Ch. 15 - Plain Local Schools
advertisement

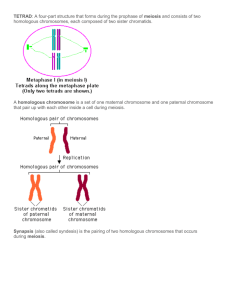
AP Biology Vocabulary & Roots: Ch. 15 1. aneuploidy- A chromosomal aberration in which one or more chromosomes are present in extra copies or are deficient in number. 2. Barr body-A dense object lying along the inside of the nuclear envelope in cells of female mammals, representing a highly condensed, inactivated X chromosome. 3. chromosome theory of inheritance-A basic principle in biology stating that genes are located on chromosomes and that the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis accounts for inheritance patterns. 4. crossing over-The reciprocal exchange of genetic material between nonsister chromatids during prophase I of meiosis. 5. cytogenetic map-A chart of a chromosome that locates genes with respect to chromosomal features distinguishable in a microscope. 6. dendrite-One of usually numerous, short, highly branched extensions of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons. 7. Down syndrome-A human genetic disease caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21; characterized by mental retardation and heart and respiratory defects. 8. Duchenne muscular dystrophy-A human genetic disease caused by a sex-linked recessive allele; characterized by progressive weakening and a loss of muscle tissue. 9. duplication-An aberration in chromosome structure due to fusion with a fragment from a homologous chromosome, such that a portion of a chromosome is duplicated. 10. genetic map-An ordered list of genetic loci (genes or other genetic markers) along a chromosome. 11. genetic recombination-General term for the production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. 12. genomic imprinting-A phenomenon in which expression of an allele in offspring depends on whether the allele is inherited from the male or female parent. 13. hemophilia- A human genetic disease caused by a sex-linked recessive allele resulting in the absence of one or more blood-clotting proteins; characterized by excessive bleeding following injury. 14. inversion-An aberration in chromosome structure resulting from reattachment of a chromosomal fragment in a reverse orientation to the chromosome from which it originated. 15. linkage map-A genetic map based on the frequencies of recombination between markers during crossing over of homologous chromosomes. 16. linked genes-Genes located close enough together on a chromosome that they tend to be inherited together. 17. map unit-A unit of measurement of the distance between genes. One map unit is equivalent to a 1% recombination frequency. 18. monosomic-Referring to a cell that has only one copy of a particular chromosome instead of the normal two. 19. nondisjunction-An error in meiosis or mitosis in which members of a pair of homologous chromosomes or a pair of sister chromatids fail to separate properly from each other. 20. parental type-An offspring with a phenotype that matches one of the parental phenotypes; also refers to the phenotype itself. 21. polyploidy- A chromosomal alteration in which the organism possesses more than two complete chromosome sets. It is the result of an accident of cell division. 22. sex-linked gene- A gene Located on A sex chromosome (usually the X chromosome), resulting in A distinctive pattern of inheritance. 1 23. translocation- (1) An aberration in chromosome structure resulting from attachment of a chromosomal fragment to a nonhomologous chromosome. 24. trisomic-Referring to a diploid cell that has three copies of a particular chromosome instead of the normal two. 25. wild type-An individual with the phenotype most commonly observed in natural populations; also refers to the phenotype itself. Word Roots a- = not or without (asexual: type of reproduction not involving fertilization) -apsis = juncture (synapsis: the pairing of replicated homologous chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis) auto- = self (autosome: the chromosomes that do not determine gender) chiasm- = marked crosswise (chiasma: the X-shaped microscopically visible region representing homologous chromosomes that have exchanged genetic material through crossing over during meiosis) di- = two (diploid: cells that contain two homologous sets of chromosomes) fertil- = fruitful (fertilization: process of fusion of a haploid sperm and a haploid egg cell) haplo- = single (haploid: cells that contain only one chromosome of each homologous pair) homo- = like (homologous: like chromosomes that form a pair) karyo- = nucleus (karyotype: a display of the chromosomes of a cell) meio- = less (meiosis: a variation of cell division that yields daughter cells with half as many chromosomes as the parent cell) soma- = body (somatic: body cells with 46 chromosomes in humans) sporo- = a seed; -phyte = a plant (sporophyte: the multicellular diploid form in organisms undergoing alternation of generations that results from a union of gametes and that meiotically produces haploid spores that grow into the gametophyte generation) syn- = together; gam- = marriage (syngamy: the process of cellular union during fertilization) 2