited area (800 km2) would be sufficient. Yet with the ~0.1 acre plots typically programmed, farmers will likely not abandon upland crops for subsistence food, cash crops, and other uses. Utilizing the same estimate of 200,000 farming families along with the estimate of 1.5 ha of upland exploited annually by a subsistence farming family, an estimated 300,000 ha are slashed and burned annually. However, as the traditional fallow period of 4-5 years per upland area is reduced, with the concomitant reduction in soil fertility, many more families will come to depend on alternative sources of food production such as wetland cultivation. 2.2 Climate The tropical atmosphere holds large amounts of moisture. Annual rainfall in the project areas ranges from 1700-4600 mm/yr. Rainstorms in Liberia are generally intense, producing even up to 75 mm during a single event lasting 1-2 hours. Evapotranspiration rates are also high owing to intense solar radiation throughout the year although no data has been found. Average rainfall can be expected to exceed average potential evapotranspiration during at least six months of the year. Rainfall patterns are bimodal in the southeastern region of Liberia, with a major peak in September/October and a minor peak in May/June. Elsewhere a unimodal pattern with a peak in August/September is normal. The information on local climate conditions is useful for many aspects of wetland development including assessing hydrologic conditions (Chapter 4) and land development (Chapter 5). 2.3 Geology The most important geological formation in most of Liberia is the basement complex comprising granites and associated metamorphic rocks. The weathering of these rocks containing silicate minerals releases nutrients. These soils have medium fertility and texture. Due to the general climate conditions, weathering processes have been intense and have caused deep soils, except in sloped areas which have been depleted. On the valley bottoms, alluvium is the parent material of the soils (that is, the soil was dislodged by water, transported in streams, and deposited in the valley). The soils therefore vary widely in characteristics – locally and regionally – sharing only the sign of being hydromorphic (periodic wetness). Hydromorphic processes include the dissolution and absorption of iron. This process causes a characteristic neutral gray color, and possibly formation of iron concretions. Mobilized iron is toxic to rice, while the concretion phase is unmanageable for tilling. Nonetheless, the superior hydrologic conditions in these valleys typically override these constraints. Soil pH in the wetlands is generally slightly acidic. Acid conditions are suitable for rice production, as the pH D:\533566517.doc 10 tends towards neutral following wetting and drying cycles. Most plant nutrients are also most available for uptake by plant roots in the slightly acidic range of water conditions. Geological information such as is described here is valuable in assessing hydrologic conditions and land suitability, as described in Chapters 4 and 5, respectively. D:\533566517.doc 11 3 ANALYSIS OF ALTERNATIVES A major purpose of these guidelines is to analyze alternative design options and strategies in terms of environmental costs and benefits. If a proposed agricultural program emphasizes conversion of wetlands to rice production, alternative approaches could be intensification of production in existing fields, conversion of other land types, crop rotation, etc. This comparative analysis of alternative programs applies indicators of environmental and social impacts and methods to evaluate and compare the indicators and, ultimately, the alternative options. Government claims that people will leave the upland slash and burn practices in favor of wetland cultivation are, however logical, not documented. Although overall human nutritional status will be improved, it will not necessarily be done to the exclusion of other destructive practices. Therefore, if not countered, slash and burn practices will continue until all of the available upland areas have been fully exploited and degraded. Wetland agricultural programs need to be introduced successfully, with the ancillary considerations related to environmental sustainability included in project activities. Fortunately, the environmental effects of agriculture activity in wetland are generally reversible, as evidenced in areas that were developed prior to the war but since then abandoned. The land returned to a quasi-natural condition after 10 years of limited use. Natural vegetation can germinate from the soil’s seed bank and proliferates within only weeks of neglect, even after 20 years of suppression. This observation indicates that the wetland development programs, if abandoned, will not have caused permanent damage to the environment. 3.1 Baseline Study Owing to the transition from emergency operations to longer-term development programs, adequate baseline studies are often overlooked. Liberia is especially difficult for planning and evaluation of projects since “all data was lost during the war.” Therefore, it is imperative that an organization intending to develop long-term development programs improves its own evaluation of activities. Collecting baseline data is the only reliable means of comparing project results to prior conditions. The monitoring program described in Chapter 8 would be more useful were appropriate baseline data available. A water budget is typically employed in hydrologic analyses of watersheds. The conceptual model of a water budget can be stated as inflow minus outflow equals the change in stored water (ground water). The difficulty in Liberia is that so little data is available to quantify the individual terms of this relationship – climate data (rainfall, evaporation), watershed conditions (area, ground cover, slope, infiltration rate), and ground water conditions (water table depth, volume stored, transmission rate). Furthermore, project schedules are typically laid out with insufficient planning time. Collecting baseline data for hydrologic conditions takes at least one full year. Therefore, only general, rule-of-thumb considerations can realistically be addressed. D:\533566517.doc 12 3.2 Land Valuation The value of wetland land can be quantified in several categories and compared between before and after development. The wetland environment can be valued for the following categories, discussed in this report: Flood mitigation (decreased flooding downstream) Reduced erosion and soil deposition Aquifer recharge/discharge Water quality maintenance (natural degradation of contaminants) Habitat for flora and fauna (especially if endangered). 3.3 Analyzing the Alternative of Developing Larger Sites According to EU recommendations, the minimum total acreage to be developed should be greater than 6 ha (~15 acres) to justify clearance and construction work. In terms of environmental degradation, however, the size of the site is directly proportional to many of the potential negative impacts. Furthermore, many sites are limited in size by physical constraints. In some areas, it is anticipated that larger tracts will eventually be developed after starting on a more manageable scale. Note that larger contiguous areas developed are more serious and may require a complete environmental assessment before approval. Cultivation effort requirements are approximately equal over the same area of uplands and lowlands. A reasonably healthy family, then, could cultivate 1 ha of wetland. To manage a paddy system of 6 ha would therefore require at least 6 families. The additional logistics and community cohesion required increases the risk of failure of these larger systems. 3.4 Wetland Uses Foregone Alternative uses of wetlands may be important, such as palm oil harvesting, water quality improvement, flood control, pastureland, fish and wildlife enhancement, peat harvesting (for heat energy), and indigenous plant production. Local farmers are expected to make their own decisions as to the relative value of uses foregone such as palm oil harvesting, pastureland, and indigenous plant production compare to paddy rice and vegetable cultivation opportunities. Development of these inland valley swamps will remove stagnant ponds, improve water movement to prevent flooding, bring under utilization land previously of no productive use to the farming community. Other potential uses are discussed throughout these guidelines. 3.5 Upland Impacts Foregone No intervention implies that farmers will continue their traditional slash and burn practices for cultivating in upland areas. With an estimated 300,000 ha of land cultivated annually among D:\533566517.doc 13 880,000 ha of arable upland available (estimated as 30% arable land on 97,750 km2 of total land area [United Nations, 1999]), average fallow periods are now less than three years. Even if farmers spend only two days per week in wetlands, that will be two days fewer in the uplands. Taken as a direct proportion (3 days in upland fields instead of 5), the annual reduction in cultivated upland could be approximately 120,000 ha. This potential reduction in slash and burn would be foregone with no action. Work effort should also be considered, in that reduced effort towards food production could go towards other household endeavors. Table 2 indicates the relative benefit-to-work ratio for upland and wetland agriculture. The wetland figures assume a double crop is practiced (2.5 tons/ha/crop). The cost-benefit ratio indicates that over double the effort is required in producing an equivalent weight of upland rice compared to lowland rice. Given another way, the benefits foregone by continuing to work in uplands, or the extra work for a given crop yield, is 97 worker days per ton of crop. Table 2. Comparison of work benefits in uplands and lowlands. Upland Lowland Average work effort required [Worker days/year/ha] 165 342 Average yield [tons/year/ha] 1 5 Cost:Benefit Ratio 165 68.4 [Worker days/ton] D:\533566517.doc 14 4 WATER MANAGEMENT Hydrology is the most important determinant of the establishment and maintenance of specific types of wetlands and wetland processes. Liberia is blessed with abundant rainfall throughout the country. With or without groundwater flow, rice cultivation will be possible during the wet season, although a second crop may require some groundwater. The seasonal wetlands are hydrologically complex, where runoff and seepage in upland areas are replaced by river valleys further downstream. The water tables are near or above the lowest ground surface during the wet season. They do not have large floodplains (generally less than 100 m wide), great lengths (generally shorter than 10 km) like large rivers, or salinity problems like drier regions. All of the streamflow eventually drains into the Atlantic Ocean. Controlling the water resources available is the dominant factor necessary for successful management of wetland crops. Water control in wetlands has three major objectives: 1) Drain off excess floodwaters effectively 2) Allow rice paddies to be filled and drained at will 3) Ensure that dry season flows are fully utilized for irrigation. Apart from the plant requirement, water is needed for: Effective and thorough land preparation and puddling Weed control by submergence Rodent control by providing an undesirable environment (standing water) Supply of dissolved oxygen Reduction of plant nutrients into available forms Enhanced control of caseworms Reduction of concentrations of carbon dioxide, iron and other reduced chemical species. A pattern of seasonally fluctuating water levels is the rule, rather than the exception, in most wetlands. It would be useful to determine a wetland’s hydroperiod, defined as the period of water availability. By way of graphical representation (Figure 1), the hydroperiod can aid in training farmers how to schedule activities, select crops, and decide on cultivation techniques as explained in Chapter 5. D:\533566517.doc 15 Excess water Fe br ua ry be r D ec em cto be r O ug us t A Ju ne pr il A a) Limited water b) Excess water Limited water No flow Figure 1. Examples of hydroperiod schedules for wetlands, indicating levels of available water in a) wetter areas and b) drier areas. Insufficient water control has been noted in many developed sites, evidenced by dryness, low grain formation, pest infestation, high weed infestation and flood damage. Construction work should begin with water control structures, allowing the managed water to be used, even before rice