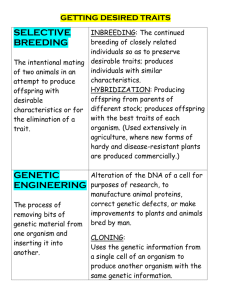
Bibliography - Rice Knowledge Bank
advertisement

Bibliography Bibliography Alston, J.M., P.G. Pardey and V.H. Smith (eds.). 1999. Paying for agricultural productivity. Baltimore and London: published for IFPRI by The Johns Hopkins University Press. Bosselmann, Klaus. 1996. Plant and Politics: The international legal regime concerning biotechnology and biodiversity. Colorado J. Int'l Envtl L & Policy. Bordwin, Harold J. 1985. The legal and political implications of the international undertaking on Plant Genetic Resources, Ecology L.Q. Bragdon, Susan H. and David Downes. 1998. Recent policy trends and developments related to the conservation, use and development of genetic resources. Issues in Genetic Resources No. 7. Rome, Italy. International Plant Genetic Resources Institute. Bridges, Vol. 1, (1), 22 November 2001. http://www.ictsd.org/biores/01-1122/story3.htm. Brockway, Lucile H. 1988. Plant science and colonial expansion: the botanical chess game. In: Seeds and Sovereignty: The Use and Control of Plant Genetic Resources (J.R. Kloppenburg, ed.). Duke University Press, London. Busch, Lawrence, W.B. Lacy, J. Burkhardt and L.R. Lacy. 1991. Plants, power and profit: social, economic and ethical consequences of the new biotechnologies. Cambridge, MA, USA: Blackwells. Byerlee, D. and G. Traxler. 1995. National and international wheat improvement research in the post-Green Revolution period: evolution and impacts. Am. J. Agricultural Economics Vol. 77(2). Downes, David. 1997. Using Intellectual Property as a tool to protect traditional knowledge: recommendations for next steps: CIEL Discussion Paper prepared for the Convention on Biological Diversity Workshop on Traditional Knowledge, Madrid, November 1997. Washington: CIEL. Cassaday, K., M. Smale, C. Fowler and P. Heisey. 2001. Benefits from giving and receiving genetic resources: The case of wheat. Plant Genetic Resources Newsl. No. 127. Charles, D. 2001. Seeds of Discontent. Science 294 (October 26, 2001) Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR). Various years. Annual Reports. Cooper, David. 1993. The International Undertaking on Plant Genetic Resources. RECIEL 2. Law and Policy of Relevance to the Management of Plant Genetic Resources 537 Bibliography Cottier, Thomas. 1998. The protection of genetic resources and traditional knowledge: towards more specific rights and obligations in world trade law. J. Intern. Econ. Law 555-582. Crosby, Alfred. 1986. Ecological imperialism: the biological expansion of Europe, 9001900. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. http://www.ers.usda.gov/Emphases/Harmony/issues/arei2000/ Enríquez, J. 1998. Genomics and the World’s Economy. Science 281 (August 14, 1998). Evenson, R. and D. Gollin (eds). 2001. Crop variety improvement and its effect on productivity: the impact of international agricultural research. CABI, Wallingford, U.K. Farney, Dennis. 1980. Meet the men who risked their lives to find new plants. Smithsonian, June 1980. FAO. 1998. The State of the World’s Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture. Rome, Italy: FAO. FAO Conference Resolution C5/89, 1989. FAO. 1998. The state of the world’s plant genetic resources for food and agriculture. Rome, Italy: FAO. www.geocities.com/willboyne/nosurrender/PotatCom.html. Fowler, Cary. 1994. Unnatural Selection: Technology, Politics and Plant Evolution. Switzerland: Gordon and Breach Science Publishers. Fowler, C. 2000. Protecting farmer innovation: the Convention on Biological Diversity and the question of origin. Jurimetrics, Vol. 41. Fowler, C., M. Smale and S. Gaiji. 2001. Unequal Exchange: Recent transfers of agricultural resources and their implications for developing countries. Development Policy Review, Vol. 19, (2). Frankel, O.H. 1986. Genetic resources: The founding years. II. The movement’s constituent assembly. Diversity. Frey, K.J. 1996. National Plant Breeding Study-1. Human and financial resources devoted to plant breeding research and development in the United States in 1994. Special Report 98, Iowa Agriculture and Home Economics Experiment Station. Ames: Iowa State University. Frey, K.J. 1997. National Plant Breeding Study-II. National plan for promoting breeding programs for minor crops in the U.S. Special Report 100, Iowa Agriculture and Home Economics Experiment Station. Ames: Iowa State University. Frison, E.A. 1991. Phytosanitary aspects of genebank management. In Proc. Inter-Centre Meeting on Germplasm Health and Movement, October 1990, Rome, Pp. 53-59. Rome: International Board for Plant Genetic Resources. 