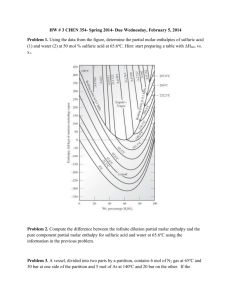
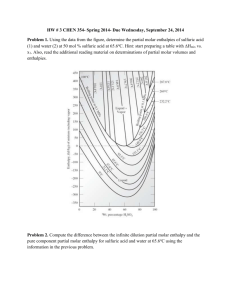
Set 6

CHE303: Problem set 6
1.
A 1000 lb-mole per hour mixture of 5% methane, 20% ethane, 25% propane, 30% n-butane, and 20% n-pentane at 14.7 psia and 90
F is to be compressed first to 50 psia, then to 200 psia using a two-stage compressor system. An inner-stage cooler is used to cool the compressed gas from the first stage to its original temperature by passing the gas stream through a heat exchanger in which water is used as a coolant. This is done to maintain a lower energy requirement for the second stage compressor. A knockout drum is installed after the first cooler to remove any liquid present in the compressed gas before feeding it to the second compressor. Use Provision to determine the power required for the two compressors and to provide a PFD with stream properties including enthalpy as shown in page C-14.
2. (6.16
1 ) At 900 o
K, solid Sr has values of enthalpy and entropy of 20.285 [kJ/mol] and 91.222
[J/mol
o
K], respectively. At 1500 o
K, liquid Sr has values of enthalpy and entropy of 49.179
[kJ/mol] and 116.64 [J/mol
o
K], respectively. The heat capacity for the solid and liquid phases is given by
( c s p
)
Sr
= 37.656 [J/mol
o K] and ( c l p
)
Sr
= 35.146 [J/mol
o K]
Using only these data, determine the temperature of the phase transition between solid and liquid. What is the enthalpy of fusion? You can use the following relation
g / T
T
P
T h
2
Ans:
T melt
1059 .
8 K ,
h fus
7.41
kJ
mol
3. ( 6.19
1 ) Consider an ideal gas mixture at 83.14 kPa and 500 o
K. It contains 2 moles of species A and 3 moles of species B. Calculate the following: a) b)
Specific molar volumes: v
A
, v
B
, v,
Total volumes V
A
, V
B
, c) d)
Ans:
Partial molar volumes
V
A , and
V
B
Change in specific molar volume
v mix
and change in total volume
V mix v
A
3
0.05 m / mol v
B
3
0.05 m / mol v
3
0.05 m / mol
V
A
0.1 m
3
V
B
0.15 m
3
V
0.25 m
3
V
A
, V
B
,
V mix
0 ,
v mix
0
1
4. (6.20
1 ) For a given binary system at constant T and P , the molar volume (in cm
3
/mol) is given by v = 100 y a
+ 80 y b
+ 2.5
y a y b
(a) What is the pure species molar volume for species a , v a
?
(b) Come up with an expression for the partial molar volume, V a
, in terms of y b
. What is the partial molar volume at infinite dilution, V a
?
(c) Is the volume change of mixing,
v mix
, greater than, equal to, or less than 0? Explain.
Ans:
(a) v a
100
cm mol
3
(b) V a
100
2 .
5 y b
1
y a
100
2 .
5 y
2 b
V a
102 .
5
cm
3 mol
(c) Since species A contributes more to a mixture than to a pure species,
v mix
0
2
5. (6.22
1 ) The molar enthalpy of a ternary mixture of species a , b , and c can be described by the following expression: h =
5000 x a
3000 x b
2200 x c
500 x a x b x c
[J/mol].
(a) Come up with an expression for H a
.
(b) Calculate H a for a solution with 1 mole a , 1 mole b , and 1 mole c.
(c) Calculate H a for a solution with 1 mole a but with no b or c present.
(d) Calculate H a for a solution with 1 mole b but with no a or c present.
Ans:
H a
x a
(b) x a
x b
x c
1
3
H a
(c) x a
1 , x b
x c
0
H a
(d) x b
1 , x a
x c
0
H b
h b
3
(6) 2 Two compounds A and B are known to form ideal liquid solutions. A vapor mixture containing 50 mol % of A and 50 mol % of B is initially at 100 o
F and 1 atm. This mixture is compressed isothermally until condensation occurs. At what pressure does condensation occur, and what is the composition of the liquid that forms? The vapor pressures of A and B at this temperature are: P
A sat
= 1.20 atm and P
B sat
= 1.40 atm.
Ans: P = 1.2933 atm, x
1
= 0.53846
(7) 2 Two compounds A and B form an ideal liquid solution and have the following vapor pressure at 330 o
K
P
A sat
= 900 mmHg and P
B sat
= 800 mmHg
For a equimolar vapor mixture,
(a) What is the due point pressure?
(b) What pressure is necessary for complete condensation?
Ans:
(8)
2
Compounds A and B are members of the same chemical family and have the following vapor pressures
(a) P = 847.06 mmHg, (b) P = x
1
P
1 sat 850 mmHg
T ( o
F)
150
P
A sat
(mmHg)
600
P
B sat
(mmHg)
500
200 1000 950
Assume that these compounds form ideal solutions and calculate the vapor mol fraction of A and the total pressure for VLE when the liquid mol fraction of A is 0.500 and the temperature is
175 o
F.
Ans: P = 740.2 mmHg, y
A
= 0.5285
1
Engineering and Chemical Thermodynamics by Koretsky M.D
2 Kyle, B.G., Chemical and Process Thermodynamics, Prentice Hall, 1999
4