seedling transplanting, for weed suppression and land leveling. Unfortunately, water management is often avoided until later in the work schedule. Controlling the hydrologic processes that played part in the development of the wetland ecosystems has its environmental consequences. There are both positive and negative environmental impacts of water management, including: Ensures good response to fertilizers Encourages nutrient availability and organic matter formation by anaerobic decomposition Ensures that water is not the limiting growth condition Suppresses weed growth Suppresses vermin infestation Improves potential for multiple crops in one year, reducing need for upland farming Increases wet season flooding downstream Decreases hydroperiod downstream. Hydrologic impact of water management on the downstream environment should be considered. Early rains that historically flooded uncultivated areas will still flood the area, only in a regulated manner. Throughout the remainder of the wet season, some increased flooding downstream can be expected (see section 4.3) as the drainage canal conducts water more efficiently that the natural channel, particularly during floods. After the wet season, additional water for rice is diverted from the stream. Fortunately, the majority of the diverted water returns to the stream through the drainage channel. D:\533566517.doc 16 Rice paddies should be inundated during the entire growth period. For a small valley, therefore, the minimum dry season flow is a potential constraint. The minimum flow rate is primarily a function of the amount of rainfall and the size of the watershed area. In Liberia’s zone, the ratio of watershed area to cultivated area needs to be at least 1 km2 for every 2-5 ha. General Water Management Mitigation Measures: Observe the ratio of watershed area to cultivated area of at least 1 km2 for every 2-5 ha. Plot the local hydroperiod for planning purposes. 4.1 Land Drainage With rice being a semi-aquatic plant, poorer drained soils are best suited for lowland rice cultivation. Conversely, continuously saturated soils are also unsuitable as some alternating oxidation and reduction cycling is required for good rice growth. Excessively drained soils pose a drought risk unless the drainage can be overcome by appropriate water management such as leveling, water retention structures (bunds and dykes), or increased water diversion into the plots. The high organic content of many wetland soils will decay with wetting-drying irrigation cycles, thereby altering the hydraulic conductivity of the subsoil and bunds. It is possible that straightening the main canals to increase water velocity will scour and subsequently destabilize the bank, leading to soil loss and flooding of adjacent land. Subsidence of the canal walls will be difficult to repair, especially where it was built up above the natural land level. Irrigation canals and the main drain can also be damaged by: Sloughing (subsidence) of saturated soil into the canals and drain Excessive flow into the canals from the tributaries following high intensity rainfall events Failure to clean and maintain the canals. Though drainage canals provide more effective drainage during the wet season (mid-April to mid-October), there is a perceived risk that this will result in over-drainage during the dry season causing a drop in groundwater levels. But replenishment from groundwater and irrigation rapidly equilibrate with the high rainfall conditions found in Liberia. As an example, if 30 cm of surface water is drained over 6 ha with soil porosity of 50%, the resulting volume is 9000 m 3. For comparison, a typical 3-m high earth-filled reservoir would contain ~80,000 m3. The drained water would also be accomplished over several weeks, not instantaneously. Interestingly, the volume of water retained in a flooded rice paddy would also be 9000 m3 assuming 15 cm of standing water is desired over the same 6 ha site. Salinity, often associated with irrigation projects, will generally not be important in Liberia. In such humid conditions, salts accumulating during the dry season (from capillary rise of groundwater and subsequent evaporation) will be leached with the first rains of the subsequent wet season before cultivation begins. The groundwater table fluctuation has been found to be adequately small in most lowlands of Liberia. It should be stated only that the water table must fluctuate around ground level, providing periods of submersion as well as periods of dryness. Trees in natural wetlands literally D:\533566517.doc 17 act as pumps, extracting soil moisture in the root zone and transpiring it into the atmosphere. The alteration to shallower rooted crops will tend to reduce evapotranspiration and deepening of the water table. The canal design proposed by the EU consists of a composite cross section with dry season flows passed in a lower drainage canal. Being centrally located, further from the paddies, the hydraulic gradient is minimized with this arrangement. The drainage canal should roughly follow the line of lowest elevation (the “thalwag”) to facilitate drainage following natural land surface gradients. Construction activity should proceed from the upstream area downstream. In fact, the ideal schedule would work only in the uplands and tributaries initially, and within the main wetland area only afterwards. Land Drainage Mitigation Measures: Work from the upstream area downstream. Design drainage canals with a composite cross-section following the thalwag. 4.2 Water Diversion M ca ai n na dr l ain M irr ain ig at io n ag ca e na l Earthen head dykes constructed at the upstream end of a wetland send water laterally and then parallel to the wetland at an elevation higher than the paddies. From that vantage, the water can flow laterally through the paddies and back down into the central drain (Figure 2). There is little storage available in the canal system, such that an inconsequential amount of water is detained from progressing downstream. If the watershed upstream of this structure is large (see section on flooding, below), the dyke risks overtopping and destruction of the structure. Rice paddy Rice paddy Figure 2. Cross-section of a typical developed paddy. Given that the lowlands are traditionally communal plots, work is often devoted to them only two days per week. During the wet season, however, hydrologic impacts occur over shorter periods. If a bund or head dyke fails during a storm and repairs are delayed for 3 days, then the entire cropping season could be compromised. For convenient access, wetlands located adjacent to roads are often selected for development. The blockage can be an impediment, however, limiting a farmer’s ability to manage the flow of water. Head dykes should be placed 5-10 m downstream of any road to avoid traffic, to allow for plot adjustments, and to store water. D:\533566517.doc 18 Water control becomes more problematic when plots are laid out in a downstream position, with development progressing to upstream areas in later years. Activities upstream will alter conditions downstream, but the converse (downstream activities affecting conditions upstream) is substantially less. Head dykes may have to be reconstructed or removed to account for the variation upstream, but only one head dyke would be required if starting upstream and continuing downstream. Single head dykes, under appropriate conditions, can serve several hectares of irrigated land. Note that digging of drainage canals typically initiated at the downstream end of a plot is helpful for initiating field drainage and that this process is not contrary to the above described recommendation of developing upstream areas first. Water Diversion Mitigation Measures: The canal lines and general plot layout should be traced with the assistance of trained personnel. Begin with development of most upstream areas. Place head dykes 5-10 m downstream of any road to avoid traffic, to allow for plot adjustments, and to store water. The responsibility for maintaining the dykes should be clearly indicated. Field staff should include scheduling a maintenance workday in follow up visits. The dyke and bund material should be of clay brought from outside the wetland area to stabilize the structure. 4.3 Exposure to Flood Risk Rainstorms of 75 mm/hr occur almost every year in Liberia, representing over 750 m 3 of water per hectare in the watershed. Approximately 10% of this water will enter the streams as direct runoff, depending on ground cover and soil conditions. A larger watershed above the wetland will obviously produce a proportionally larger volume of flood runoff. For typical conditions, a very rough approximation gives a maximum runoff rate of 0.06 m3/s from a 1-ha watershed. Local farmers are not always reliable sources for hydrologic information, and this estimate should be considered over casual comments. Uncontrolled flooding can cause crop failure if crops get completely submerge for long periods. Overtopping bunds, eroding canals, and depositing sediment are other undesired impacts. Without relying on computational models, one can only say that a watershed area of 70 km 2 is a preferred maximum. Some technicians prefer starting downstream to drain the most waterlogged areas first. If starting upstream, the lower areas, without drainage canals, tend to be subjected to more flooding by the evacuated flows above. The risk of starting lower in the stream, however, is having less control over larger potential volumes of water (floods) during the wet season. 4.3.1 On-Site Flooding Issues The permanently and seasonally flooded zones’ boundaries will be altered with water management. Formerly, flooding in these areas would be intermittent, and some poorly drained D:\533566517.doc 19 areas inundated well into the dry season. Within the rice paddy, flooding will be continuous during growth periods and dry otherwise. Many damages of wetland plots result from insufficient water control. Much of the neglect is tied to the common schedule of working only two days per week in the community field. By not observing and adjusting to hydrologic conditions (floods, bund breaks, etc.), greater effort must later go into reparations. Flows in the main drainage canal can be controlled somewhat. Recognize that not all of the peak flows will arrive at the outlet concurrently. However, the improved drainage system will increase peak flows. The main drainage canal must be large enough to handle extreme flow conditions. A typical drain cross-section (see section 4.1) on a 3% slope can pass approximately 0.8 m3/s of water. Then the maximum watershed area that this could accommodate is only 13 ha, based on the estimated potential flood flow noted above of 0.06 m3/s per hectare. The main irrigation canals located on either edge of the wetland serve two hydrologic purposes: sending irrigation water to the secondary canals in the dry season and draining lateral inflows during the wet season. Flows in the main irrigation canal should be adequate to transport flow from a 10-year storm event. Effects of potential alterations in upstream land use should be considered when designing drainage structures. The most common example in Liberia is a rubber plantation or other forest cover is harvested. The reduced ground cover will increase runoff volume and sediment loads that could easily damage a small irrigation system. 4.3.2 Downstream Flooding Issues The flood attenuation capacity of these swamps is limited, and therefore less valuable than, say, riverine wetlands which are often protected for that purpose. The change in flooding magnitudes downstream owing to development is difficult to predict given the many (and often counter-acting) influences. It can only be clarified what is increasing the potential for flooding and what is decreasing it (Table 3). If each of the activities could be definitively quantified, then the flood hazard downstream could be predicted. However, the complexity of the system requires that we instead monitor the cumulative impact. The maximum depth of flow during a flood can be estimated based on evidence of wetness, scaring, or debris snags. Table 3. Downstream flooding impacts from various wetland development activities. Increases Flood Potential Decreases Flood Potential Replacing natural vegetation with rice reduces infiltration. Reduced land slopes increase infiltration. Digging drainage ditches rapidly channels runoff downstream. Clearing vegetation in canals increases flow velocity. Canals, especially the outer irrigation canals, and the head dyke temporarily store water. Rice paddies temporarily store water. D:\533566517.doc 20 As a general rule, deeper water and water more open to large rivers support a greater variety and abundance of fish. With generally increased flooding downstream, those areas will improve as fish habitat. The natural vegetation will adapt to altered conditions as more hydromorphic plants populate the area. 4.3.3 Flood Mitigation Measures Restrict site selections to a maximum watershed area of 70 km2. Development should include the head of the wetland to facilitate complete water control. Instructed farmers that the main drainage canal would require periodic clearance of vegetation and side slope maintenance. Assign more permanent tenants of the areas, at least inspecting and making minor adjustments daily. Use sandbags or other sturdy material (logs) for the diversion structure’s spillway. 