538 Law and Policy of Relevance to the Management of Plant Genetic Resources Bibliography GRAIN. 1999. TRIPS 27.3(b). An update on where developing countries stand with the push to patent life at WTO. March 2000. www.grain.org/publications/tripsfeb00-en.cfm Griliches, Z. 1957. Hybrid corn: An exploration in the economics of technological change. Econometrica 25 Harlan, J.R. 1971. Agricultural origins: centers and noncenters. Science, Vol. 174. Harlan, J.R. 1975. Geographic patterns of variation in some cultivated plants. J. Heredity, Vol. 66. Heisey, P.W., C.S. Srinivasan and C. Thirtle. 2001. Public sector plant breeding in a privatizing world. Agricultural Information Bulletin No. 772. Washington, DC.: Economic Research Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture. Heisey, P.W., M.A. Lantican and H.J. Dubin. Assessing the benefits of international wheat breeding research in the developing world: The Global Wheat Impacts Study, 1966-1997. CIMMYT, Mexico, D.F. (in press) Heisey, P.W., M.L. Morris, D. Byerlee and M.A. López-Pereira. 1998. Economics of hybrid maize adoption. In M.L. Morris (ed.), Maize seed industries in developing countries. Boulder, Colorado: Lynne Rienner Publishers. Henson-Apollonio, Victoria. May 2002. International agreements and Intellectual Property/Intellectual Property Rights. CAS Bulletin No. 3. The Hague, The Netherlands: ISNAR. Jackson, John H. 1997. The World Trading System: Law and Policy of International Economic Relations. 2nd edition. Cambridge, Mass.: The MIT Press. Jordaan, J.P. 1996. Hybrid wheat: advances and challenges. In M.P. Reynolds, S. Rajaram, and A. McNab (eds.), Increasing yield potential in wheat: breaking the barriers. Kahn, R.P. 1977. Plant quarantine: principles, methodology and suggested approaches. In W.B. Hewitt and L. Chiarappa (eds.). Plant health and quarantine in international transfer of genetic resources. Cleveland: CRC Press. Kahn, R.P. 1977. Plant quarantine: principles, methodology and suggested approaches. In W.B. Hewitt and L. Chiarappa (eds.). Plant health and quarantine in international transfer of genetic resources. Cleveland: CRC Press. Kloppenburg, Jack R. Jr. 1988. First the Seed. The Political Economy of Plant Biotechnology. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. Kloppenburg, Jack R. Jr. and Daniel Lee Kleinman. 1988. “Plant genetic resources: the common bowl.” In: Seeds and sovereignty: the use and control of plant genetic resources (Jack R. Kloppenburg, ed.). London: Duke University Press. Law and Policy of Relevance to the Management of Plant Genetic Resources 539 Bibliography Knowles, M.S. 1970. The modern practice of adult education. New York, NY, USA: Association Press. Knowles, M.S. 1978. The adult learner: A neglected species. Houston, TX, USA: Gulf Publishing Co. Kolb, D.A. and R. Fry. 1975. Toward an applied theory of experiential learning. In Theories of group processes (Cary Cooper, ed.). London, UK: John Wiley & Sons. Knudson, M.K. 2000. The Research Consortium Model for Agricultural Research. In K.O. Fuglie and D.E. Schimmelpfennig (eds.), Public-private collaboration in agricultural research: new institutional arrangements and economic implications., Ames: Iowa State University Press. Knudson, M.K. and V.W. Ruttan. 1988. Research and development of a biological innovation: hybrid wheat. food research institute studies 21(1):45-68. Leskien, D. and L. Sperling. 2001. Participatory plant breeding and property rights, Report submitted to The International Development Research Centre (IDRC) by the. Systemwide Program on Participatory Research and Gender Analysis (PRGA), August 2001. L. Sperling, J. Ashby, E. Weltzien, M. Smith and S. McGuire, 2001. A framework for analyzing participatory breeding projects and results. Euphytica 122 (3)- December 2001. Lucken, K.A. 1987. Hybrid Wheat. In E.G. Heyne (ed.), Wheat and Wheat Improvement. Madison, Wisconsin: American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, and Soil Science Society of America. McCaffery, J.A. 1986. Independent effectiveness: A reconsideration of cross-cultural orientation and training. International Journal of Intercultural Relations 10:159-178. Mooney, P.R. 1983. The law of the seed: another development and plant genetic resources. Development Dialogue. Morris, M.L. (ed.) 1998. Maize seed industries in developing