MicroElectronics Section `C`
advertisement

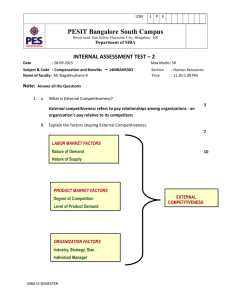
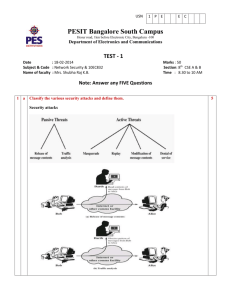
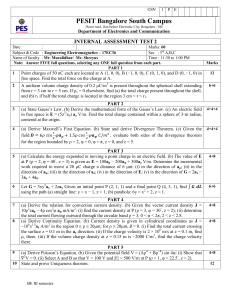
USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering Scheme and Solution of First Internals Subject & Code : Microelectronics/10EC63 Name of faculty : M Raghavendra Answer any 5 Questions Section : 6th “C” Time : 1Hr 30Mins Q.No Questions a. Consider a process technology for which Lmin=0.4µm, tox=8nm, µn=450 cm2/V and 1 Vt=0.7 V i. Find Cox and k’n. ii. For a MOSFET with W/L=8µm/0.8µm, calculate the values of VGS and VDSmin needed to operate the transistor in the saturation region with a dc current ID=100µA iii. For the device in (b), find the value of VGS required to cause the device to operate as a 1000Ω resistor for very small VDS. Solution : 1 Marks 07 USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering 2 USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering 2 b. Sketch a CMOS realization for the function Solution: 03 Design a fixed bias circuit with and without source resistance for drain current of 0.5mA, k’n(W/L)=1mA/V2, Vt=1V, VDD=10V. Calculate percentage change in drain current in both bias circuits with same k’n(W/L) and Vt=1.5V. Plot iD – vGS characteristics for both types of biasing technique. 10 3 USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering 3 Determine Rin, Gv and Rout of CS amplifier, CG amplifier and CD amplifier. Given VDD=VSS=10V, RG=4.7kΩ, RD=15kΩ, k’n(W/L)= 1mA/V2 and Vt=1.5V. Biasing is done using constant current source of 0.5mA. RL = 15kΩ. Solution 1. CS Amplifier : Rin= RG=4.7kΩ , Rout= RD=15kΩ, Gv=Av=-15V/V 2. CG Amplifier: Rin= RG=1/gm=1kΩ , Rout= RD=15kΩ, Gv= 7V/V 3. CD Amplifier: Rin= RG=4.7kΩ , Rout= RD=15kΩ, Gv=0.135V/V 4 10 USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering 4 a. Derive the analytical expression for the transfer characteristics of CS amplifier. Solution: Circuit Diagram- 1M Av in Cut-off -2M Av in saturation region- 2M Av in triode region – 2M 7+3 b. Construct VTC for the case k’n(W/L)= 1mA/V2, Vt=1 V, RL = 18kΩ and VDD = 10V. Solution: Point X=(0,10V) Point A =(1V,10V) Point B = (2V,1V) Point C= (0V,0.061V) 5 Using two transistors Q1 and Q2 having equal lengths but widths related W2/W1=5. Given VDD=-VSS=5V, k’n(W/L)= 0.8 mA/V2, Vt=1 V and λ=0 10 a. Design constant current source to obtain I=0.5mA. Solution: R=85KΩ b. What is the voltage at the gates of Q1 and Q2. Solution: VG1=VG2 = -3.5V c. What is the lowest allowed voltage at the drain of Q2 while Q2 remains in saturation region? Solution : VDmin = -4.5V 6 Consider a cmos inverter fabricated in a 0.25µm process for which Cox=6fF/µm2, µn Cox = 115µA/V2 , Vtn= -Vtp=0.4V and VDD = 2.5V. The W/L ratio of QN is 0.375µm/0.25µm and Qp =1.125µm/0.25µm. The equivalent capacitence value is 6.25fF. Find tPHL, tPLH and tp. Solution: tPHL=23.3ps, tPLH=30ps, tp=26.5ps 5 10 USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering 7 For each of the circuits shown in Figure. Find the labeled node voltages. The NMOS transistors have k’n(W/L)= 2 mA/V2, Vt=1 V Solution: (a) V1=0.9V, V2=-1.6V (b) V1=4.1V, V2=2.5V, V3=0.9V 6 10