4.4 Water Conservation Impact There is little need for soil conservation work in the watersheds of most of Liberia’s upland valley wetlands, as erosion is low throughout much of Liberia*. Water extracted from the inlet streams is used locally and will largely return to the wetland to progress downstream. In areas with insufficient dry season flow, head dykes can serve in a limited capacity to increase infiltration rates and store water for dry season use. Less than 20% of the water impounded in a wetland enters the groundwater supply. A typical head dyke (50 cm deep on a land slope of 2%) can store only 100 m3 of water. With such limited water volume stored, the reservoir is generally used to simply extend the period of available surface water, after which time shallow wells are dug for bucket irrigation on plots of vegetables. Soils throughout most of West Africa are composed of the Basement Complex, granite and associated metamorphic rocks. The presence of high transmissivity soils is rare. Therefore, infiltration from the dykes can not be expected to be a significant component of the water budget. Additionally, the dykes have these potential disadvantages: Loss of agricultural land Negligible attenuation of floods Increased water-related disease habitat Increased operation and maintenance requirements Decreased storage volume from sedimentation * Clearly, large-scale tree harvesting is not included in this statement. D:\533566517.doc 21 Entrapment of nutrients with sediments. Typically, farmers will alter their cultivation pattern to adapt to local hydrologic conditions rather than attempt to adjust them. If dry season flows are unreliable, farmers will choose to do a crop of vegetables irrigated with water from shallow hand-dug wells. Somewhat reliable flow conditions would encourage a ratoon crop of rice that grows adequately on soil moisture. Perennial flows could be utilized for up to three rice crops. Other mitigation measures for these impacts are noted elsewhere in these guidelines. D:\533566517.doc 22 5 LAND DEVELOPMENT Although much of Liberia’s wetland area is viable for rice cultivation based solely on water availability, it is important initially to develop only the very best sites available as a means of both maximizing benefits and demonstrating the best potential benefits under favorable circumstances. The publications on swamp development by Brewer (1984) and Weedor (1997) are recommended. Information given in those sources is at times highlighted in this report, but the reader is encouraged to obtain copies for full instructions. The average plot size per worker should be considered. Under conditions of average crop yields, the average family would need approximately 0.22 ha to fulfill nutritional requirements. Given that typical plot sizes allocated (or averaged, as for communal sites) are often smaller (on the order of 0.1 ha), it must be assumed that farmers will still practice upland cultivation. Land improvement techniques use manual labor and local materials such as leveling boards. Some development will bring under utilization land that was previously unproductive to the farming community. Rehabilitation of wetland sites will increase rice yields, and provide at least one extra crop (rice or vegetables) during the dry season. Soil fertility in some areas could increase as a result of the application of appropriate inter-cropping and crop rotation. Soil aeration, augmented by water level fluctuations associated with irrigation, will also increase agricultural production. 5.1 Land Tenure and Other Social Issues Land tenure is not often an issue given the abundant amount of unused land owned by the government. The population density of Liberia is roughly estimated to be less than 22 people/mi 2 (United Nations 1999), markedly low compared to countries such as Rwanda with over 300 people/km2. Notwithstanding, land tenure could be an issue where absentee farmers return to find their land being cultivated by the community. Individually owned lands were often the first to be cultivated in the 1980s and are now the most amenable for rehabilitation. The value of these neglected lands is often only realized once others exploit them. Also, taboos exist in some areas whereby people will not use the wetlands for any purposes. Families will generally organize themselves in irrigation plots of a few families. Swamp cultivation holds less credibility for a man, being looked upon as women’s work. Consequently, men typically do only 15-20% of the manual labor required to work a rice paddy, otherwise still doing slash and burn in the uplands. Land usually fallow (but that can be cultivated hereafter with irrigation water) will become less available for grazing. Livestock used to be a more important part of the culture in Liberia, serving as food security, dietary supplement, and manure. But today, animal husbandry is not widely practiced in Liberia. Community-based management of labor and land rights can develop effective limitations to overuse of wetland areas. A key element will be to develop along with farmers an understanding D:\533566517.doc 23 of how to maintain and enhance water and soil resources, so that the qualities of wetland are increased in order to allow, and as part of, intensification strategies. The responsibilities and expectations of both the NGO and the farmers should be adequately discussed. A clearly written and understood Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) has proven useful in resolving disputes related to these issues. The MOU will be a recognized documentation of land ownership and relinquishment thereof for community work. An example MOU is given in Appendix 6. Land Tenure and other Social Issues Mitigation Measures: Clearly establish land tenure. Require land owner to be a member of the participating farming community. Write and sign an MOU with the participating community farmers. 5.2 Land Clearing and Leveling Organic matter serves as storage for plant nutrients, provides nitrogen and other nutrients for later plant growth, increases the soil’s water holding capacity, and improves the soil structure for cultivation. Initial land clearing often invites burning, since that is the popular practice in the uplands. Weeds pulled during the rice-growing phase should be submerged into the soil in the plot, rather than removed from the plot as these will decompose and restore soil fertility. Rice stalks are often left on the fields, although some farmers effectively till them into the soil as compost. This process enhances pest control (burns larvae) and adds nitrogen. Weeds grow rapidly during the dry season fallow period, so land exposed to surface runoff is typically not denuded before planting. Rather, fields are weeded only after being inundated. In areas with extensive peat (partially decomposed plant material) deposits, large (up to 10m diameter) zones could become pools. The peat decomposes more rapidly from water management effects, producing methane and sulfur gases that literally lift it up to float away. Leveling performed by manual labor with no surveying equipment is commonly not adequate. The consequences are rat and groundhog entry, high/dry spots, and waterlogging. The recommended technique is to flood the plots after initial clearing and leveling, to use the water level as a guide to further refinement. Where leveling is not done adequately, it is important that extension workers advise farmers and schedule maintenance after harvesting. Land slopes within the wetland vary significantly. Recommended maximum slopes of the canals depend on the soil conditions as well as the flow velocity but generally vary from 2-5%. Where wetlands are gently sloped and have a cover of clay, erosion from irrigation runoff would generally be insignificant. Greater slopes will require more effort for leveling and providing drop structures. Land leveling within blocks should be accomplished by the landowners with advice from irrigation specialists. Poor leveling could cause excessive pooling of stagnant water and soil erosion. Construction work should commence after the December harvesting period, and continue through May when early rains will moisten the soil. Final smoothing and leveling can then be D:\533566517.doc 24 conducted with less haste. Land leveling need not be rushed and may take 2-3 years depending on the farmer’s interest. The most labor-intensive activity in developing wetlands is the initial clearing. Large trees and sturdy shrubs able to withstand the arduous environmental conditions are difficult to remove. Consequently, and in conjunction with the fact that many suitable wetland sites have already been minimally cleared for traditional rice cultivation (broadcasting seeds), clearing of virgin forest is only reluctantly carried out. Where debris and stumps must be removed, selective burning is common. Land Clearing and Leveling Mitigation Measures: Commence construction work after the December harvesting period. Encourage only selective burning. Leave the residue from land clearing on (or tilled into) the fields to decompose. Where large depressions or unsuitable soil conditions are encountered, import soil from outside the swamp. Do not extensively excavate bund material from the paddies. Encourage progressive improvements in field leveling. Use termite mound clay, where available, for sealing porous bunds. Practice minimum tillage of the brushed perimeter vegetation. 5.3 Erosion Where plots are gently sloped (2-5%) and have a cover of clay, erosion from irrigation runoff is typically minimal. Canals and bunds containing them can erode excessively, causing undermining that ultimately leads to failure of the bunds and draining of the wetland. Care must be taken to ensure that curves are as gentle as possible to avoid erosion and even overtopping. Erosion could be enhanced if the natural thalwag is underlain by sand deposits (see section 4.1). Vegetable crops can be planted along the fringes of inundated rice paddies and canals to reduce soil erosion, with the additional benefit of utilizing available soil moisture. Trees can be planted on steep slopes along the perimeter of wetlands to minimize erosion there. Erosion Mitigation Measures: Decrease standard plot sizes in areas of steeper slopes. Plant vegetable crops along the fringes of inundated rice paddies and canals to reduce soil erosion and utilize available soil moisture. Design gentle curves in drainage canals. Irrigate plots individually from the canal and through plots. Practice minimum tillage of the brushed perimeter vegetation. Encourage tree planting on the slopes of wetland perimeters. D:\533566517.doc 25 5.4 Soil and Rice Productivity Loss Factors Generally, the lowland valleys are soil deposition zones for alluvium, material eroded from the watershed. As the land slope decreases and floodplain widens, stream flow velocities decrease. The decreased turbulence can not maintain the high sediment load and deposits it there. This soil is relatively fertile, having been topsoil upstream. Soil fertility in some areas could increase as a result of the application of appropriate intercropping and appropriate crop rotation. Soil aeration, augmented by water level fluctuations associated with irrigation, will also increase agricultural production. Decomposition in wetlands is slower in the anaerobic standing water than it is under dry conditions. Nutrient cycling is enhanced by hydrology-mediated inputs, and nutrients are often more bioavailable with reduced conditions in the wetland substrates. Productivity could be negatively impacted by these factors: Iron toxicity Excess