countries. Boulder, Colorado: Lynne Rienner Publishers. Morris, M.L. and B.S. Ekasingh. Plant breeding research in developing countries: what roles for the public and private sectors? In D. Byerlee and R. Echeverría (eds.) Agricultural Research Policy in an Era of Privatization: Experiences from the Developing World. Wallingford, UK: CABI. (In press) Morris, M.L. Impacts of International maize breeding research in developing countries, 1966-98. Mexico, D.F.: CIMMYT. (in press) Odek, James O. 1999. Bio-piracy: creating proprietary rights in plant genetic resources. J. Intell. Prop. Law 540 Law and Policy of Relevance to the Management of Plant Genetic Resources Bibliography Palacios, X.F. 1998. Contribution to the estimation of countries’ interdependence in the area of plant genetic resources. Background Study Paper No. 7. Rome: FAO. Pardey and V.H. Smith (eds.). 1999. Paying for agricultural productivity. Baltimore and London: published for IFPRI by The Johns Hopkins University Press. Pardey, P.G. and N.M. Beintema. 2001. Slow magic: Agricultural R&D a century after Mendel. IFPRI Food Policy Report., Washington, DC: IFPRI. Pickett, A.A. and N.W. Galwey. 1997. A Further Evaluation of Hybrid Wheat. Plant Varieties and Seeds 10:15-32. Mexico, D.F: CIMMYT. Plucknett, D.L. et al. 1983. Crop germplasm and developing countries. Science 163:220. Pray, C.E. and D. Umali-Deininger. 1998. The private sector in agricultural research systems: will it fill the gap? World Development 26:1127-1148. RAFI. 1997. Life Industry. RAFI Communique, November/December 1997. Rusike, J. 1995. An institutional analysis of the maize seed industry in Southern Africa. Ph.D. dissertation. Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan. Shoemaker, R. (ed.), with contributions from J. Harwood, K. Day-Rubenstein, T. Dunahay, P. Heisey, L. Hoffman, C. Klotz-Ingram, W. Lin, L. Mitchell, W. McBride, and J. Fernandez-Cornejo. 2001. Economic issues in agricultural biotechnology. Agricultural Information Bulletin No. 762. Economic Research Service. Washington, DC.: U.S. Department of Agriculture. Smale, M., K. Day-Rubenstein, A. Zohrabian and T. Hodgkin. 2001. The demand for crop genetic resources: international use of the U.S. national plant germplasm system. EPTD Discussion Paper No. 82. Environment and Production Technology Division (EPTD). Washington, DC: IFPRI. System-wide genetic resources programme (SGRP) of the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research. 1996. Report of the internally commissioned external review of the CGIAR genebank operations. Rome: IPGRI. Tilford, David S. 1998. Saving the blueprints: the international legal regime for plant resources. 30 Case W. Res. J. Int’l 373:389. USDA Economic Research Service. 2000. Agricultural resource and environmental indicators, 2000. Washington, D.C.: Resource Economics Division, Economic Research Service, USDA. USDA Economic Research Service. 2000. Agricultural resource and environmental indicators, 2000. Washington, D.C.: Resource Economics Division, Economic Research Service, USDA. USDA/OICD/ITD. (no date). Agricultural trainer development, Training of trainers, Instructors’ manual. Law and Policy of Relevance to the Management of Plant Genetic Resources 541 Bibliography SGRP 2000. Annual Report 1999 of the CGIAR System-wide Genetic Resources Programme. Rome, Italy: International Plant Genetic Resources Institute. Van Dusen, E. 2001. The International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture. Presentation at USDA Economic Research Service, December 11, 2001. www.upov.int/eng/ratif/pdf/ratifmem.pdf (UPOV web site). States party to UPOV, as of 1 April 2001. Wilkes, H. Garrison. 1988. Plant genetic resources over ten thousand years: from a handful of seed to the crop-specific mega-genebanks. In: Seeds and sovereignty: the use and control of plant genetic resources (Jack R. Kloppenburg, ed.). London: Duke University Press Wright, B. 2000. IPRs in Biotechnology: Agricultural applications. Presentation at the symposium on Intellectual Property Rights: how far should they be extended? 3 February 2000, Board on Science, Technology, and Economic Policy, National Academy of Sciences, Washington, DC. Zemke, R. and S. Zemke. 1981. 30 Things we know for sure about adult learning. In Training: The magazine of human resources development (June). Minneapolis, MN, USA: Lakewood Publications. 542 Law and Policy of Relevance to the Management of Plant Genetic Resources