Network Security TEST1-Solution
advertisement

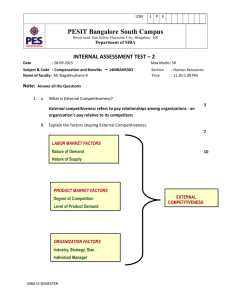
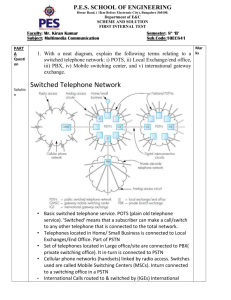
USN 1 P E E C PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics and Communications TEST - 1 Date : 18-02-2014 Subject & Code : Network Security & 10EC832 Name of faculty : Mrs. Shubha Raj K.B. Marks : 50 Section: 8th CSE A & B Time : 8.30 to 10 AM Note: Answer any FIVE Questions 1 a Classify the various security attacks and define them. Security attacks 5 USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics and Communications E C USN 1 P E E C PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics and Communications b With a neat diagram, explain network security model. Network Security Model 5 All the techniques for providing the security has 2 components A security-related transformation: ex: Encryption of messages and decryption Secrete information Ex: Encryption key Third party is needed to achieve the secure transmission Distributing the secret key There are 4 basic tasks in designing a particular security service 1. Design a suitable algorithm for the security transformation 2. Generate the secret information (keys) used by the algorithm 3. develop methods to distribute and share the secret information 4. 2 a specify a protocol to be used by the principals that make use of the security algorithm and secret information to achieve a particular security service What are the principles elements of a public-key cryptosystems – a public-key, which may be known by anybody, and can be used to encrypt messages, and verify signatures – a private-key, known only to the recipient, used to decrypt messages, and sign (create) signatures 5 USN 1 P E E C PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics and Communications is asymmetric because – those who encrypt messages or verify signatures cannot decrypt messages or create signatures Encryption algorithm Decryption algorithm Plaintext Ciphertext b Define the following terms with relation to cryptography. i) Algorithm ii) Key iii) Plaintext iv) Steganography v) Cryptanalysis • plaintext - original message • key – secrete info used in cipher known only to sender/receiver • encipher (encrypt) - converting plaintext to ciphertext – • Encryption: converting original message into a form unreadable by unauthorized individuals decipher (decrypt) - recovering ciphertext from plaintext 5 USN 1 P E E C PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics and Communications • cryptography - study of encryption principles/methods • cryptanalysis ( breaking the code) - study of principles/ methods of – • 3 deciphering ciphertext without any knowledge of the encryption details. Steganography: “covered writing” Insert secrete binary info into the data during digitization process List and briefly define categories of security services and security mechanisms Authentication - assurance that the communicating entity is the one claimed Access Control - prevention of the unauthorized use of a resource Peer entity authentication Data origin authentication Data Confidentiality –protection of data from unauthorized disclosure Data Integrity - assurance that data received is as sent by an authorized entity Non-Repudiation - protection against denial by one of the parties in a communication Availability Service - accessible and usable by an authorized system entity Denial of Service attacks Virus that deletes files specific security mechanisms: encipherment, digital signatures: To prove source as well as integrity of data unit access controls, data integrity, authentication exchange, traffic padding: The insertion of bits into gaps in a data stream to frustrate traffic analysis attempts, routing control: Enables selection of particular physically secure routes for certain data. Notarization: The use of a trusted third party to assure certain properties of a data exchange. pervasive security mechanisms: trusted functionality: Which perceived to be correct with respect to some criteria. 10 USN 1 P E E C PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics and Communications security labels: event detection, security audit trails, 4 a security recovery Encrypt the plaintext = "SECURITY" using Hill Cipher technique. Key= 7 19 5 8 3 b Briefly define the Caesar Cipher • earliest known substitution cipher • by Julius Caesar • first attested use in military affairs • replaces each letter with the letter standing 3 places further down the alphabet • example: 5 meet me after the toga party PHHW PH DIWHU WKH WRJD SDUWB 5 a With a neat diagram, explain the single round of DES encryption. 10 USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics and Communications E C USN 1 P E E C PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics and Communications b What is the purpose of the S-boxes in DES 5 USN 1 P E E C PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics and Communications S-Boxes The S-boxes do the real mixing (confusion). DES uses 8 S-boxes, each with a 6-bit input and a 4-bit output. USN 1 P E E C PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics and Communications 6 a Write the RSA algorithm. 5 1. Pick two distinct primes p and q 2. Compute n = pq and ɸ(n) = (p – 1)(q – 1) 3. Pick e where 1 < e < ɸ(n) and gcd(e, ɸ(n)) = 1 4. Compute d where de ≡ 1 (mod ɸ(n)) 5. Public key is (n, e), private key is (n, d) 6. Encrypt with C ≡ M e (mod n) Decrypt with M ≡ C d (mod n) b Perform the encryption and decryption using RSA algorithm. for the following 5 USN 1 P E E C PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics and Communications P=17, Q=31, e=7, and M=2. 7 a Construct a Playfair with the key=largest, Encrypt the following message 5 “must see you over Cadogan West” b Briefly define the transposition Cipher with examples • these hide the message by rearranging the letter order • without altering the actual letters used • can recognise these since have the same frequency distribution as the original text • write message letters out diagonally over a number of rows • then read off cipher row by row Plaintext: Meet me after the toga party eg. write message out as: m e ma t r h t g p r y e t e f e t e o a a t • giving ciphertext MEMATRHTGPRYETEFETEOAAT Row transposition Cipher • a more complex transposition • write letters of message out in rows over a specified number of columns • then reorder the columns according to some key before reading off the rows Key: 4312567 5 USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics and Communications Plaintext: a t t a c k p ostpone duntilt woamxyz Ciphertext: TTNAAPTMTSUOAODWCOIXKNLYPETZ E C