denitrification Poor soil zones Neglect of overly ambitious plot sizes. Iron toxicity is often problematic in Liberia. Iron oxide can coat plant roots, immobilize phosphorus, and be excessively absorbed by the plants. Iron toxicity shows a characteristic brown discoloration of the leaves starting with the older leaves. Flushing iron from soils would take ~15 years, so it is generally recommended to use iron-tolerant rice varieties and reduce Fe through better water movement. Nitrogen is often the limiting nutrient in flooded soils. Nitrate-nitrogen is the first soil nutrient to be reduced. The denitrification reaction produces nitrogen gas, which escapes and is lost from the soil. The reaction is particularly enhanced by altering oxidizing and reducing conditions associated with wetting and drying (respectively) cycles. But if intense reduction occurs (i.e. maintained stagnant water), hydrogen sulfide can be produced. The formation of this compound also releases ferrous iron. Both compounds are toxic to rice. The optimal water condition thus maintains water levels in the paddies with low flow periodically or continuously drained off. Very sandy soils have high percolation rates. The increased rate of water movement through the root zone will tend to leach nutrients from the soil. An additional problem with sand is its poor stability, restricting its use as bund material. The coarse soil matrix makes it more troublesome to bury weeds and stubble that would add nutrients. Over-extending plot sizes can reduce the potential value of work effort if cultural practices such as de-weeding and maintenance are neglected. The situation develops when too much land is initially developed or when farmer participation decreases. Soils can be sampled with augers to examine the subsurface soil profile. A visual inspection of the topsoil and vegetative cover can even yield some meaningful information. CRS catalogues soil profiles from auger samples and puts the information on a map overlay of the developed area. Rather than cultivating even poor soil zones within a site’s boundary, the unsuitable areas could be segregated by bunds and used for refuse dumping (composting) or material for bunds. D:\533566517.doc 26 Alternatively, planting of short duration upland rice varieties, gardening or fruit trees can be attempted in these zones. It is also suggested to use reliable seed varieties initially and then adjust in subsequent years based on the observed problems. Soil Productivity Loss Mitigation Measures: Use iron-resistant rice varieties where necessary. Encourage soil amendment practices. Control water stagnation period. Take soil samples before making final site decisions. Instruct farmers in proper water management in paddies. Encourage local fertilizer (manure, compost) production and use where necessary. Restrict individual plot size with planned extensions later. Use reliable seed varieties initially. Other factors reducing crop yields discussed next are: Poor water control Poor weed control Excessive turnaround time. 5.4.1 Poor Water Control Rice evolved as a wetland species, and although varieties suited to upland conditions have developed, it remains more sensitive to water deficiency than most other crops. Critical factors in rice productivity are the supply of water to the soil from rain, reservoir or ground water, and the ability of the soil to retain water. Landscape position largely determines the way in which water can be supplied to the soil, and soil texture and drainage characteristics, the extent to which it is retained. Although rice will grow as an upland crop, yields are almost always considerably less than when it is grown under flooded conditions. Most experimental studies have shown that it makes little difference to rice yields whether the soil is flooded 1 cm or 10 cm deep, but even a few days when the soil is not covered by water can cause a significant loss of yield (Wielchman and Sen, 1978). Excessive water can also be a serious problem as it can damage bunds and canals (see section 4.3). Thus, control of water deficits and excess is a major biophysical factor in sustaining rice yields. Water use and moisture stress effects vary at different growth stages of rice. Moisture stress reduces crop yields most when it occurs during the critical growth stages. Water is most required during the reproductive stage – 20 days before heading to 10 days after heading. Lack of sufficient water during this period causes high sterility. Water requirement at transplanting to early vegetative phase is low but the field should be kept saturated to a few centimeters of D:\533566517.doc 27 standing water to enhance tillering. The field is kept flooded 5-10 cm during the late vegetative phase (from panicle primordia development) through heading. The level of water is reduced to saturation after heading to promote rapid ripening and to facilitate harvesting. 5.4.2 Poor Weed Control Weeds are often called “plants out of place”. Crops and weeds compete for the same resources – nutrients, water, space and light. Competition begins when crop and weeds grow in close proximity and the supply of any necessary growth factor falls below the demands of both. Competition from weeds is dependent on such factors as the environment, the crop/variety grown and its density, the stages of the crop, weed density, and stage of weed growth. Flooded or moist soils favor an abundant supply of viable weed seeds in rice fields. Rice yield losses caused by weeds in flooded paddies vary with the time of weed infestation, soil fertility, rice varietal type and planting method. Competition from weeds during the early growth stages (first 30 days after planting) of the rice crop is more serious than no competition in the early growth stages followed by competition during the later growth stages. Short stature and low tillering varieties are more prone to high yield loss than tall and high tillering varieties. Weed competition is less in closely planted plots than where rice is planted at wide spacing. Flooded the fields after crop establishment gives significant control over the weeds. Weed interference causes: Reduction in rice yield and quality Intensification of the problem of pests and diseases by harboring and serving as habitat Reduction of efficiency of certain cultural practices Reduction of efficiency of irrigation. The primary objective of all weed control practices is to reduce the undesirable effect of weeds to a minimum such that their presence will not cause any adverse effect on the crop with which they are growing in association. No single method has been found to be totally effective, but a combination of two or more methods. These include: Proper and thorough land preparation Planting of weed-free seeds Clearing of bunds and canals by slashing Proper plant spacing (close) and density Use of high tillering tall rice varieties Maintenance of flood levels 5-15 cm after transplanting for most parts of the crop cycle Observing crop rotation by planting vegetables after two successive rice crops. More information on weed management is provided in Chapter 7. D:\533566517.doc 28 5.4.3 Excessive Turnaround Time The turnaround time, which is the time interval between harvesting of one crop and planting of the next in a cropping sequence, is important in all two-crop rice cultures. A delay in the turnaround time can be a serious impediment to intensification in the rice-based cropping system. Long turnaround time results in crops being planted too late into the season of dependable water supply. Turnaround time ranges from 5 to 37 days, but 21 days was found to be most suitable (Roxas et al., 1978). The turnaround time can be influenced by the method of second crop establishment. This method was found to average 16 days for wet-seeded rice and 26 days for transplanted fields. Any increase in the intensity of tillage causes more total tillage time for establishing a second crop. Turnaround time mitigation measures: Plant short duration varieties. Use pre-germinated seeds in direct-seed rice. Minimize tillage in the establishment of a second crop. D:\533566517.doc 29 6 ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH Swamps are generally recognized by Liberians as an unhealthy place to work. As is the case in with most rivers and streams, surface waters throughout Liberia are not potable. The only potable water sources available in most rural settings are open, hand-dug wells. However, it is common for people to make use of whatever water is available when needed. Wetlands, being often in close proximity to housing and previously undeveloped, have often been used as the de facto trash dump. Indeed, even discarded, buried medical waste has been found by children working barefoot to develop some wetlands in Liberia. Additionally, urban runoff carrying human excrement poses other obvious health hazards. In many areas, farmers working in wetlands will defecate “in the bush” adjacent to their plots. Communal latrines have not been effective in Liberia since it is culturally improper to be seen entering one and few individuals would ever take personal responsibility for maintaining its proper sanitary conditions. Most rural communities in Liberia are not served by any health centers. Consequently, traditional medicines are still popular treatments for illness. Prolonged flooding and cleared lowland areas associated with the cultivation of paddy rice could increase incidences of water-related diseases. Disease transmission could become more prevalent if people are in greater contact with and drinking from these surface water resources. Head dykes, for example, may be a source of disease as people bathe in the reservoirs and children flush out fish by walking through them. Common diarrhea diseases are associated with consumption of stream, canal, and drainage water. Few households have toilet facilities. The Ministry of Health and Social Welfare (MOH&SW) stated that wetland-related illnesses in Liberia included Schistosomiasis, malaria, and river blindness. Leeches and red ants (stinging) were noted to be major nuisances. The major illnesses noted by the Institute of Biomedical Research were Schistosomiasis and malaria, although no data is available for supporting either of these statements. No cases of river blindness were mentioned by any farmers during site visits by the evaluation team. Disease transmission through domesticated animal vectors is not noteworthy in Liberia owing to both limited numbers of animals and sound mitigation practices of containment in pens. Most methods to avoid negative effects of irrigation on human health involve changing human behavior. Most development programs can readily incorporate a health and sanitation component for complimentary activities. Most farmers, for example, simply do not know that irrigation water may be a contaminated reservoir for transmittable diseases. Encouraging proper methods to dispose of sewage can also reduce the spread of disease. General Environmental Health Mitigation Measures: Contract LIBR to do baseline and impact surveys of illnesses related to wetland development. Incorporate health education in training programs. D:\533566517.doc 30 Avoid development of sites known to be waste dumps or immediately downstream of housing. Encourage use of protective clothing where contact transmitted diseases/nuisances are prevalent. Conduct research on the natural enemies of snails and mosquitoes to identify potential predators such as ducks and geese. Utilize health guidelines by Tiffen (1991) and Birley (1991) throughout the project cycle. 