History of Life on Earth
advertisement

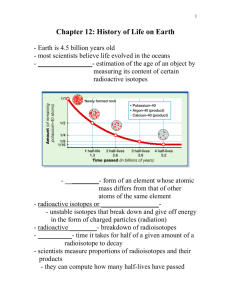
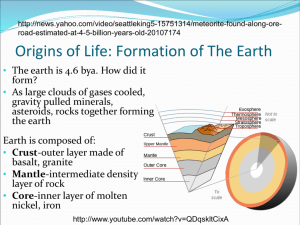
History of Life on Earth Chapter 12 The Age of the Earth ____________________________ Radiometric dating – Radioactive isotopes break down over time – ____________________ – time it takes for half of amount to decay – Using this can estimate age of earth – Non-living chemicals reacted and produced organic molecules Combination of chemicals and energy from lightning/heat/Sun’s UV created ____________________________ 2 Theories about how Primordial Soup Oceans filled with organic molecules Sparks simulate _______________ Amino acids, fatty acids. And other hydrocarbons formed 1 problem: no _____________ to protect from _____, certain compounds couldn’t have existed Bubble Model Gases from ____________________________ trapped in bubbles that protect them from UV and concentrate them Reactions Bubbles Energy happen faster rise, burst, release compounds from UV and lightning creates more reactions ____________________________ fall into ocean and start again Precursor of 1st Cells Molecules _______ RNA of life can arise from ____________________________ can be made in lab believed to be 1st ____________________________storing molecule Makes proteins and changes from generation to generation; acts as an enzyme _______________ –____________________________form droplets in water _______________ –Droplet made of different kinds of molecules like amino acids and sugars These are steps toward cellular organization Microspheres last longer and longer and bring other molecules in Origin of Heredity _______ came after RNA RNA catalyzed early proteins Many believe RNA was brought into microsphere and could pass traits on But how DNA, RNA, and hereditary mechanisms first developed is still not known 12.2 The Evolution of Cellular Life: Prokaryotes ___________: preserved or mineralized remains or imprints of an organism that lived long ago Oldest (__________________________) photosynthetic prokaryotes - ___________________________ Created oxygen but took millions of years to build up to current amount Two Groups of Bacteria Split Very Early _____________________ –__________________________ –Many in cell walls cause disease and decay _____________________ –No peptidoglycan –Unique lipids in cell membrane –Believed to resemble ancient archaebacteria Evolution of Eukaryotes _______________ Larger; first eukaryotes showed up __________________________; DNA in nucleus –Mitochondria in almost all –Chloroplasts in plants and protists __________________________ Theory states bacteria entered large cells as _____________ or ________________ Begin to live inside host and performed cellular respiration or photosynthesis Mitochondria Chloroplasts – descendents of symbiotic, ____________ eubacteria – descendents of symbiotic, ________________ eubacteria Support for Endosymbiosis ____________________________ –Mitochondria like eubacteria –Chloroplasts like cyanobacteria ____________________________ –Circular DNA similar to bacteria is different than hosts DNA ____________________________ –Similar in size to those of bacteria ____________________________ –Simple fission independent of host Multicellularity All living things are broken into ____kingdoms ________________________________________________________ – Eubacteria and Archaebacteria ____________; single celled prokaryotes Protista – first _____________ kingdom, multicellular and unicellular All other eukaryotes, fungi, plants, and animals, came later and all came from _________________ Unicellular Almost is very successful every cell you can see is multicellular Origins of Modern Organisms ________________________________________________________ –Most animal phyla originated during late _____________________ and early _________________________ periods –Great evolutionary expansion –Many unusual marine organisms appear that have no living relatives Burgess Shale 1909 geological formation in Canada found Ordovician Period – 505 mya – 438 mya –______________ – extinct 250 mya Burgess Shale Mass Extinctions Large ___ number of species become extinct Major extinctions –440 mya –360 mya –245 mya – _______________________________ –210 mya mya – ________________________________ –65 Today? –½ Human activity might be causing another of rainforests destroyed –Keep up our current rate 22% to 47% of plants gone 2,000 of the 9,000 birds 12.3 Life Invaded Land ____________________________ –Life evolved protected in oceans from dangerous UV rays from Sun –No life on land during Cambrian period –2.5 bya photosynthesis puts O2 into air which reacts and forms Ozone, O3 –Blocks UV Eventually enough to make it safe to live on land – Plants and Fungi on Land 1st organisms on land were probably a combination of plants and fungi; 430 mya –Plants can make nutrients by photosynthesis –Fungi can absorb minerals from rock –Together called _______________________, these exist today _______________________ – 2 species live together and both benefit