Chapter 6 Review
advertisement
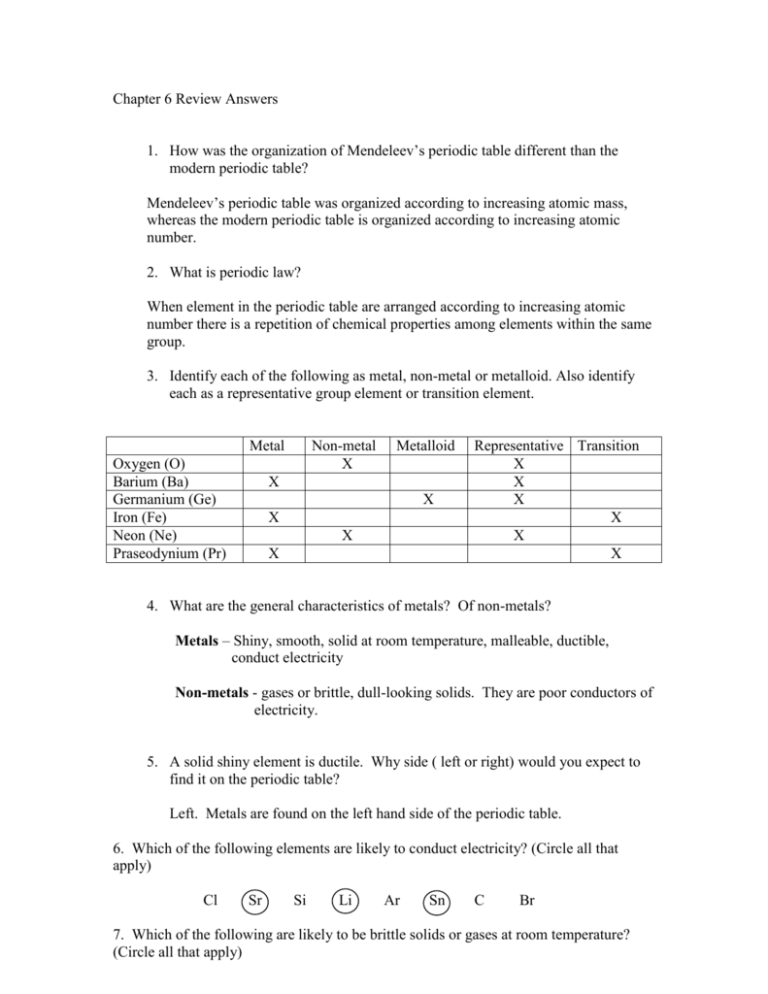
Chapter 6 Review Answers 1. How was the organization of Mendeleev’s periodic table different than the modern periodic table? Mendeleev’s periodic table was organized according to increasing atomic mass, whereas the modern periodic table is organized according to increasing atomic number. 2. What is periodic law? When element in the periodic table are arranged according to increasing atomic number there is a repetition of chemical properties among elements within the same group. 3. Identify each of the following as metal, non-metal or metalloid. Also identify each as a representative group element or transition element. Metal Oxygen (O) Barium (Ba) Germanium (Ge) Iron (Fe) Neon (Ne) Praseodynium (Pr) Non-metal X Metalloid X X X X X Representative Transition X X X X X X 4. What are the general characteristics of metals? Of non-metals? Metals – Shiny, smooth, solid at room temperature, malleable, ductible, conduct electricity Non-metals - gases or brittle, dull-looking solids. They are poor conductors of electricity. 5. A solid shiny element is ductile. Why side ( left or right) would you expect to find it on the periodic table? Left. Metals are found on the left hand side of the periodic table. 6. Which of the following elements are likely to conduct electricity? (Circle all that apply) Cl Sr Si Li Ar Sn C Br 7. Which of the following are likely to be brittle solids or gases at room temperature? (Circle all that apply) Cl 8. Sr Si Li Ar Sn C Br Give the chemical symbol for the following elements. a. b. c. d. 9. Two elements that are liquid at room temperature Hg, Br The noble gas with the greatest atomic number Rn Any metal from group 4A C Any inner transition element U Why do the elements chlorine and iodine have similar chemical properties? They have the same electron configuration. Valence electrons are responsible are involved in chemical reactions. 10. How many valence electrons do each of the noble gases have? 8 11. Write the electron configuration for the following elements. a. The halogen in period 5 [Kr]5s24d105p5 b. The transition metal in group 11 period 5 [Kr]5s24d9 c. The metalloid in period 6 [Xe]6s24f145d106p4 12. Given any two elements within a group, is the element with the larger atomic number likely to have a larger or smaller atomic radius than the other element? Larger 13. Explain why it is harder to remove an inner shell electron from an atom than it is to remove a valence electron from an atom? Inner shell electrons are closer to the nucleus and therefore experience greater electrostatic force than valence electrons. 14. An element forms a negative ion when ionized. On which side of the periodic table is this element located? Right. Nonmetals gain electrons to form negative ions. Nonmetals are on the right side of the periodic table. 15. Define electronegativity and ionization energy. Electronegativity – The ability of an atom to attract electrons Ionization energy – The energy required to remove an electron from an atom. 16. Which element in each pair has the larger ionization energy? a. Li, N b. Kr, Ne c. Cs, Li 17. Use the illustration of spheres A and B to answer ach of the following questions. A B a. If A is an ion and B is an atom of the same element, is the ion a positive or negative ion? Negative b. If A and B represent the atomic radii of two elements in the same period, what is their correct order (left to right)? A, B c. If A and B represent the ionic radii or two elements in the same group, what is their correct order (top to bottom)? B, A 18. Which element I each pair is more electronegative? a. K, As b. N, Sb c. Sr, Be 19. Identify each of the following as an alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, transition metal, or inner transition metal. a. Cesium (Cs) Alkali Metal b. Zirconium (Zr) Transition c. Gold (Au) Transition d. ytterbium (Yb) e. uranium (U) f. francium (Fr) Inner Transition Inner Transition Alkali Metal