6.1 Malaria Malaria cases are reported throughout the year in Liberia. Yet mosquito breeding in swamps was not positively correlated with increased incidences of malaria in a recent study conducted in conjunction with the MOA. Furthermore, interviewees during the field visits indicated a perception of reduced mosquito populations since development of their wetlands. Increased water velocities, managed weed growth and fish populations should serve to reduce habitat for mosquitoes (the vector for malaria) which prefers confined, stagnant waters. Malaria Mitigation Measures: Raise fish in the rice paddies that will eat mosquito larvae. Promote de-weeding and brushing of perimeter vegetation. Reduce stagnant water zones in managed area. 6.2 Schistosomiasis Schistosomiasis is endemic throughout Liberia since the regional environment is a favorable habitat for aquatic snails. Its prevalence is found to increase with swamp rice production. Both urine and feces transmit Schistosomiasis parasites in Liberia. Modern treatment (Praziquantel) is very effective and inexpensive. Education programs have also been effective in Liberia. However, preventing contraction does not prevent contamination if the snails carrying Schistosomiasis parasites are removed from plots but inflow water is still contaminated upstream. The life cycle of the parasite depends on human hosts, such that it could be eliminated from an area if contamination ceased. Boots could be provided to each worker, although project workers could not enforce their use and maintenance. Boots are also troublesome after transplanting owing to conditions of deep, sucking mud. Upper body protection would also be required to reduce transmission through exposed arms and hands. The cost of boots would also be considerable. Schistosomiasis Mitigation Measures: Include health education in farmer training programs. Encourage latrine construction (and use) near developed swamps. D:\533566517.doc 31 Conduct mass distribution of the curative treatment (Praziquantel). 6.3 Nuisances Leeches and red ants (stinging) were noted as worrisome for farmers in many areas. Leeches are annelids, in the same the group of animals as earthworms. They are parasites of fish. The bucal cavity consists of suckers used to suck the blood of its host. A single blood meal taken in by a leech can last for a long period of time (1-2 months). Although they are not major vectors of diseases to humans, by their blood-sucking habit they impose serious problems as a nuisance to farmers in the paddy fields of rice-based ecosystems. Depending on the level of population build-up, farmers are sometimes tempted to abandon their rice paddies. Lindane and carbofuran (furadan) are effective chemical control reageants. But their subsistence within the soil lattice and the environment poses serious residual problems. Stinging ants exist on the fringes of paddy fields. They belong to a group of social insects of the family formicidae. Some species contain high levels of formic acid in a sac located in their abdomen. When they bite the abdomen is raised and a significant content of the sac is oozed into the wound inflicted, thereby leading to an acute burning sensation. These bites are quite irritating to their victims. Groups of these insects are found on the bunds or periphery of the paddy fields in burrows. Whenever these burrows are opened or otherwise disturbed the agitated ants come out en masse to defend their nest. In most instances when such situations arise, the cultivators are stung, thereby causing acute and irritating pains on the feet or wherever the bite occurs. Even though there is no evidence to prove that they are vectors for any known diseases, their potent sting is uncomfortable or even unbearable. Depending upon how allergic or sensitive the victim is, a repeated stinging exacerbates the situation much further, which in some cases leads to a rise in body temperature and chill. The ants are not adapted to water, and scattering the burrow dirt into the water will eliminate them. As noted in section 6.2, the use of boots may be problematic. Nuisance Mitigation Measures: Remove un-submerged debris and dirt bounds from paddy areas. Encourage the prevention of access to skin – wearing jeans, hip boots, or plastic sheets; smearing exposed skin with lime. Use controlled heat therapy (burn plant debris) to kill off ants in their burrows. Control water appropriately by draining to immobilize leeches or eliminate ants. 6.4 Hazardous Waste Chemical waste (by-product) dumped in valleys as a result of iron ore mining is a potential source of chemical waste to which farmers could be exposed in wetlands. This is particularly prevalent in Bong County’s Bong Mines area. Chemicals including limestone, ammonium nitrate and bentamone cause blisters. Suggested mitigation measures for projects in such contaminated areas is to provide skin protection (boots) or abandon the site. D:\533566517.doc 32 7 BIODIVERSITY AND ECOLOGY Wetlands are a major feature of the landscape in almost all parts of the world. They are unique because of their hydrologic conditions and their role as ecotones between terrestrial and aquatic systems. Wetlands are sometimes described as “the kidneys of the landscape” because of the function that they perform in hydrologic and chemical cycles and because they function as downstream receivers of wastes from natural and human sources. They cleanse polluted waters, prevent flood, protect shorelines, and recharge groundwater aquifers. Wetlands have also been called “biological supermarkets” for the extensive food chain and rich biodiversity they support. They provide unique habitats for a wide variety of flora and fauna. Now that we have become concerned about the health of our entire planet, wetlands are being discribed by some as carbon dioxide sinks and the stabilizers of the climate on a global scale. Wetlands are an enigma to scientists. They are difficult to precisely define. Not only because of their great geographical extent, but also because of the wide variety of hydrologic conditions in which they are found. They are found at the interface of terrestrial ecosystems, such as upland forests and grasslands, and aquatic systems such as deep lakes and oceans making them different from each other. Because of their nature in combining attributes of both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems, but are neither, they fall between the cracks of the scientific disciplines of terrestrial and aquatic ecology. These unique characteristics of wetlands provide a common ground for study that is neither terrestrial nor aquatic ecology. They provide opportunities for testing “universal” ecological theories and principles involving succession and energy flow, as well as an excellent laboratory for study of principles related to transition zones, ecological interfaces and ecotones. This niche in the landscape leads to high biodiversity in wetlands which “borrow” species from both terrestrial and aquatic systems. Rehabilitation of the wetland creates an opportunity to produce high value vegetables for the fresh market. These crops encourage pest control that may result in unsafe use of pesticides and contamination of surface and groundwater. Although no pesticides and no inorganic fertilizers are being considered in project activities, it must still be considered if their use will be encouraged by the increased agricultural activity. The independent use of fertilizers and pesticides will prejudice certain aquatic animals and their predators. Present rates of fertilizer and pesticide use in Liberia do not appear to have significantly impacted native wildlife and plants. Given the generally conservative use of chemical applications, small-scale development activities are expected to have little further impact on the wild animal and plant populations. Environmental impacts could include a potential increase in local biodiversity. Biodiversity of certain animal families such as insects could increase, and reports of increased dragonflies and fish are common. D:\533566517.doc 33 7.1 Disruption of Native Flora and Fauna With the flora and fauna of the Liberian wetlands, there is a range of vegetation from primary (untouched) to secondary and tertiary (previously cultivated), consisting of rafia palms, oil palms, aboreal plants, ferns, hard and soft wood, herbaceous plants, sedges, grasses, aquatic grasses and algae. The fauna is abundant in a wide range of wildlife species: duiker, elk, baboons, monkeys, squirrels, rodents, birds, bats, snakes, crabs, catfish, crayfish, toads, spring frogs, annelids (earthworms), insects, nematodes, and others. The wetland fauna serve as a food source; herbs serve as medication; trees provide timber and building materials and valuable products. More significantly, the interaction of the plant, animal and fish species in that habitat provides an ecological balance which is of local, national, and global importance. Therefore, any modification, disturbance, or degradation creating an imbalance may lead to extinction of some species. Therefore, environmental factors leading to a vulnerable ecosystem must be examined to provide mitigation measures ensuring sustainability and an ecological balance between production and nature conservation. There will likely be an increase in bird populations and species diversity resulting from wetland agricultural. Birds often obtain nesting material from wetland grasses. The loss of suitable material in rice paddies is inconsequential given the distances that birds can travel for collecting nesting material compared to the scale of the developed areas. Furthermore, rice is a preferred food for birds, as farmers can attest, and does not usually replace a unique food source. Irrigation activities could disturb fish-breeding habitats in mangroves. Irrigation can reduce the inflow of fresh water that is necessary to ensure a sufficient supply of nutrients and stability of the substrate into mangrove areas. Drainage of coastal wetlands for irrigation has also reduced considerably the number of avian species in some African countries. But given the limited scale of the rural development-level irrigation schemes compared to mangrove and bird nesting area needs, the potential effects on these areas are of no measurable consequence. Disruption of native flora and fauna mitigation measures: Given the complex nature of the rainforest environment, and the wetland environment in particular, a baseline study of the flora and fauna should be conducted in each area. Particular emphasis should be placed on animals that depend on large tracts of undeveloped wetlands (larger herbivores, baboons, etc.), aquatic life needing migratory passages (fish), and any protected species (see Appendix 7). Trap setting should be discouraged. Instead, fencing of farm periphery should be encouraged to keep away animals feeding on farm crops (see section 7.5). 7.2 Integrated Natural Systems Fish ponds upstream can be used conjunctively such that drained detritus-rich water from the ponds is directed into the paddies as fertilizer. The contained fish can be fed termites, cassava leaves, and other kitchen compost. Pigs have been integrated into farming systems in Buchanan. The pigs are fed kitchen and farm compost. Contained in pens, their excrement is converted into fertilizer for crops. D:\533566517.doc 34 Crayfish production has been combined with some rice farmers elsewhere in the world. The crawfish can be collected when they emerge from their burrows after fields are drained and harvested, foraging on the remaining vegetation. 7.3 Fertilizer Use Farmers do not depend on fertilizer and pesticides due to high costs and lack of transport. The fact that farmers typically apply less fertilizer than recommended leads to the assumption that increased nutrient fluxes into drainage water will be minimal. To argue against growth of fertilizer use in developing countries by pointing to its direct adverse environmental impacts in developed countries is both hasty and shortsighted. In fact, some of the considerations suggest that the positive contributions of chemical fertilizer in arresting environmental degradation could be greater than its direct negative effects. Fertilizer could also be an important tool in combating soil erosion, a dominant elements in environmental degradation. In areas where the applied fertilizers do dissolve in rainfall runoff, plants and organisms in the downstream water bodies may proliferate. This process of nutrient enrichment leading to higher productivity, called eutrophication, has both positive and negative impacts. Increased weed growth leads to stagnant water but also increases organism growth. Fisheries may benefit from the eroded, fertilized soils. Also, many common weeds can be harvested as animal feed. Fertilizer Use Mitigation Measures: Develop guidelines and farmer training for proper fertilizer uses where applicable. Develop guidelines and training for farmers in the practice of composting. Conduct training programs on the production of green manure crops as a source of plant nutrients (for example, Azolla). 