SCH3U_04_05a combustion and hydrate analysis
advertisement
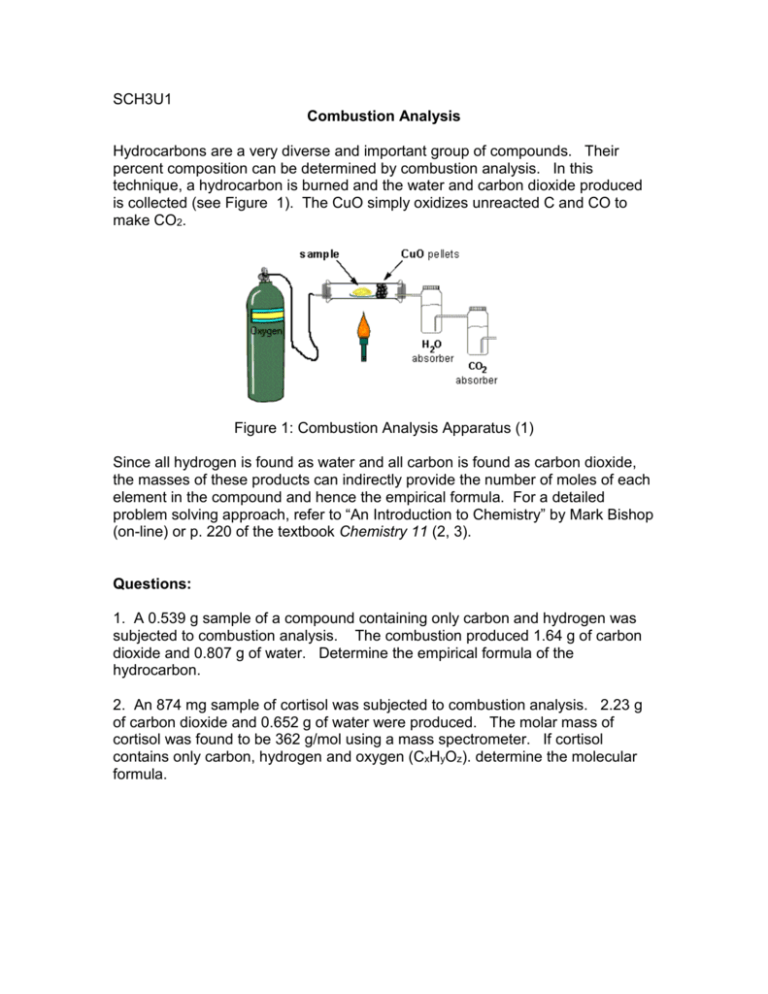
SCH3U1 Combustion Analysis Hydrocarbons are a very diverse and important group of compounds. Their percent composition can be determined by combustion analysis. In this technique, a hydrocarbon is burned and the water and carbon dioxide produced is collected (see Figure 1). The CuO simply oxidizes unreacted C and CO to make CO2. Figure 1: Combustion Analysis Apparatus (1) Since all hydrogen is found as water and all carbon is found as carbon dioxide, the masses of these products can indirectly provide the number of moles of each element in the compound and hence the empirical formula. For a detailed problem solving approach, refer to “An Introduction to Chemistry” by Mark Bishop (on-line) or p. 220 of the textbook Chemistry 11 (2, 3). Questions: 1. A 0.539 g sample of a compound containing only carbon and hydrogen was subjected to combustion analysis. The combustion produced 1.64 g of carbon dioxide and 0.807 g of water. Determine the empirical formula of the hydrocarbon. 2. An 874 mg sample of cortisol was subjected to combustion analysis. 2.23 g of carbon dioxide and 0.652 g of water were produced. The molar mass of cortisol was found to be 362 g/mol using a mass spectrometer. If cortisol contains only carbon, hydrogen and oxygen (CxHyOz). determine the molecular formula. Hydrate Analysis Many ionic compounds contain loosely bound water molecules in their crystal structure, forming what are known as hydrates. On the other hand, an anhydrous compound has no water attached. For example, magnesium sulfate can exist as the heptahydrate form (MgSO4 • 7H2O) or in the anhydrous form (MgSO4). The molar mass and percent composition of a hydrate must take into account the bound water molecules. Since hydrates can be converted into the anhydrous form by heat, we can easily determine the number of water molecules bound to a salt and hence the chemical formula of the hydrate. + heat AB • xH2O (s) AB (s) + xH2O Questions: 1. A 3.34 g sample of the hydrate form of strontium thiosulfate has the formula SrS2O3 • xH2O and contains 2.30 g of the anhydrous salt. Find the value of x. 2. A hydrate of zinc chlorate (Zn(ClO3)2 • xH2O) contains 21.5% zinc by mass. Find the value of x. References: 1. Pennsylvania State University, Dept. of Chemistry. Accessed Nov. 2, 2009. (http://www2.hn.psu.edu/faculty/dmencer/combustion/combust_app.htm) 2. Bishop, M. An Introduction to Chemsitry. Accessed Nov. 2, 2009. (http://preparatorychemistry.com/Bishop_Combustion_Analysis.htm) 3. Mustoe, F. Chemistry 11. McGraw-Hill Ryerson. Toronto. Answers: Combustion Analysis: 1. C5H12 2. C21H30O5 Hydrate Analysis: 1. 5H2O 2. 4H2O