Solutions & Solubility Curves
advertisement

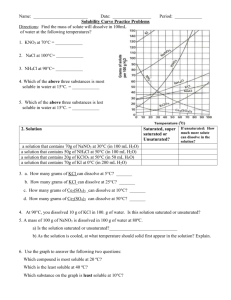
Solutions Review Name______________________________ Period_______Date___________________ Part A: Choose the correct term for the blanks. All words are used at least once; some used more than once. small gas solid increase dissolve filtration miscible electrolyte homogeneous filter paper polar crushing solute liquid nonpolar solvent solution pressure A solution is a __________________________ mixture of two or more substances. A solution is composed of a solvent and at least one _______________. One substance is uniformly dispersed, or spread, throughout the other. In an ordinary solution, the substance present in the greatest amount is called the ________________. The other substance, called the _________________, is uniformly dispersed throughout the solvent. Two liquids that dissolve completely in one another are called _______________ whereas a solid that dissolves completely in a liquid is called ___________________. Ionic solutes dissolve more in _____________ solvents, while covalent solutes dissolve more in __________________ solvents. Ionic solutes dissolve in water to form solutions which conduct electricity, a(n) _____________________ Water is known as the universal ________________ because it can dissolve many common solids. Table salt and sugar dissolve in water to form solutions in the _____________ phase. Liquids such as ethyl alcohol and glycerine also ______________ in water. Ammonia is a ________ that is very soluble in water. If the solution is cooled, other gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide also ________________ in water. Another factor that affects the solubility of gases is ________________. Pressure does not affect the solubility of _______________ solutes. The particles of solute within a solution are very _________________ in size. Since the particle size is so small, solutions cannot be separated into solute and solvent by _____________________. Solute particles are too small to be trapped by the fibers of the ________________________. A sample of a true ____________________ is clear and transparent. Solutions may have a color. 1 Solute particles will dissolve faster if you stir the solution and _________________ the surface area. This will allow more _________________ particles to surround solute particles. ________________ a solid solute will also speed up the dissolving process. Part B: 1. Which of the following will have a higher solubility? a. (Circle one) Then EXPLAIN! Salt and water at 50oC or at 25oC? Why? b. Oxygen and water at 50oC or 25oC? Why? c. Salt and water at 1 atm or 3 atm? Why? d. Oxygen and water at 1 atm or 3 atm? Why? e. Water with a polar solute or a non-polar solute? Why? 2. Does a sugar cube dissolve faster or slower than granulated sugar? ________________ Why? 3. What is the name of a solution consisting of zinc dissolved in copper? _______________ 4. When a crystal of a solid solute is added to a solution containing that solute, the solution begins to completely crystallize. What kind of solution was it before it crystallized? _____________________ 5. What kind of solution was it after it crystallized? _____________________ 6. Describe what would happen if a single crystal of solute were dropped into a: saturated solution:__________________________________________________________________ unsaturated solution:________________________________________________________________ supersaturated solution:______________________________________________________________ 2 Part C: Use your solubility curve to answer the following questions: 1. What is the solubility of NaNO3 at 20oC? ________________________________________ 2. What is the solubility of NaNO3 at 40oC? ________________________________________ 3. What type of solution will be formed if 120.g of KI dissolve in 100.g of water at 40 oC? _________________________ 4. What type of solution will be formed if 80.g of NH4Cl dissolve in 100.g of water at 70.oC? _________________________ 5. How many grams of KCl are needed to make a saturated solution at 100oC in 200g of H2O? __________ 6. A saturated solution of KNO3 is made in 100g of H2O at 70oC. The solution is cooled to 50oC and stirred. How many grams of solid KNO3 will appear on the bottom of the beaker? _________ 7. At 100.oC, the least soluble solid compound is ___________________. 8. At 0oC, the most soluble solid compound is _____________________. 9. NH3 and SO2 are gases. As temperature increases, what happens to their solubilities?________________ 10. Over the temperature range shown, the least soluble gas is ____________________ 11. The gas which shows the greatest change over the temperature range is _________________ 12. To make a saturated solution of NH4Cl at 60.oC, you would add ___________grams to 50.g of H2O. 13. To make an unsaturated solution of KClO3 at 40.oC, you can add no more than __________g of KClO3 to 100.g of H2O. 14. 100.g of a saturated solution of NH3(g) in H2O was heated from 20.oC to 50.oC. How many grams of NH3 gas could be collected? _____________________ 3