7.4 Pesticide Use Pesticide use has numerous potential negative environmental impacts, including poisoning, destruction of non-target organisms, disruption of natural control, and development of resistant organisms. Poisoning of pest animals is a further detriment when the carcasses are consumed. In spite of the many hazards of pesticide use, the Government of Liberia has yet to develop legislation related to the importation, distribution, or use of such chemicals. Training in irrigation cultivation should include lessons on appropriate pesticide use in wetland environments. Integrated pest management (IPM) could be considered as a possible alternative (see section 7.5), perhaps researched in collaboration with CARI. Successful IPM programs have been developed for various pests of food crops in several developing countries, such as for rice pests in Indonesia. Pesticide Use Mitigation Measures: Develop guidelines and farmer training for proper pesticide uses where applicable. D:\533566517.doc 35 Study opportunities for IPM where potentially applicable. Study biotypes of pest population. Breed crops for resistance. Promote pest scouting. Determine epidemiology of pests/diseases. Identify species and possible biocontrol. Understand density-dependent and density-independent factors in pest ecology. 7.5 Pest Management The environmental implications associated with the use of agro-chemicals has led to the development of a sound and safe approach which takes into account a balance of compatibility among all measures involved in pest control. This is a scheme that uses a variety of technologies compatible in a single pest management system. In an integrated management system, realistic economic injury levels are used to determine the need for control actions. Pesticides are used when they can be justified based on economics and ecology. All precautions are taken to preserve natural enemies of the pests. The ultimate objective involved is to produce optimum crop yield at minimum cost, taking into consideration ecological and socioeconomic constraints under a given agro-ecosystem. The principles are the same for insects, diseases, weeds, and other crop pests. The principles involved include: Identifying pests Defining the agro-economic system – knowledge of interrelationships between pests and crops gives understanding of mobility of key pests in the agro-ecosystem Developing the management strategy – coordinated use of multiple tactics in a single integrated system aimed at holding pest numbers and damages to tolerable levels Establishing economic injury thresholds – crop loss determination based upon pest intensity in terms of quantity and quality of crop and its value Monitoring and using predictive techniques – monitoring pest incidences and weather conditions helps to reduce costs of control Developing a descriptive and predictive model Overcoming the socio-economic constraints to the establishment of the IPM Selecting mechanisms that assure group planning and action by all farmers within project areas Implementing training and extension programs in IPM at all levels (TA, extension agents and farmers) Creating an import delivery system – for timely execution of plans. D:\533566517.doc 36 Indications seem to suggest that with the establishment of developed wetland paddies with good soil and water management schemes there could be an upsurge in the number of dragonflies, frogs, bats, and birds. Considering that the habitats of these organisms were disrupted, their return into a semi-homogeneous ecosystem is a clear indication of biodiversity. These organisms will occupy special niches within the agro-ecosystem. Appropriate pest management measures: The establishment of IPM approaches allows for the tolerance of certain pest numbers as prey for natural predators/parasites. Brushing vegetation on bunds will discourage rats and groundhogs from entering rice paddies. Good water management in paddy fields controls pests such as caseworms, rats, and weeds. Alternatives to agro-chemical use in rice-based agro-ecosystems: Rice grows in diverse soils and climates but it is best adapted to a warm, humid environment. In that environment where continuous cropping is practiced, there are overlapping generations of a complex population of pests and disease vectors. Pesticides are toxic; if not, their use in pest management would not be possible in the control of pest numbers. The non-judicious use of such chemicals have far-reaching negative repercussions in the environment. To ameliorate their effects in the environment, alternative practices and principles are herein advanced for adoption in permanent wetland cultivation to ensure environmental stability and enhance biodiversity: Accurate assessment of biotype variability – biotypes vary not only in their ability to attack different varieties in their susceptibility to control by pesticides. It is therefore important to study races, strains, and biotypes of rice insect pests and vectors of rice diseases. Biological control of rice pests and diseases – this is a natural control device which depends on parasites, predators and pathogens that kill pest species and vectors of rice diseases. Conservation of existing natural enemies, if not their manipulation, is called for in rice pest management. In the tropics breeding for resistant rice varieties is perhaps the only realistic solution to the fungus, virus and bacteria disease problems. By accumulating genes with a broad spectrum of resistance into a variety, more stable resistant varieties may be developed. Optimum management of rice diseases requires knowledge of the epidemiology of the disease. Rice diseases, irrespective of cause are controlled by appropriate measures taken before the disease develops, not after an outbreak. Cultural control – cultural practices such as management of fertility, weeds, water, crop residue, plant spacing and cropping pattern greatly affect pests and disease occurrence in rice. These measures have no deleterious environmental effects. Integrated pest management (IPM) – uses a variety of technologies compatible in a single pest management system. Rodent control in rice – keeping the bunds free from weeds, fencing and making fields, flooding fields, and making farm house and storage areas rat-proof. D:\533566517.doc 37 Bird control – various sound-making devices are used (pebbles in tin cans attached to ropes, gas-operated cannons). Snails in rice fields – control measures include hand-picking, and knowing which stage of the rice the attack is mounted and accurate assessment of population dynamics. 7.6 Encroaching on Protected Areas Sapo National Park is the only place yet listed as a UN Protected Area. However, there are other areas (three parks and four nature reserves) identified (Government of Liberia 1983). A national Ramsar Site (ecologically important wetland designate for protection) has not been designated. The internationally acclaimed recommendation is intended, as with the IEE, to get leaders thinking about setting aside land for other things besides human exploitation. Yet wetland policy, in spite of the overwhelming ecological importance of these systems throughout Liberia, has not been developed. Encroaching on Protected Areas Mitigation Measures: Project activities should avoid protected areas and land that drains into them. Authorities should enforce legislation to curb encroachment. Monitor protected areas to ensure that no trespassing is allowed. A framework of guidelines should be put into place and a number of national awareness workshops should be conducted to sensitize the public. (To be done by the Environmental Commission.) D:\533566517.doc 38 8 MONITORING AND EVALUATING Projects are monitored to confirm that a project investment is resulting in the anticipated benefits and to decide whether there are other unintended effects. In evaluating a project, managers must have data reflecting the conditions at the start of the project and on changes, anticipated and unanticipated, that have resulted from project activities. The overall rationale for monitoring and evaluation is to assure that performance data is collected and used to monitor regularly, analyze, review, and assess performance to: Inform management decisions aimed at achieving intermediate results and strategic objectives, and overall objectives. Meet reporting and accountability requirements at all levels. Enhance organizational learning Evaluate whether the farmers are properly managing water themselves or are in need of more extension services. The World Wildlife Fund suggests the following guidelines for developing a participatory monitoring and evaluation system: Activities should be implemented by a team of people, including project staff and representatives of interest groups who are involved in the activity. Information should be gathered that is used directly for testing the project’s hypotheses and achieving its objectives. Information should be gathered routinely as part of project implementation. Community members (e.g., extension workers, guides, and scouts) should be trained and compensated to collect and analyze data. The suggested monitoring program is given in Appendix 8. The program sections are divided into the same categories as have been used in chapters 4-7 of these guidelines. The monitoring should be conducted annually, most appropriately at the end of the wet season. Environmental trends can be evaluated by comparing data collected in consecutive years. This program is for monitoring the development of both individually owned and managed wetlands. Since the chosen monitors would generally be the same people who conducted the work, it is not suggested to monitor more frequently indicators that show whether the work was done correctly. Rather, the monitoring program should provide information to address the impacts of the activities and their mitigation measures. 8.1 Baseline Data The following information should be collected for each site to be developed: - outstanding land tenure disputes - water management practices D:\533566517.doc 39 - community participation in other development activities - present land use on project site (both wet and dry season) - crop yields on project site, if presently used - vegetation density in project site (scale of 1-10 with 1 for cleared land and 10 for dense forest cover) - flow characteristics of streams on site (month when stream dries, maximum flood depth/areal extent/frequency) - dry season water table depth - downstream flooding frequency - upstream land use - % farmers using protective clothing (jeans, boots, etc.) - Prevalence of malaria, Schistosomiasis, and other water-related diseases - Existence of nuisances (leeches, stinging ants) - Presence and species composition of fish in natural stream (upstream and downstream of project site) - Pest problems (pest type and extent of land coverage) - Lowland crop diseases - Indicated use of pesticides 8.2 Equipment Needs No highly technical equipment is necessary in this monitoring program. But rather data collected will be based on interviews and visual observations. From this information, a formative evaluation of the project can take place annually, with a view to improve the program on the basis of lessons learned. The equipment suggested for purchase and use with the monitoring program are the following: 1. Rain gauge – one per field office, cost ~US$10 ea., to measure total daily rainfall. 2. Thermometer – one per field office, cost ~US$5 ea., to measure average daily air temperature. 3. Tape measurer – one per field office, cost ~US$60 ea., to measure fixed structures and lengths of degradation. 4. Auger – one per field office, cost ~$200 ea., for sampling subsoil conditions (Note that if several are needed, one could be purchased and others replicated locally.) D:\533566517.doc 40 APPENDIX 1. EVALUATION TEAM MEMBERS AND KEY CONTACTS The evaluation team of environmental experts involved with this report was comprised of the following individuals: Frank Brockman – Agricultural Technical Advisor, CRS Southern Africa Region office, email: fbrockm@catholicrelief.org Stephen McCord – Hydrology Consultant, CRS-Malawi, email: sam@malawi.net Essa Drammeh – Rice Agronomist, National Agricultural Research Institute, The Gambia, email: nari@qanet.gm Andrew Paye – Director, Central Agricultural Research Institute, Liberia (contact through UNDP/FAO office fax 231-226-104) With environmental assessment assistance from: William Draper, Environmentalist/ Conservationist, Society for the Conservation of Nature of Liberia, Monrovia. The key contacts for the organizations that funded this evaluation are the following: CRS: Mulbah Jackollie and Augustine S. Lavelleh WVL: Dr. Sizi Morris and David D. Wounuah LWF/WS: James Yarsiah and Jarsiah Weedor D:\533566517.doc 41 APPENDIX 2. REFERENCE SOURCES Altieri, Miguel. 1988. Environmentally Sound Small-Scale Agricultural Projects. Revised edition. Arlington, Virginia: CODEL and VITA. Birley, M. H. (1991). “Guidelines for forecasting the vector-borne disease implications of water resources development.” PEEM Guidelines Series 2. Available from Tom Remington (CRS East Africa Region). Brewer, B. (1984). Appendix 1. Swamp Development Manual for IEADP. Available at the European Commission in Liberia, Monrovia office. De Datta, S. K. (1981). Principles and Practices of Rice Production. John Wiley and sons, NY, Chichester, Brisbane, Toronto, Singapore. 618 pp. Republic of Liberia (1983). Planning and Development Atlas. By the Ministry of Planning and Economic Affairs in conjunction with GTZ, 67 pp. Greenland, D.J. (1997). The Sustainability of Rice Farming. CAB International, Wellingford, Oxon, Ox108DE. Uk. 273 pp. Hekstra, P., and W. Andriesse (19??). Phase I: The Inventory, Volume II: The Physical Aspects. Wetland Utilization Research Project, West Africa. Ingram, K.T. (1995). Rainfed Lowland Rice Agricultural Research for High Risk Environents. International Rice Research Institute, P.O.Box 933, Manila 1099, Philippines. Mitsch, W.J. and J.G. Gosselink (1993). Wetlands, Second Edition. Van Norstrand Reinhold, New York. 722 pp. Oosterbaan, R.J., H.A. Gunneweg, and A. Huizing (198). “Water control for rice cultivation in small valleys of West Africa.” Annual Report of the ILRI. Tiffen, M. (1991). “Guidelines for the incorporation of health safeguards into irrigation projects through intersectoral cooperation.” PEEM Guidelines Series 1. Available from Tom Remington (CRS East Africa Region). United Nations (1999). Liberia UN System Common Country Assessment, Volume 1. 102 pp. Weedor, R.J. (1997). Swamp Development and Rice Cultivation. N’zerekole, Guinee. 14 pp. (Available at LWF/WS). World Bank (1991). “Environmental Assessment Sourcebook. Volume II Sectoral Guidelines.” WB Technical Paper No. 140. Available at the CRS-Kigali office in the Internal Environmental Review binder or from the World Bank. D:\533566517.doc 42 APPENDIX 3. ORGANIZATIONS CONSULTED NATIONAL GOVERNMENT Ministry of Agriculture (MOA); contacted Roland Massaquoi, Minister; Joseph Musah, Agric. Economist; Dr. James Kazolu, Deputy Minister for Extension, Rural Development and Research. Ministry of Planning and Economic Affairs (MPEA); contacted Mr Melville Harris, Assistant Minister; Francis Edwin, Project Analyst. Liberia Forest Development Authority (LFDA); contacted Mr Theopholus Freeman. Ministry of Rural Development (MRD); contacted Mr Sam Mann, Deputy Minister of Planning and Programming and Mr. George Yarngo, Director, National Rural water Program. Ministry of Health and Social Welfare (MOH&SW); contacted Dr. Omarley Yeabah and Dr. Moses Duopo Liberian Institute of Biomedical Research (LIBR); contacted Dr. Nuahn T. Marbiah, Director. FOREIGN GOVERNMENT UNOPS; contacted Mr. Tuah, Senior Agronomist and J. Gbieh-bo, Sr. Program Assistant. FAO; contacted Mr. Kasa Kimoto, Resident Representative and Mr. William Massaquoi, Agric. Officer. USAID; contacted Mrs Minnie Wright and Mr MacArthur Paye-Bayee European Commission (EC); contacted Mr Brewer GTZ; contacted Alan Gobeh, Project Supervisor, Ferdinard Takatsch, Program Manager and Angela Schwat, Program Assistant. NGOs Society for the Conservation of Nature in Liberia (SCNL); contacted Mr. William Draper, Project Officer Environmental Foundation for Africa (EFA); unable to contact D:\533566517.doc 43 APPENDIX 4. MITIGATION MEASURES FOR ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS OF WETLAND DEVELOPMENT Project Activity Potential Negative Impacts Mitigation Measures WATER MANAGEMENT Install drainage canal Canal erosion Align canal sections with natural stream course; trace canal with the assistance of trained personnel Land drying Observe minimum watershed area of 1 km2 for every 2-5 ha drained; use composite drain cross section; plot site’s hydroperiod for planning purposes Downstream flooding Extend drainage canal further downstream Divert streamflow Insufficient water control Site head dyke away from obstructions; begin work in upstream reaches first; clarify responsibility for maintenance/adjustment, use stable materials in construction Exposure to flood risk Failure of irrigation system and crop Consider hydrology in design of drainage canals (maximum watershed area); clarify responsibility for monitoring; begin work in upstream reaches first; promote permanent tenants; use sturdy materials for diversion spillway LAND DEVELOPMENT Land distribution and other social issues Inequitable allocation of plots Allocation of plots is responsibility of community; require signing of MOU Land tenure disputes Require signing of MOU Clear and level land Uncontrolled burning Encourage selective burning and composting of residue, minimize excavations Pool formation from peat decomposition, improper leveling Commence construction work early; do not extensively excavate bund material from the paddies; encourage progressive improvements to land Soil erosion Minimize plot sizes in sloped terrain; practice minimum tillage; plant on bunds and perimeter slopes; design gentle curves in drainage canals D:\533566517.doc 44 Project Activity Develop canal irrigation system Potential Negative Impacts Mitigation Measures Reduced production from iron toxicity Distribute iron-resistant rice varieties; analyze soil conditions before site selection Enhanced denitrification Encourage soil amendment practices; control water stagnation period Poor crop yields of unsuitable zones Identify soil conditions with auger sampling; use reliable seed varieties initially Neglected land development Restrict individual plot size with planned extensions later Poor water control Moisture stress, anoxia stress, CO2 & reduced chemical stress Encourage regular maintenance of entire water control system Poor weed control Reduction in rice yield and quality; intensification of the of pest and disease problems; reduction of efficiency of certain cultural practices & irrigation Proper and thorough land preparation; planting of weed-free seeds; clearing of bunds and canals by slashing; proper plant spacing (close) and density; use of high tillering tall rice varieties; maintaining flood levels; observe crop rotation by planting vegetables after two successive rice crops Excessive turnaround time Impede crop intensification Plant short duration varieties; use pregerminated seeds in direct-seed rice; minimize tillage in the establishment of a second crop ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH Encourage work in wetlands D:\533566517.doc Increase general health risk Program health training and sensitization; conduct illness surveys Increase exposure to hazardous materials Avoid developing in waste dumps Increase exposure to remaining mosquitoes Stock fish in paddies, promote de-weeding and brushing of perimeter vegetation Increase exposure to Schistosomiasis Encourage latrine construction (and use); mass distribution of Praziquantel 45 Project Activity Potential Negative Impacts Increase exposure to nuisances (leeches, ants) Mitigation Measures Encourage use of protective clothing (jeans, boots, plastic, lime); remove un-submerged debris and dirt bounds from paddy areas; control water appropriately; use controlled heat therapy BIODIVERSITY AND ECOLOGY Disruption of native flora and fauna Loss of biodiversity; ecological health degradation Discourage trap setting; examine wetland values before site selection; monitor effect of water management Application of fertilizers Eutrophication Train proper fertilizer application techniques Use of pesticides Contaminate ecological community; alteration of biodiversity Promote IPM; train proper pesticide application techniques; study biotypes of pest population; breed crops for resistance; promote pest scouting; determine epidemiology of pests/diseases; identify species and possible biocontrol; understand density-dependent and density-independent factors in pest ecology Wetland development near protected areas Affect habitats of endangered species Locate project sites relative to protected areas; conduct baseline survey of local biodiversity D:\533566517.doc 46 APPENDIX 5. WETLAND ENVIRONMENT CHECKLIST This checklist covers environmental information that would be useful in evaluating potential development sites. Following this standard format for each site would allow for a comparison of the environmental situations. This list is more comprehensive that the necessary baseline data, serving also to warn potential developers of the myriad issues to be addressed. Wetland Classification Identify any dominant landscape features and classify the site as one of these wetland types: - Tidal/coastal flood plain (salt water) - Coastal river plain (brackish estuary) - Inland tidal river plain (above salt wedge yet influenced by tides) - River flood plain (influenced by rainfall and river discharge only) - Inland depression (regime determined by rainfall, local runoff, and evaporation) - Small inland valleys (upper valley reaches) Gather information on the local climate: - Mean annual precipitation - Mean annual potential evapotranspiration - Mean annual temperatures Land Uses - Identify (quantify) lost land uses due to development (traditional medicinal plants, pastureland) - Identify sites or areas of religious or spiritual significance - Identify sites or areas of special social or cultural interest - Identify farmer groups, capacity for training and disseminating - Characterize upstream and downstream land uses and ground cover - Characterize livestock systems (#, care, grazing zones, uses, illnesses) - Note dry season and wet season activities in wetlands - Note earliest use of wetlands - Note any water and soil conservation measures - Note existing physical degradation of the local environment - Note any potential gender, age bias - Note political considerations such as land claims and historical rights D:\533566517.doc 47 - Note access to land and rights to use - Note legal considerations such as servitudes and access/movement patterns - Note community cohesion - Estimate population with no access to wetlands - Estimate decreased slash and burn land area (#farmers not involved) - Estimate % of land remaining under natural or derived vegetation Hydrology - Note sinusoidal patterns in stream bed forms - Note any traditional/existing water management techniques - Note changes to flood plains - Note stream turbidity (inflow and outflow) - Locate erosion/deposition zones - Locate stagnant/flowing water zones - Locate infiltration/discharge zones - Estimate various land slopes within the watershed - Estimate the ratio stream length : watershed area - Estimate the ratio stream number : watershed area - Estimate stream velocities - Estimate stream flow rates (high, low, mean annual) - Estimate depth and duration of flooding in different zones - Estimate percolation rate - Estimate water table depth, amount of seasonal fluctuation, change due to activities - Sketch wetland width (high and low water marks) vs. Distance downstream - Sketch wetland elevation vs. Distance downstream - Sketch stream cross sections - Suggest monitoring options (maximum flow rate, rainfall, groundwater depth) Mangroves Note and/or estimate the following characteristics particular to mangrove swamps: - wave and tidal action - deposition/removal of sand D:\533566517.doc 48 - sedimentation rates and patterns - turbidity - salinity - chemical processes or nutrient balances - functioning of estuary systems - river mouths Environmental Health - Note availability and adequacy of clinics/health services - Visit health clinics for water-related disease data, program information, concerns - Question local inhabitants about health concerns, pests, animals - Note parasitological considerations (schistosomiasis, elephantiasis, river blindness) - Identify sources of water pollution (animals, latrines, agricultural runoff) - Identify drinking water sources - Identify toilet facilities/practices - Identify causes and quantify stagnant water areas - Note if manure isavailable and used as a fertilizer in the project and weather it’s use could result in the spread of disease through human contact - Note existing use of leguminous crops to restore soil fertility Agriculture - Note method of irrigation (sprinkle, seepage, canal) - Note potential pest management interventions (ipm) - Describe agricultural calendar, crop patterns, fallow schedule - Characterize topsoil (organic and clay content, limiting nutrient, porosity, gradation) - List major lowland crops grown with related cultivation practices and by whom - List major upland crops grown with related cultivation practices and by whom - Estimate land area with potential for rice cultivation, barren (iron-ladden) - Estimate soil productivity (kg rice/acre) - Estimate potential for other crops (orchards, garden produce) in periphery - Estimate land area requiring leveling or other soil disruption - Estimate land area requiring tree/vegetation clearing D:\533566517.doc 49 - Establish field visits and farm walks at major stages of development - Estimate present turnaround time between succeeding crops - Sketch typical toposequences (cross-sectional and lateral views) - Sketch layout of parcels (plan view) - Sketch typical soil profile (noting organic material, iron, high permeability layers) Biodiversity Note the survival (and needs for) and diversity of: - Wild animals (previously and presently, large and small) - Birds - Fish - Note number of different cultivated rice varieties - Vegetation (trees, shrubs, grasses) both native and invasive - Endangered species - Note major diseases (blast, brown spot, RYMV) - Note major pest problems - Note fertilizer use - Note any evidence of overexploitation, eutrophication, siltation, salinization D:\533566517.doc 50 APPENDIX 6. SAMPLE MEMORANDUM OF UNDERSTANDING Entered between _____(NGO)_____ and the _____________ community, _____________ Clan, ______________District, _____________ County on this ______ day of ______________ 1999. The _______________ community has been targeted by _____(NGO)_____ in good faith for needs in the community. Activities to be undertaken include the following: << brief description of all project activities >> _____(NGO)_____ will: 1. Provide in a timely manner all inputs listed in Appendix 1 of this agreement in full and complete support of this intervention. 2. Provide technical service to the community until completion of this community project. 3. Deliver the inputs to the project community upon availability of adequate and secure storage. 4. Monitor distribution and use of all inputs provided. 5. Request and consolidate project progress and final report data from the participants. The _______________ community will: 1. Establish a credible project management committee consisting of community members. 2. Establish and follow a project work schedule. 3. Establish full ownership for project location by providing valid documentation witnessed by local and tribal authorities. Indicate recognition of land values to be lost by development. 4. Provide inputs listed in Appendix 2 of this agreement through the project management committee to the project activities. 5. Provide adequate and secure storage for all inputs delivered. 6. Account fully with valid receipts for all inputs delivered and received. 7. Provide all labor required for completing the project activities. 8. Submit to _____(NGO)_____ monthly reports of project progress and problems. D:\533566517.doc 51 Both _____(NGO)_____ and this community have agreed to cooperate and to share all risks associated with the implementation of this project. __________________________ Date: _____________________ Project Committee Chairman __________________________ Date: _____________________ Project Committee Member __________________________ Date: _____________________ Chief __________________________ Date: _____________________ Elder or Local Authority __________________________ Date: _____________________ _____(NGO)_____ Representative Attached: Appendices 1 and 2 for inputs required by _____(NGO)_____ and the community, respectively. D:\533566517.doc 52 APPENDIX 7. LIST OF PROTECTED SPECIES AND AREAS IN LIBERIA A) FULLY PROTECTED (PROHIBITED) ANIMALS Animal Local Name Scientific Name PERIMATA Chimpanzee Baboon Pan troglodytes Western Black and White Lion Monkey Colobus polykomos Colobus Monkey Diana Monkey Cercopithecus diana SIRANIA Manatee Mammy water Trichechus senegalensis PROSCIDEA Elephant Loxondonta african cyclo ARTIODACTYLA Hippopotamus Hippopotamus amphibius Pygmy Hippopotamus Water cow Choeropsis liberiensis Bongo Elk Boocerus euryceros Buffalo Bush cow Jentink’s Duiker Yanbe(k) Royal Antelope Zebra Duiker Cephlophus jentinks Neotragus pygmaens Making Deer Ogilby’s Duiker Cephlophus zebra Cephlophus ogilby CARNIVORA Serval Felis serval Leopard Panthera pardus Golden Cat Felis aurata African Civelt Recoon Veverra civetta Ants Beer Manis gigantea PHILDOTA Cient Pangolin REPTILES D:\533566517.doc 53 Animal Nile Crocodile Local Name Alligator Scientific Name Crocodylus niloticus Long Snouted Crocodile “ cafaphractus Dwarf Crocodile “ osteolaemus tetraspis SQUATAMA Rock Python Boa constructor Python sebae “ Ball Python regius CHELONIA Green turtle Chelonia mydas BIRDS All birds of prey PICATHARTIDAE Grey Necked Rockfowl Picatharyes gymnocephalus White Necked Rockfowl Picathartes creas PSITTACIDAE All Parrots ARDEIDAE Cattle Egret Bubulcusibis BUCEROTIDAE All Horn Bills MOSCOPHAGIDAE All Turacos B) PARTIALLY PROTECTED ANIMALS Animal Local Name Scientific Name MAMMALS: PRIMATA Red Colobus Monkey Red Monkey Colobus badius Olive Colobus Monkey Green Monkey Colobus versus Mona Monkey D:\533566517.doc Cercopithecus mona 54 Animal Local Name Scientific Name Greater White Nosed Monkey Cercopithecus nictitans Lesser White Nosed Monkey Cercopithecus petayrista White Collard Mamgabey Jako Cercocebys Bosman’s Potto Bush Baby or Perodictus potto Lesser Calago Sofyly – Softly Calago senegalensis Torquatus(atys) Dwarf Calago Calagoides demidovi ARTIODACTYLA Water Chevrontain Water Deer Hyemosichus aquaticus Bay Duiker Black Deer Cephalophus dorsalis Maxwell Duiker Foulintongor Cephalophus niger Black Duiker Bush Goat Cephalophus niger Yellow Backed Duiker Maxwelli sylvicyltor Bush Buck Red Deer Targelaphus scriptus Giant Forest Hog Bush Hog Hylochoerus meinert Red River Forest Hog Bush Pig Potamocherus porus CARNIVORA Two Spotted Palm civet Mandinia binotata Forest Genet Genetta pardina African Linsang Poiana richardsoni Large spotted Genet Genetta tigrina PHOLIDOTA Long Tailed Pangolin Manis tetradactyal Tree Pangolin Manis tricuspis REPTILES: SQUAMATA Nile Monitor Lizard Verena niloticus BIRDS: PHASIANIDAE D:\533566517.doc 55 C) NATIONAL PARKS Name County Estimated Area [km2] Sapo Sinoe 1250 Cape Mount Cape Mount Lofa Mano Lofa 2750 Wonegisi Northern Lofa 175 Cavalla Grand Gedeh 75 Nimba* Nimba 550 Cestos Sehn kwehn Sinoe and Grand Bassa 1500 50 * Same site as East Nimba National Forest. # Same site as Sapo National Forest. D) NATIONAL FORESTS Name County Estimated Area [km2] Gola Forest (Yoma) Bomi Hills 100 Gola Cape Mount and Lofa 1375 North Loma Northern Lofa 575 Kpelle Lofa 1050 Belle Lofa 775 Loma Lofa 550 West Nimba Nimba 330 East Nimba* Nimba 550 Gio Nimba 715 Gbee Nimba 600 Sapo# Sinoe 1250 Krahn-Bassa Sinoe, Grand Bassa 9350 Grebo Grand Gedeh 5390 * Same site as Nimba National Park. # Same site as Sapo National Park. D:\533566517.doc 56 APPENDIX 8. MONITORING PLAN FOR ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES OF WETLAND DEVELOPMENT NOTE: I = Input; OP = Output; OC = Outcome Indicator Threshold Levels Threshold Actions GENERAL OC: Number and type of grievances: Community members regret involvement; significant decrease in number of participants Improve community sensitization plans OP: Grass and shrub density in canals Excessive clogging reduces stream flow Encourage brushing of grasses in canals OP: Degree of irrigation engineering development: Degree 3 or 4 Improve training methods; increase farmer exposure to improved sites Canals or drains overflow Short-term canal repairs; long-term redesign (widening) of canal crosssection and slope Canal dries Convert to vegetable crops during dry season, with irrigation water from hand-dug wells Flood damage results in Increase dyke and drain sizes - land tenure disputes - poor water management - community participation WATER MANAGEMENT I: Local rainfall I: Local air temperature 1) Bunds and canals in good condition 2) Bunds irregular, canals slightly clogged 3) Bunds inefficient, variable canal cross sections, clogging and crumbling 4) No engineering development OP: Flow rate characteristics in major tributary OC: Flood frequency D:\533566517.doc 57 Indicator (uncontrolled flooding of paddies) Threshold Levels Threshold Actions crop damage OC: Downstream flooding Standing water for >1 period (Identify week; complaints of downstream users and flood damage interview them as to altered hydrology.) Dig drainage canal further downstream; increase water conservation works in watershed OC: Dry season water table depth (if below land surface) Depth is great enough to discourage gardening Encourage water conservation measures above head dyke; possibly abandon site OC: Upstream land use changes (i.e. tree harvesting, slash and burn intensity) Flooding or sedimentation impacting irrigation system operation Include training in land management LAND DEVELOPMENT I: New or rehabilitated site OP: Farmer group composition: # males : # females % of community Male:female ratio > 0.5; Review group selection criteria % of community < 20% OP: Seed varieties being used No use of improved varieties Improve promotion and dissemination of improved seed varieties where useful OP: Dry season activities (crop type, water source) Non-use of dry season paddies Distribute appropriate seeds; encourage year-around land cultivation OC: Slash and burn coverage within catchment area (based on indication from interviewees of change) Increase in upland cultivation rather than reduction Improve animation of environmental degradation from slash and burn; increase wetland cultivation area to include more farmers OC: Crop yield Yield < 1 ton/ha Change variety selection; improve cultural practices OC: Effects of erosion Failure of irrigation system due to sedimentation, bund damage Encourage cultivation of appropriate cover crops (i.e., legumes) D:\533566517.doc 58 Indicator Threshold Levels Threshold Actions OC: Plant stress 30% of paddy Fertilizer use may be justified OC: Technology replication (# farmers, total area developed) No farmers are replicating demonstrated rice cultivation techniques Increase availability of extension services, increase on-site demonstrations OC: Bird interactions: 30% crop loss, significant tree cutting Reduce nesting sites; introduce rice varieties with awns and erect flag leaves 1) % crop lost by scavenging 2) habitat loss by farmers cutting trees ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH OP: Site proximity to any pollution sources Sewage/debris found on site Relocate site and/or dumps; encourage use of protective clothing OP: % farmers using protective clothing (jeans, boots, etc.) No protection measures Encourage use of protective clothing where contact transmitted diseases/nuisances are prevalent OC: Prevalence of malaria cases Warning levels determined by health workers Increase health training if correlated with project activities OC: Prevalence of Schistosomiasis Warning levels determined by health workers Increase health training if correlated with project activities OC: Existence of nuisances: Increased prevalence in plots Increase health training if correlated with project activities; encourage mitigation measures Warning levels determined by health workers Increase health training if correlated with project activities 1) leeches 2) stinging ants OC: Prevalence of other water-related diseases BIODIVERSITY AND ECOLOGY I: Presence and species composition of fish in natural stream (upstream and downstream of project site) D:\533566517.doc 59 Indicator OP: Fish farming practice: 1) type of operation (in paddies, above head dyke, or in canals) Threshold Levels Threshold Actions Unsuccessful fish production, decline in fish population Modify design of head dyke and canals (open passages, reduce flow velocity); provide training in aquaculture if desired by community Crop damage > 30% of cultivated area Institute appropriate pest management practices 2) fish catch rate 3) Presence and species composition of fish in natural stream OC: Pest problems (pest type and extent of land coverage) OC: Rice disease problems Crop damage > 30% of (disease type and extent of cultivated area land coverage) Introduce high-yielding disease resistant rice varieties OC: Pesticide poisoning of farmers (# incidences reported) Training in proper pesticide use; study alternatives to pesticide use such as bio-control and biotype manipulation D:\533566517.doc Any complaints of health problems related to pesticide use 60